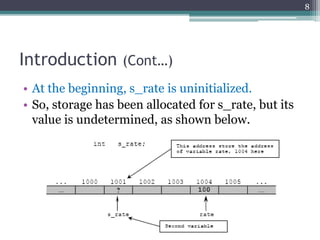
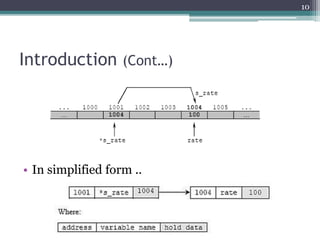
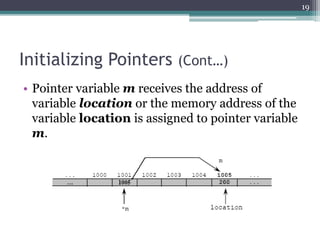
Pointer variables allow programmers to indirectly access and manipulate the memory addresses where variables are stored. Pointers must be declared with a data type and initialized by assigning the address of an existing variable using the address-of operator (&). Pointer variables can then be used to read from and write to the memory location of the variable being pointed to using indirection (*). Pointers enable operations like traversing arrays, passing arguments by reference, and dynamically allocating memory. Key pointer concepts covered include declaration, initialization, dereferencing, arithmetic, comparisons, NULL pointers, and their usage with arrays.





















![Pointer Operation (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
const int MAX = 3;
int main () {
int var[] = {10, 100, 200};
int i, *ptr;
/* let us have array address in pointer */
ptr = var;
for ( i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
printf("Address of var[%d] = %xn", i, ptr );
printf("Value of var[%d] = %in", i, *ptr );
/* move to the next location */
ptr++;
}
return 0;
}
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-30-320.jpg)
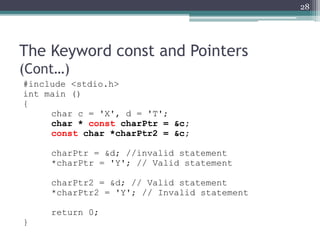
![Pointer Operation (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
const int MAX = 3;
int main ()
{
int var[] = {10, 100, 200};
int i, *ptr;
/* let us have array address in pointer */
ptr = &var[MAX-1];
for ( i = MAX; i > 0; i--)
{
printf("Address of var[%d] = %xn", i-1, ptr );
printf("Value of var[%d] = %dn", i-1, *ptr );
/* move to the previous location */
ptr--;
}
return 0;
}
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-31-320.jpg)

