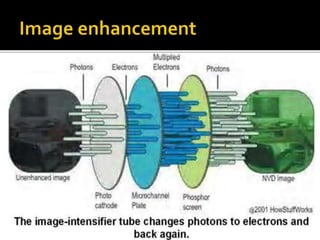
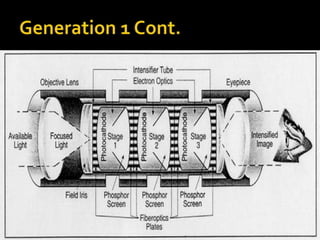
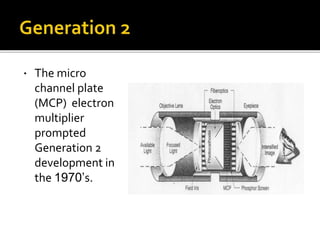
Night vision devices were first created during World War II to help with night operations. They functioned by placing infrared filters over searchlights. Since then, technology has advanced through generations. Generation 1 used intensified natural light while Generation 2 added microchannel plate electron multipliers in the 1970s. Currently, Generation 3 and 4 devices provide clearer, longer lasting images but Generation 4 has shorter life. Night vision devices were originally for military use but are now commonly used for civilian applications such as law enforcement, hunting, security, and navigation.