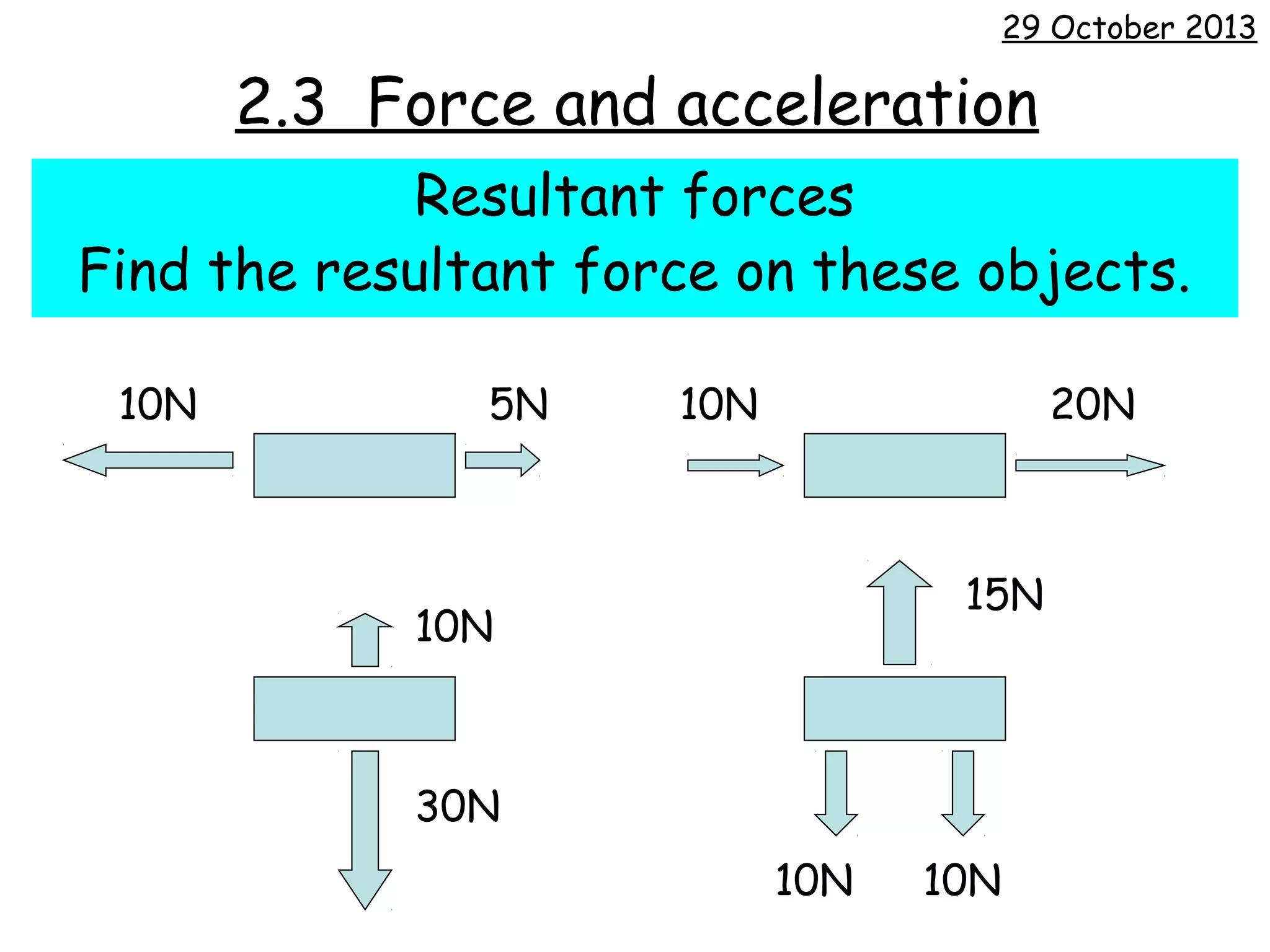
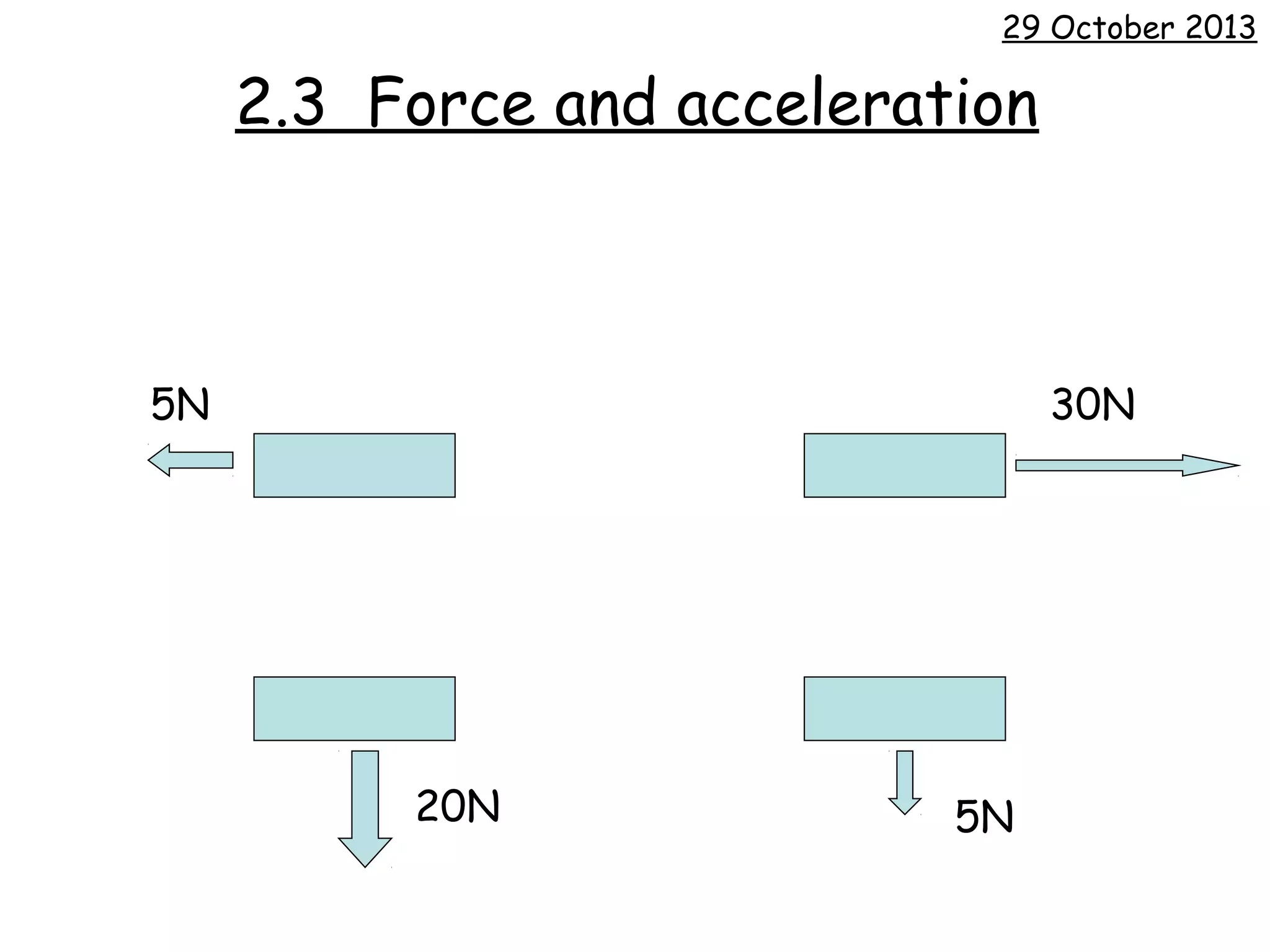
