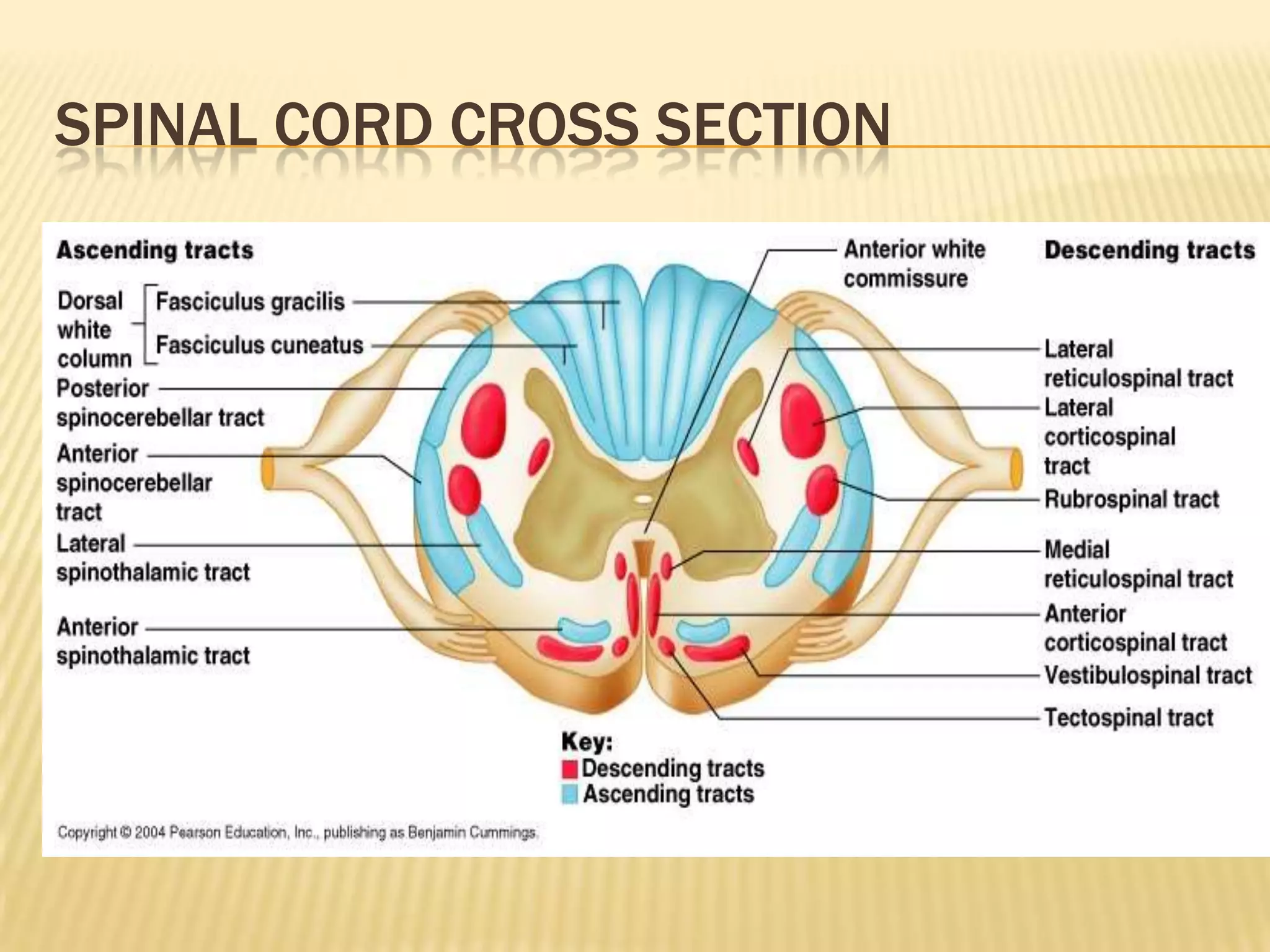
