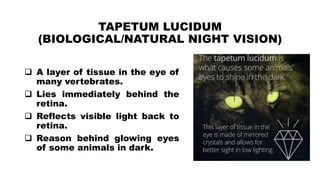
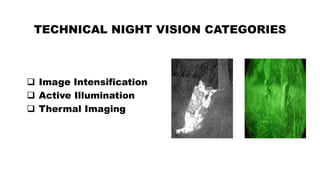
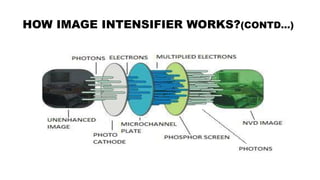
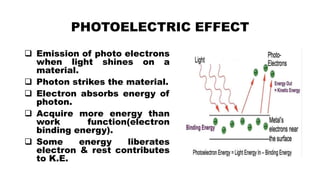
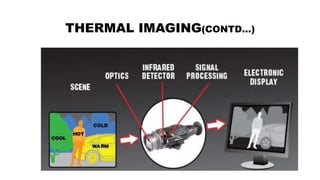
The document provides a comprehensive overview of night vision technology, detailing its history, biological and technical aspects, and various applications, especially in military and automotive contexts. It explains the mechanisms of image intensification, active illumination, and thermal imaging, and outlines different night vision devices like goggles, cameras, and scopes. The technology is highlighted as essential for low-light visibility and has numerous modern applications ranging from security to wildlife observation.