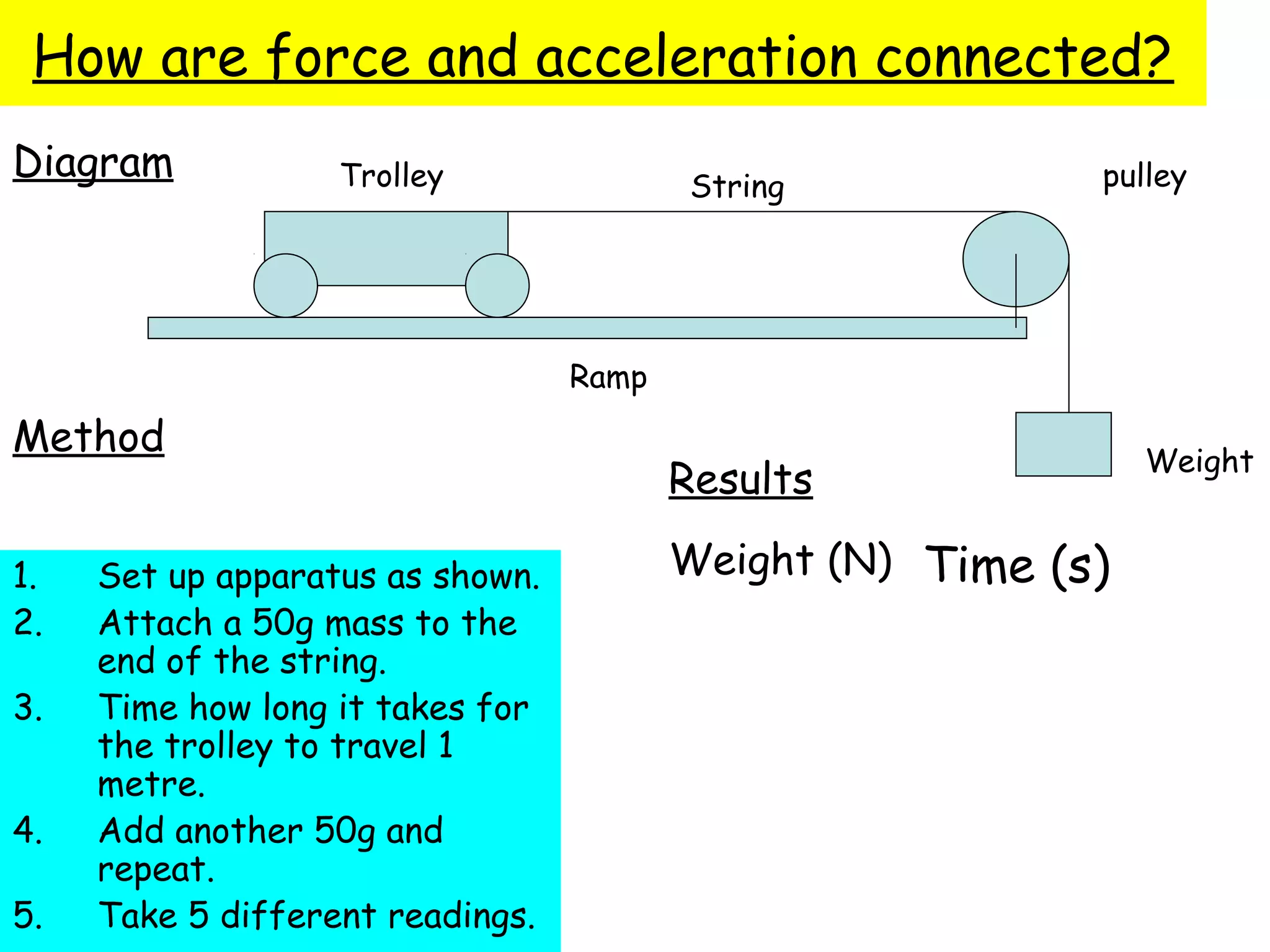
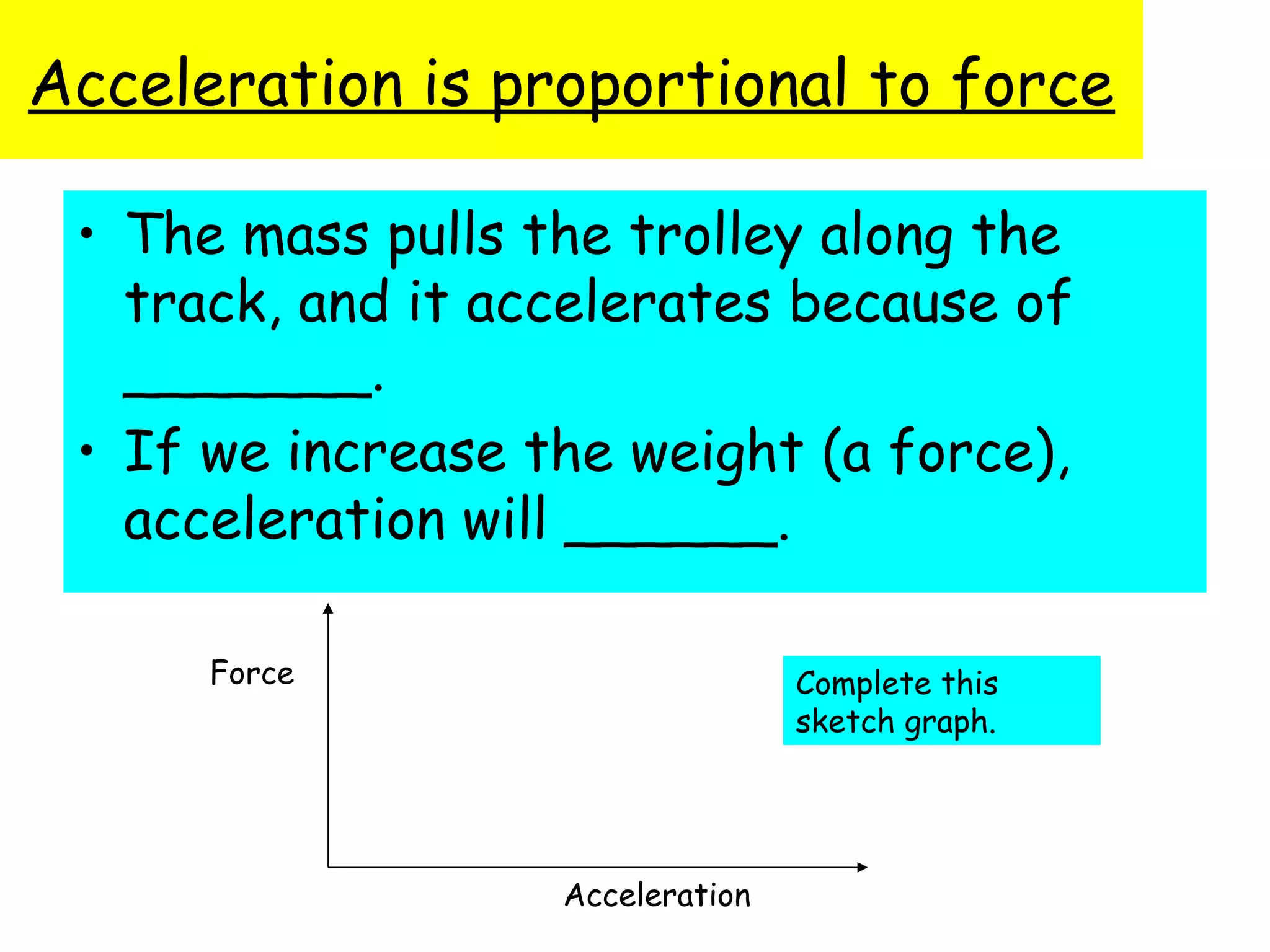
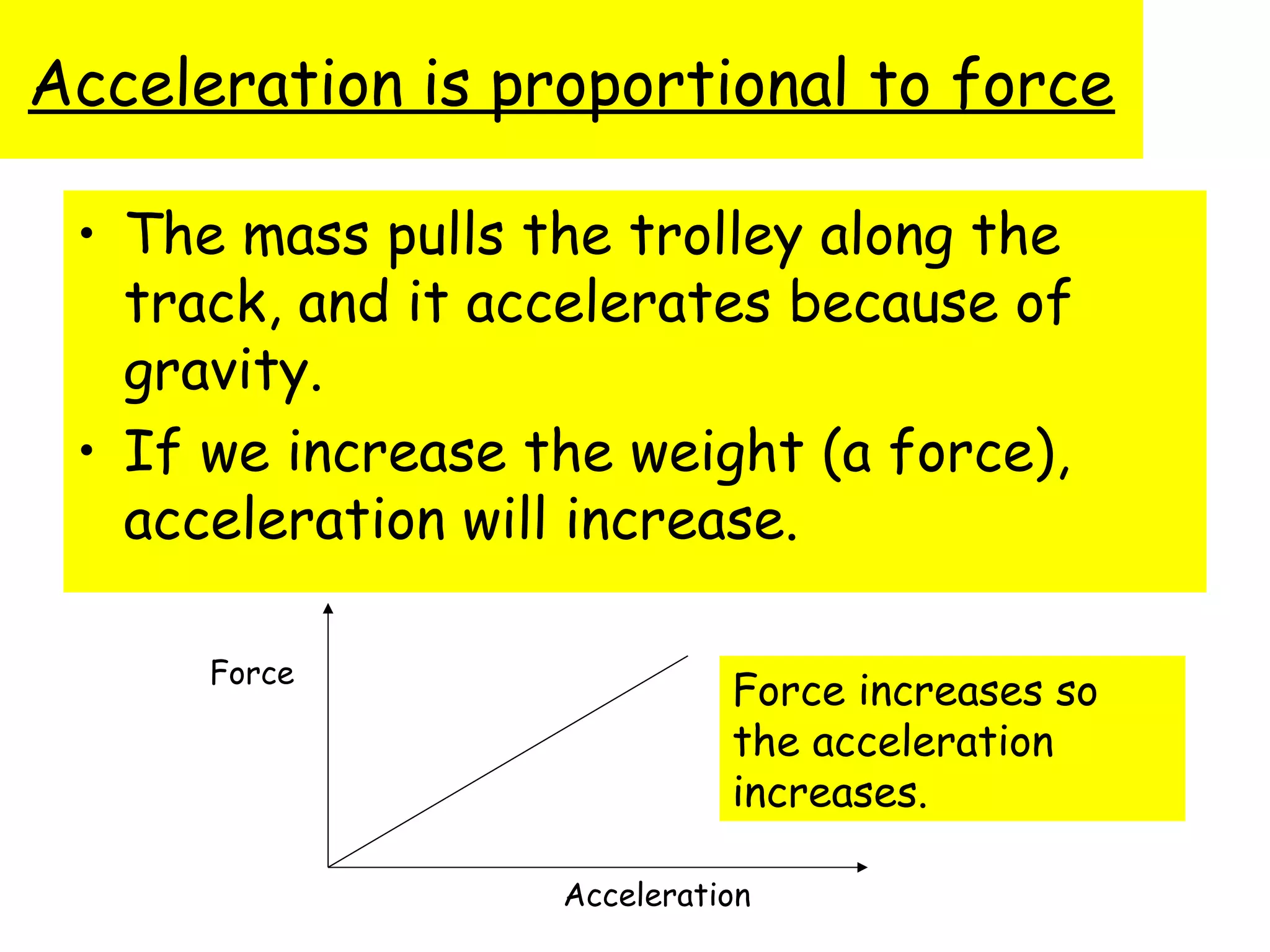