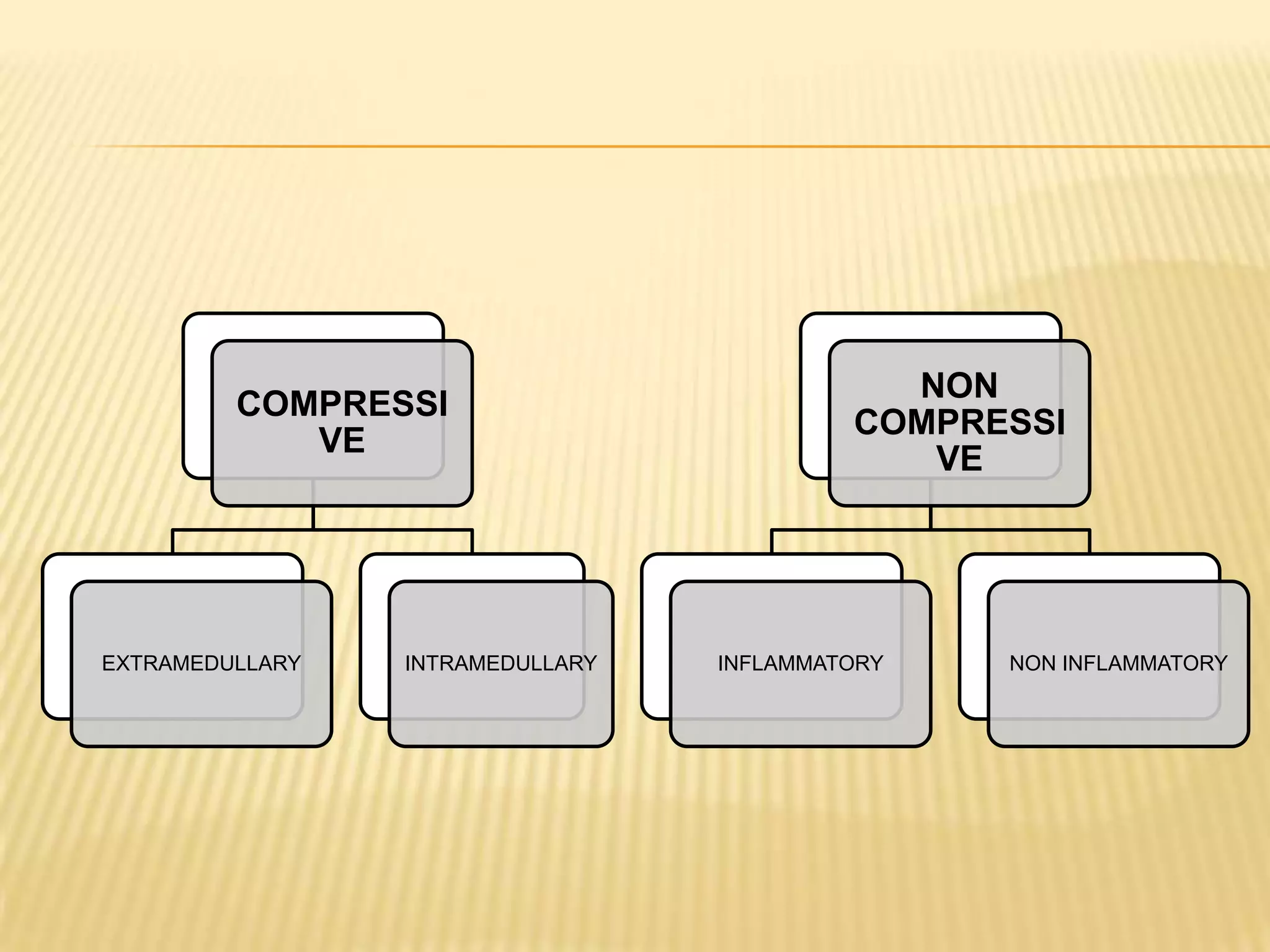
