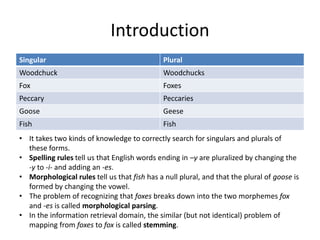
The document discusses English morphology, including singular and plural forms, morphological parsing and stemming, and the different types of morphology in English such as inflectional, derivational, compounding, and cliticization morphology. It provides examples to illustrate singular and plural forms, morphological rules for changing word endings, and how prefixes, suffixes, and other morphemes can be added to word stems to change word classes or derive new words.