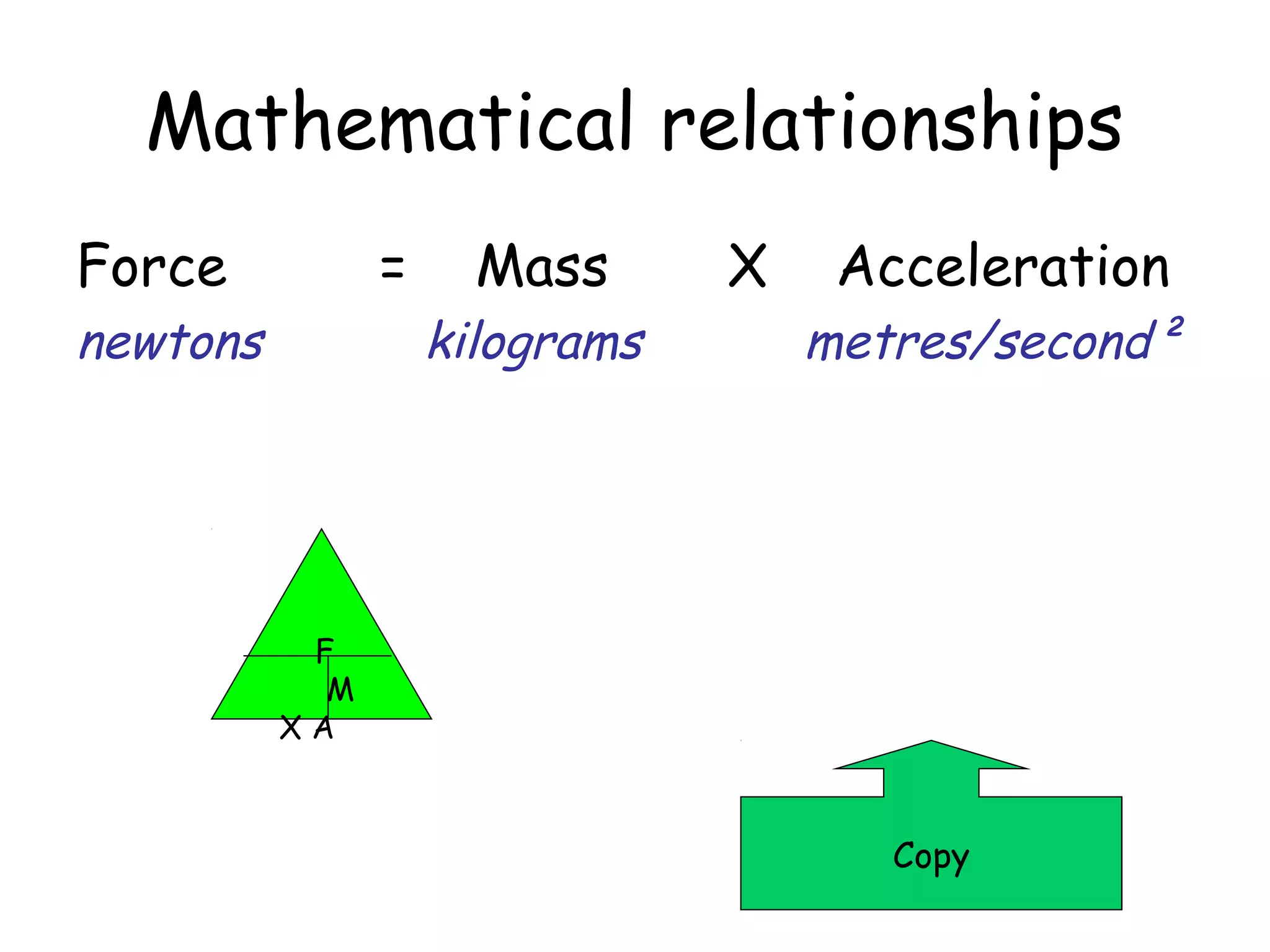
The document discusses force, acceleration, and their relationship. It provides examples of experiments measuring the acceleration of a trolley pulled with different masses and forces. The results show that acceleration increases as force increases, and decreases as mass increases. This follows the mathematical relationship that force equals mass times acceleration.