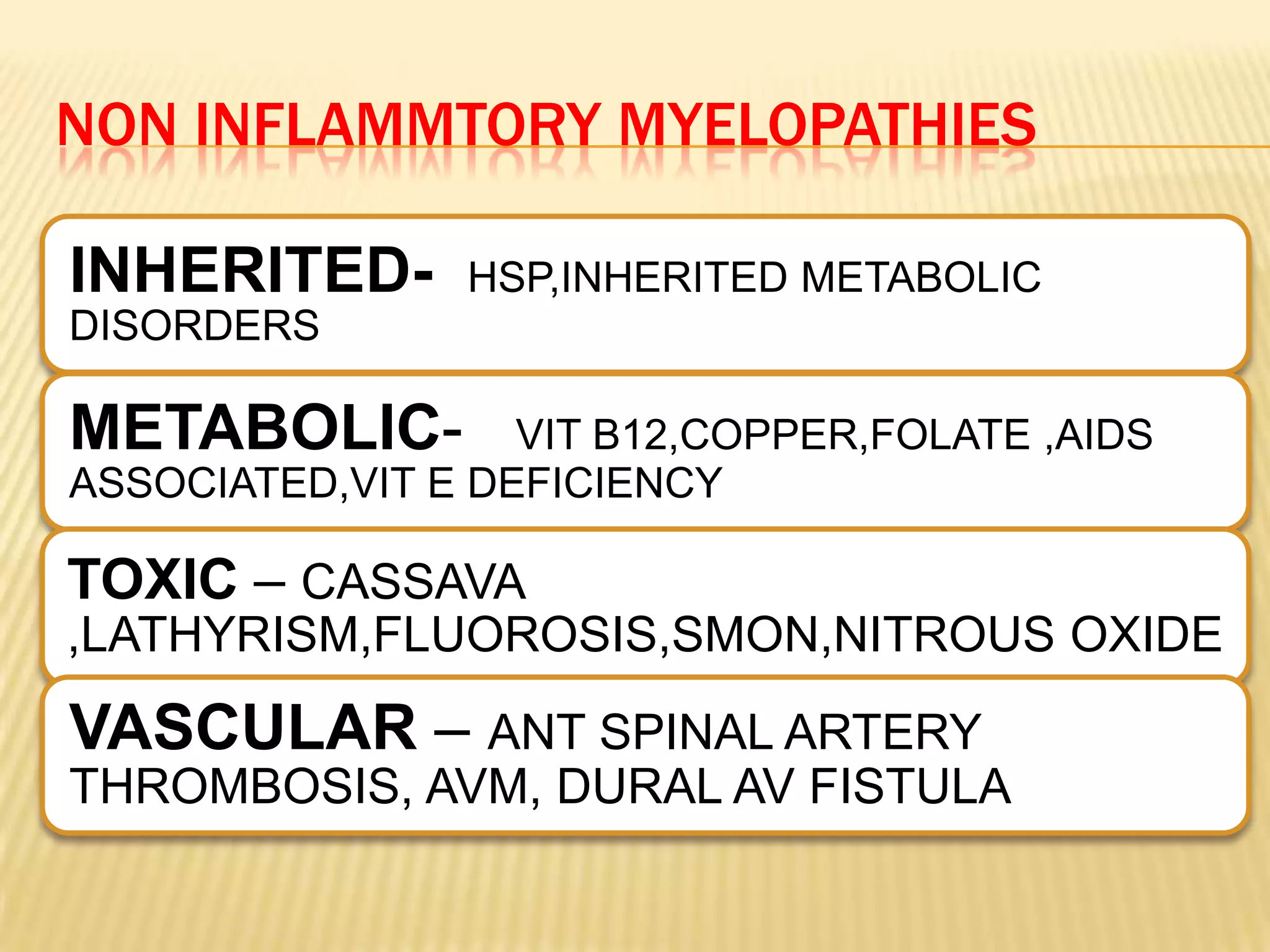
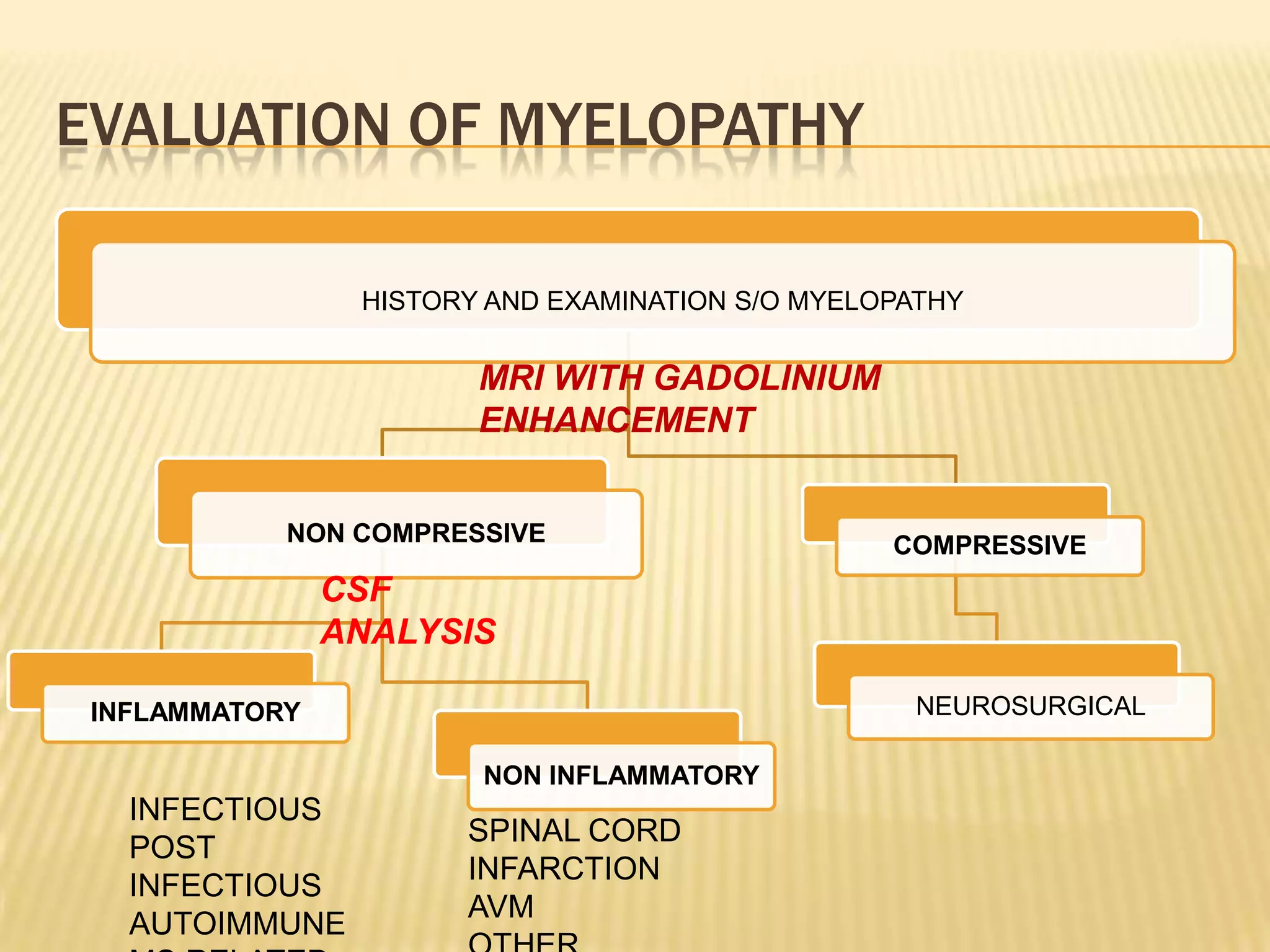
