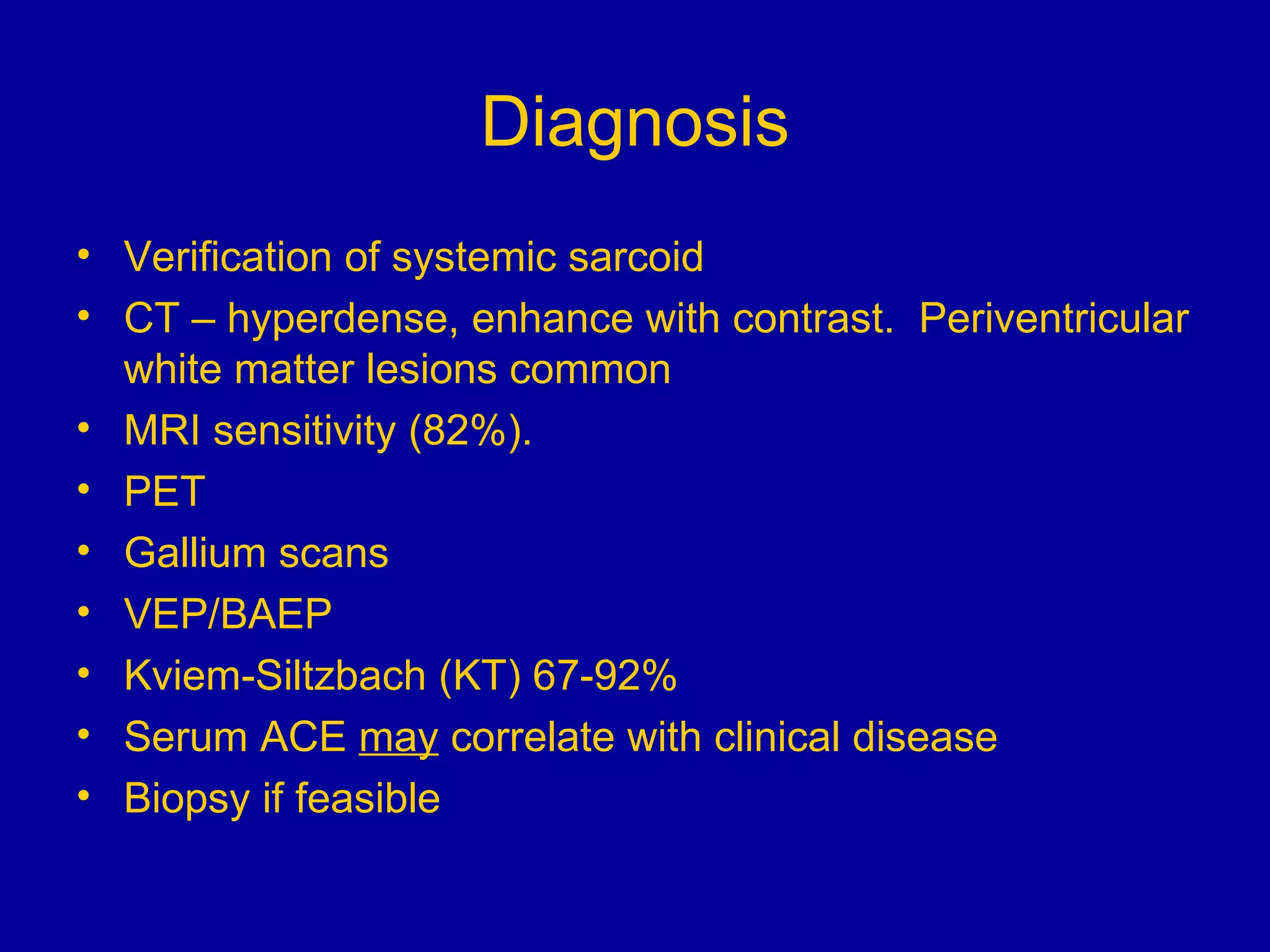
Neurosarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown etiology where noncaseating granulomas can affect multiple organs including the lungs, heart, skin and nervous system. It most commonly involves the lungs in 90% of cases. The central nervous system is involved in 5-16% of cases, with cranial neuropathies, encephalitis, meningitis and mass lesions being common neurological manifestations. Treatment involves corticosteroids as the mainstay, with immunosuppressants also used in refractory cases. Prognosis depends on location and type of involvement, with 72% of neurological cases deteriorating within 18 months if not treated.