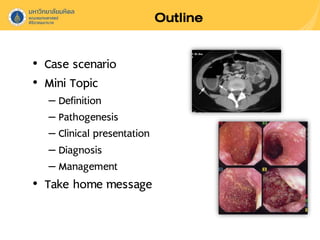
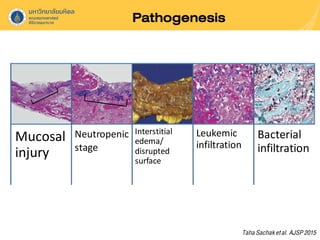
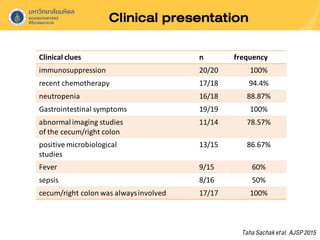
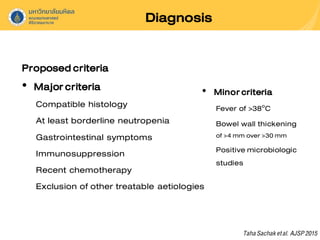
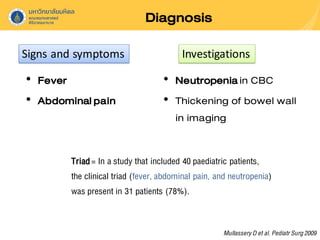
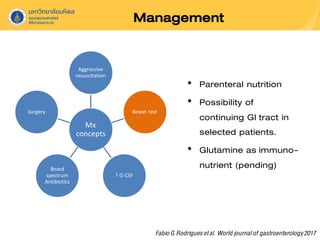
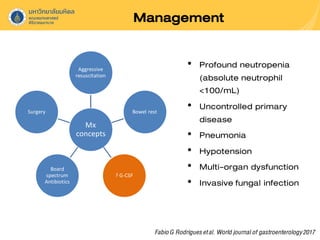
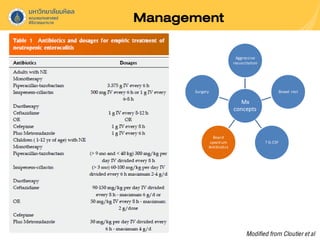
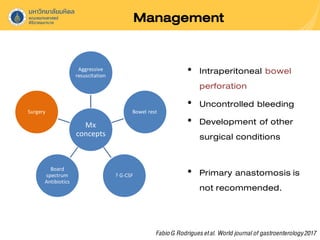
Neutropenic colitis, also known as typhlitis, is characterized by ileocolonic inflammation in immunosuppressed patients with neutropenia, fever, and abdominal pain. It is most commonly seen in patients with hematologic malignancies or following chemotherapy and is caused by bacterial translocation during neutropenia. Clinical presentation includes gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain in addition to fever. Diagnosis involves imaging showing bowel wall thickening as well as ruling out other causes. Management is usually conservative involving antibiotics, bowel rest, and correction of neutropenia, though surgery may be needed for complications like perforation.