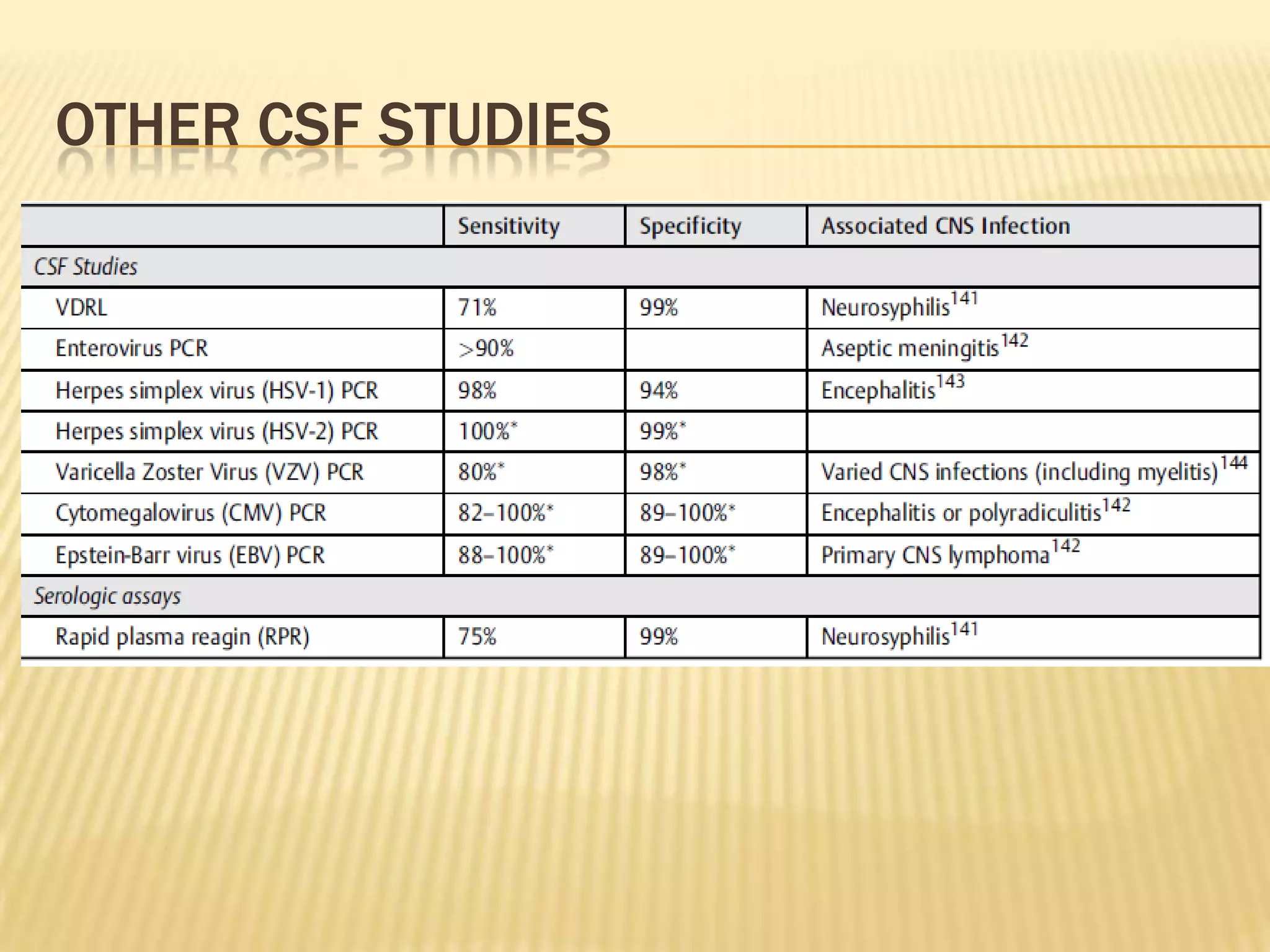