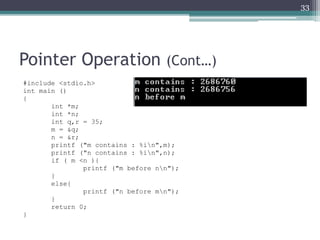





![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
• An array name without brackets is a pointer to the
array’s first element.
• So, if a program declared an array data[], data
(array’s name) is the address of the first array
element and is equivalent to the expression
&data[0] that means references the address of the
array’s first element.
• data equivalent to &data[0] or a pointer to the
array’s first element.
• The array’s name is, therefore a pointer to
the array’s first element.
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-39-320.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
int values [100] = {1,2,…, 100};
int *valuesPtr;
valuesPtr = values;
Or
valuesPtr = &values[0];
If you do following
valuesPtr = &values[1];
It points to second element
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-40-320.jpg)
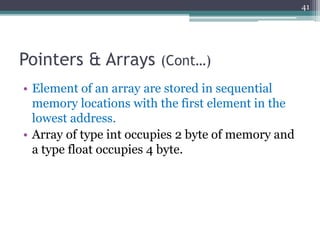
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int i[10], x;
float f[10];
double d[10];
printf("nArray's el. add of i[x] add of f[x] add of d[x]");
printf("n|================================");
printf("======================|");
for(x=0; x<10; x++)
printf("nElement %i:t%pt%pt%p",x,&i[x],&f[x],&d[x]);
printf("n|================================");
printf("======================|n");
printf("nLegends:");
printf("nel.- element, add - addressn");
printf("ndifferent pc, shows different addressesn");
return 0;
}
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-43-320.jpg)
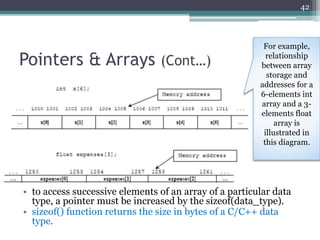
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
• Notice the difference between the element addresses.
▫ 0027FF04 – 0027FF08 = 4 bytes for int
▫ 0027FEE0 – 0027FEE4 = 4 bytes float
▫ 0027FE90 – 0027FE98 = 8 bytes double
[The size of the data type depends on the specification of your compiler, whether your target is 16, 32 or 64 bits
systems, the output of the program may be different for different PC]
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-44-320.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 10
int main()
{
int array1[MAX] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int *ptr1, count;
float array2[MAX] = {0.0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9};
float *ptr2;
ptr1 = array1;
ptr2 = array2;
printf("narray1 values array2 values");
printf("n-------------------------");
for(count = 0; count < MAX; count++)
printf("n%itt%f", *ptr1++, *ptr2++);
printf("n-------------------------n");
return 0;
}
45
The increment and
decrement operators are
particularly handy when
dealing with pointers.
Applying the increment
operator to a pointer has
the same effect as adding
one to the pointer, while
applying the decrement
operator has the same
effect as subtracting one
from the pointer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-45-320.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char name[50]= "RAJARATA UNIVERSITY OF SRI LANKA";
printf("%snn",name);
printf("%s,%inn",name,&name);
printf("%c,%i,%inn",name[0],name[0],&name[0]);
printf("%c,%i,%inn",name[1],name[1],&name[1]);
return 0;
}
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-46-320.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
• Generally, the relationship is as follows:
*(array1) == array1 [0] //first element
*(array1 + 1) == array1 [1] //second element
*(array1+ 2) == array1 [2] //third element
…
…
*(array1 + n) == array1[n] //the nth element
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-47-320.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
int main (void)
{
int sum = 0, *ptr;
int values[10] = { 3, 7, -9, 3, 6, -1, 7, 9,
1, -5 };
int * const arrayEnd = values + 10;
for ( ptr = values; ptr < arrayEnd; ++ptr )
sum += *ptr;
printf ("The sum is %in", sum);
return 0;
}
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-48-320.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays (Cont…)
• In general, the process of indexing an array takes
more time to execute than does the process of
accessing the contents of a pointer.
• In fact, this is one of the main reasons why pointers
are used to access the elements of an array—the
code that is generated is generally more efficient.
• Of course, if access to the array is not generally
sequential, pointers accomplish nothing, as far as
this issue is concerned, because the expression
*(pointer + j) takes just as long to execute as
does the expression array[j].
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-49-320.jpg)
![Pointer Arrays
• Pointers may be arrayed like any other data type.
• The declaration for an int pointer array of size 20 is:
int *arrayPtr[20];
• To assign the address of an integer variables called var to the first
element of the array, we could write something like this:
arrayPtr[0] = &var;
• To find the value stored in var, we could write something like this:
*arrayPtr[0]
50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-50-320.jpg)









![Pointers to Character Strings (Cont…)
#include <stdio.h>
void copyString (char *, char *);
void copyString (char *to, char *from)
{
for ( ; *from != '0'; ++from, ++to )
*to = *from;
*to = '0';
}
int main (void)
{
char string1[] = "A string to be copied.";
char string2[50];
copyString (string2, string1);
printf ("%sn", string2);
copyString (string2, "So is this.");
printf ("%sn", string2);
return 0;
}
60
pointer to that constant
character string is passed
here.
Whenever a constant
character string is used
in C, it is a pointer to
that character string that
is produced.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-60-320.jpg)

![Pointers to Character Strings (Cont…)
• Be careful to make the distinction here between
character pointers and character arrays, as the type of
assignment just shown is not valid with a character
array.
• So, for example, if text is defined instead to be an array
of chars, with a statement such as
char text[80];
then you could not write a statement such as
text = "This is not valid.";
• The only time that C lets you get away with performing
this type of assignment to a character array is when
initializing it, as in
char text[80] = "This is okay.";
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-62-320.jpg)
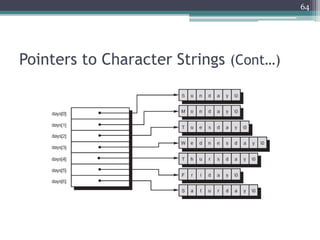
![Pointers to Character Strings (Cont…)
• If text is a character pointer, initializing text with the
statement
char *text = "This is okay.";
assigns to it a pointer to the character string "This is okay.“
• As another example of the distinction between character
strings and character string pointers, the following sets up an
array called days, which contains pointers to the names of the
days of the week.
char *days[] = { "Sunday", "Monday",
"Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday",
"Friday","Saturday" };
• So days[0] contains a pointer to the character string
"Sunday", days[1] contains a pointer to the string "Monday",
and so on.
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l11-170928090354/85/COM1407-Working-with-Pointers-63-320.jpg)