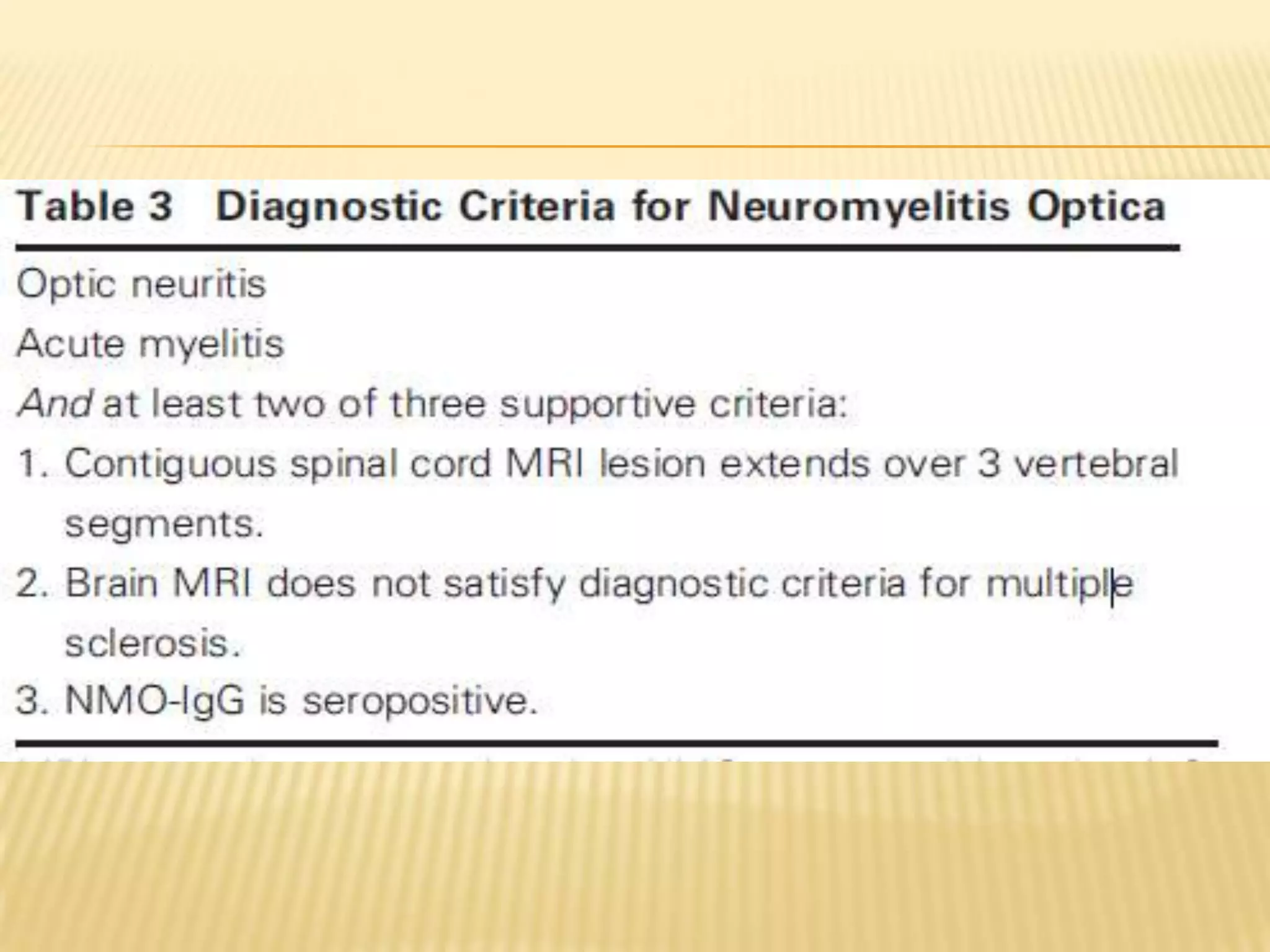
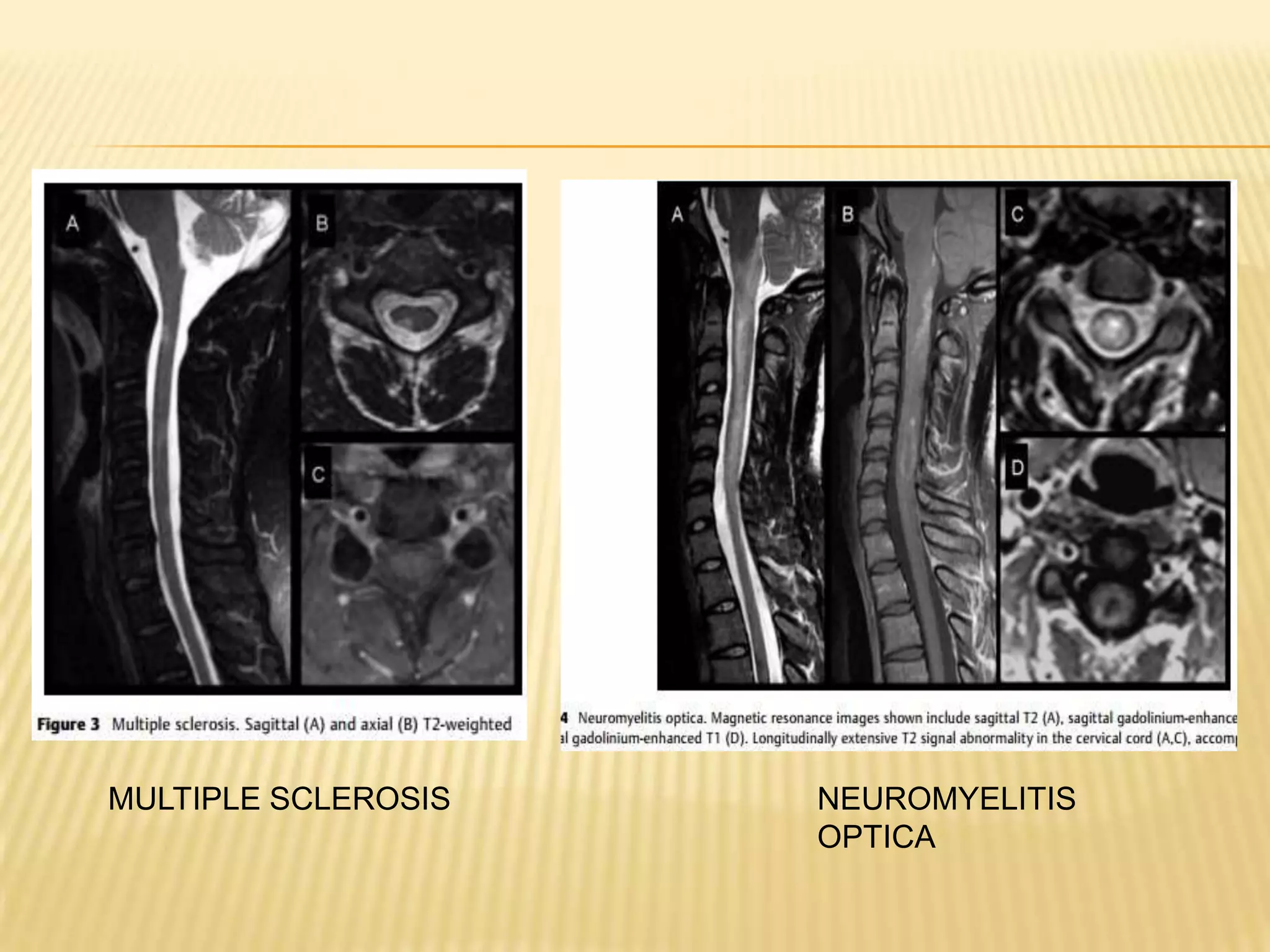
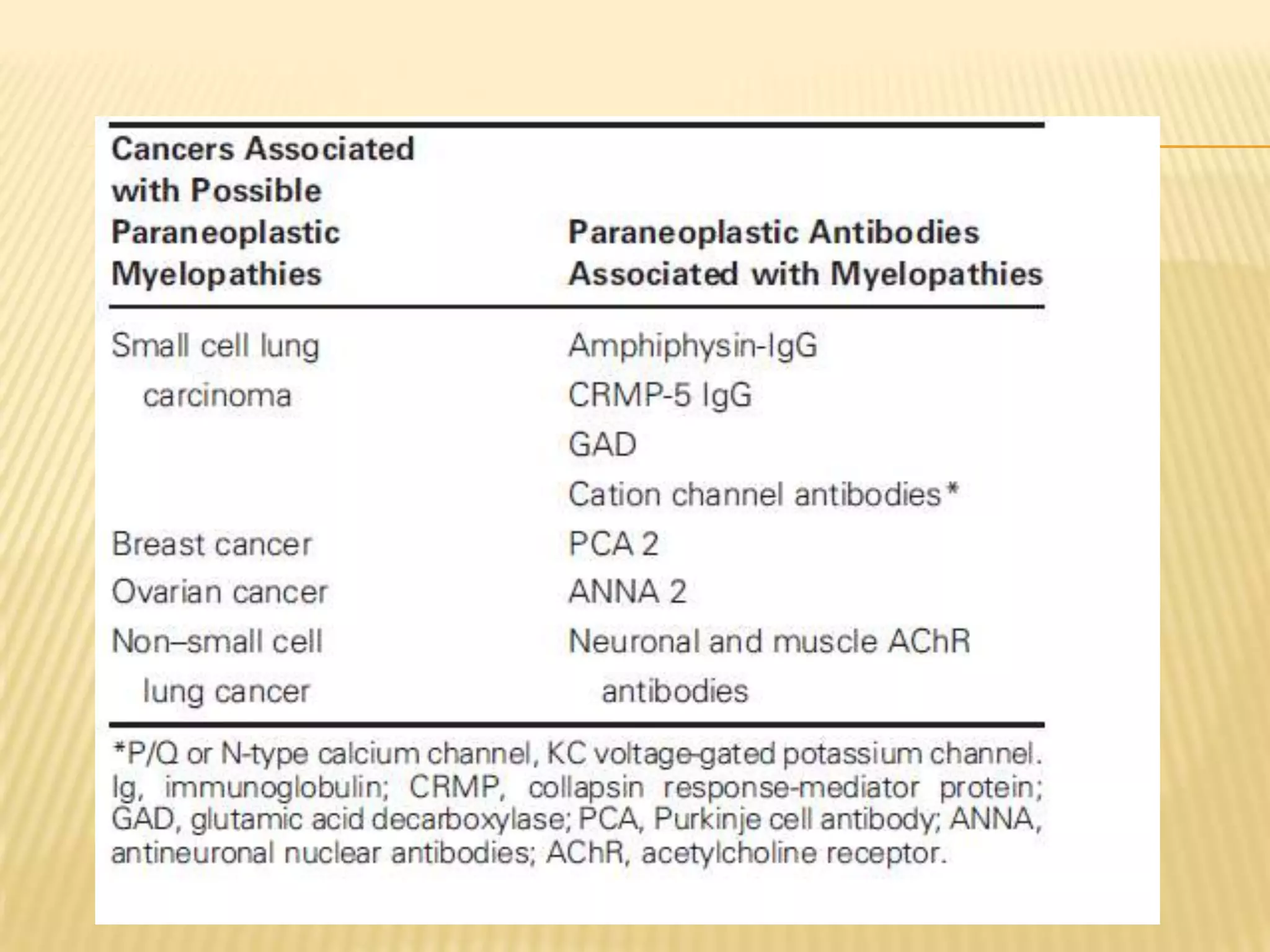
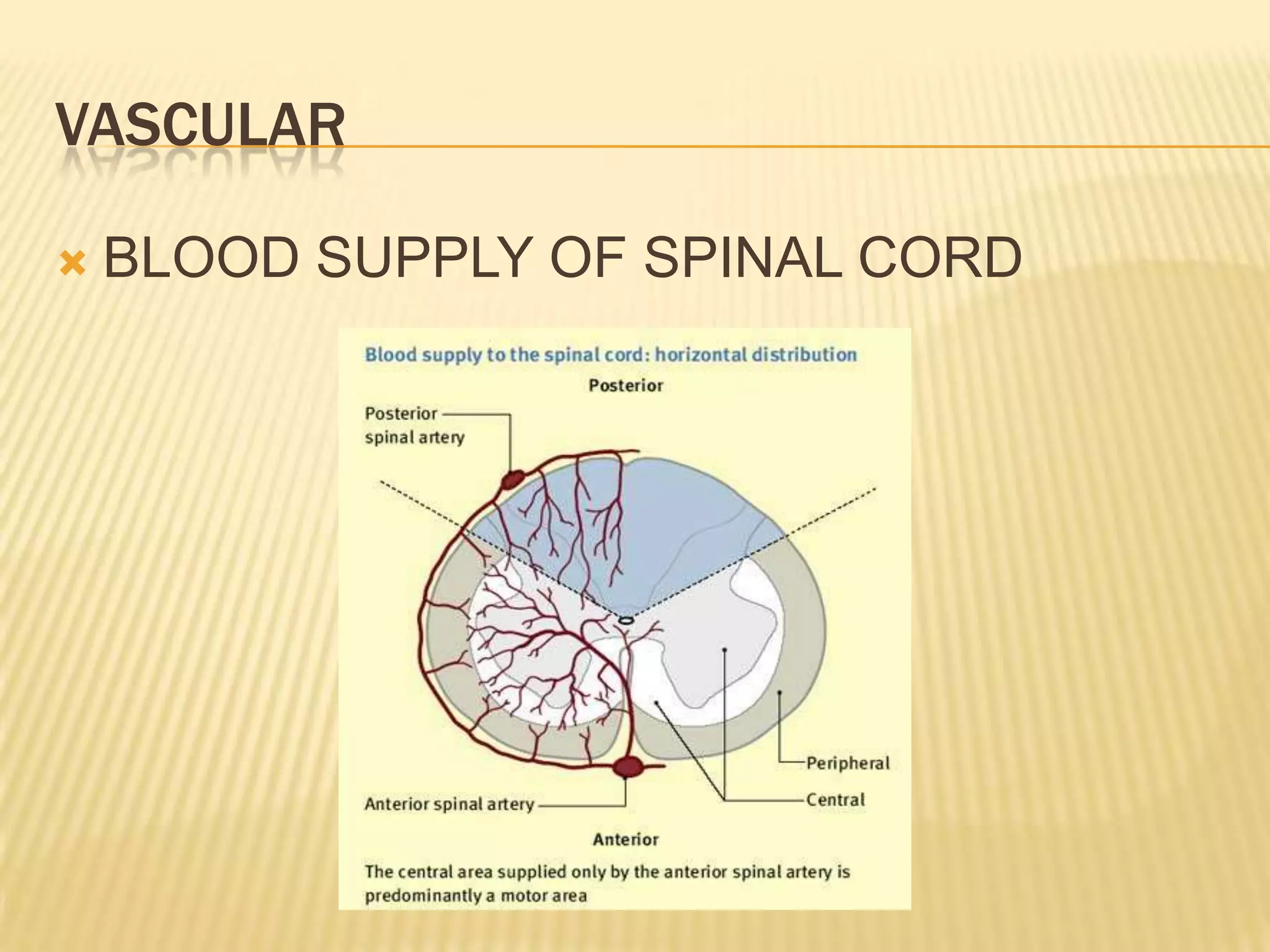
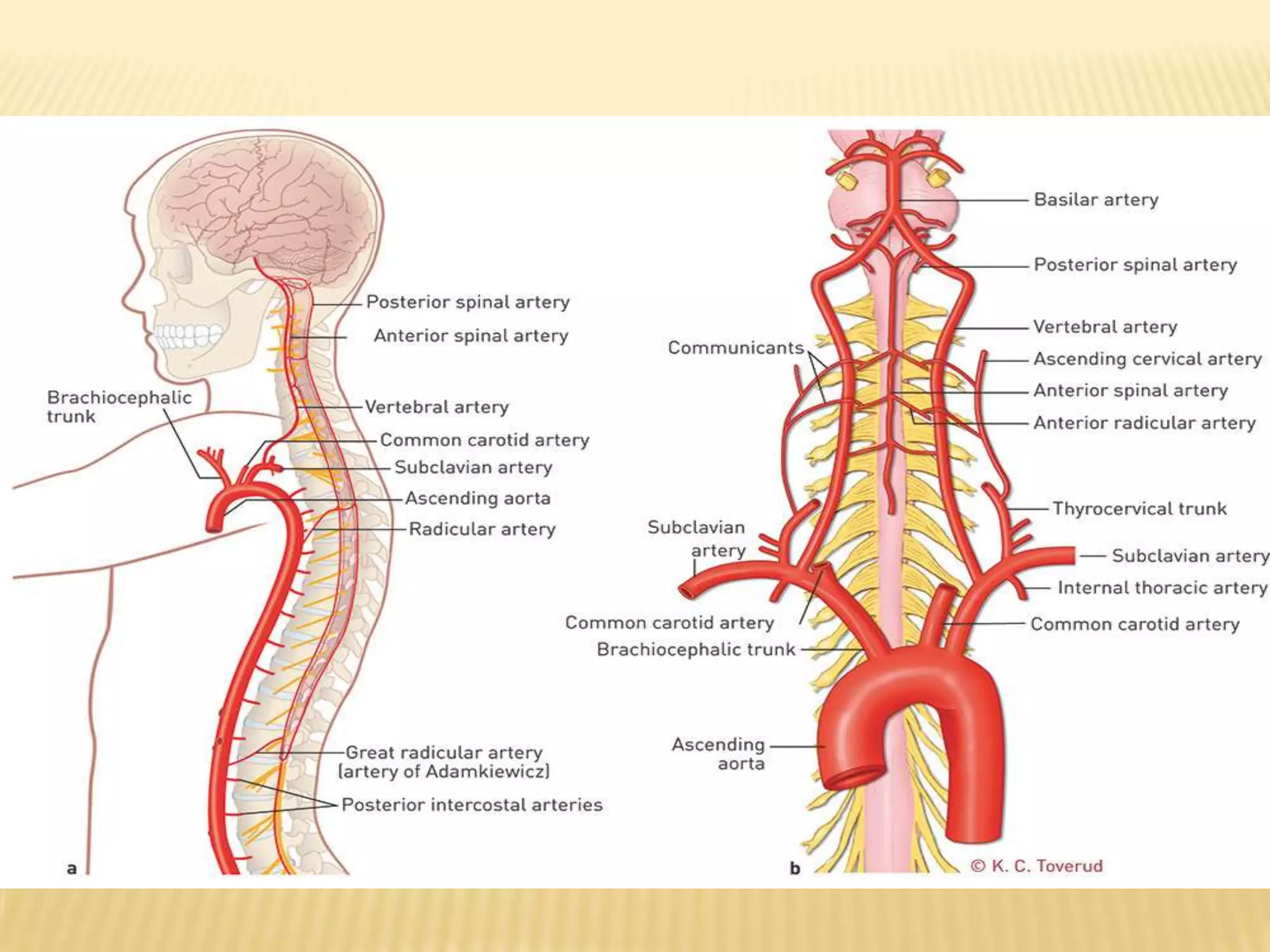
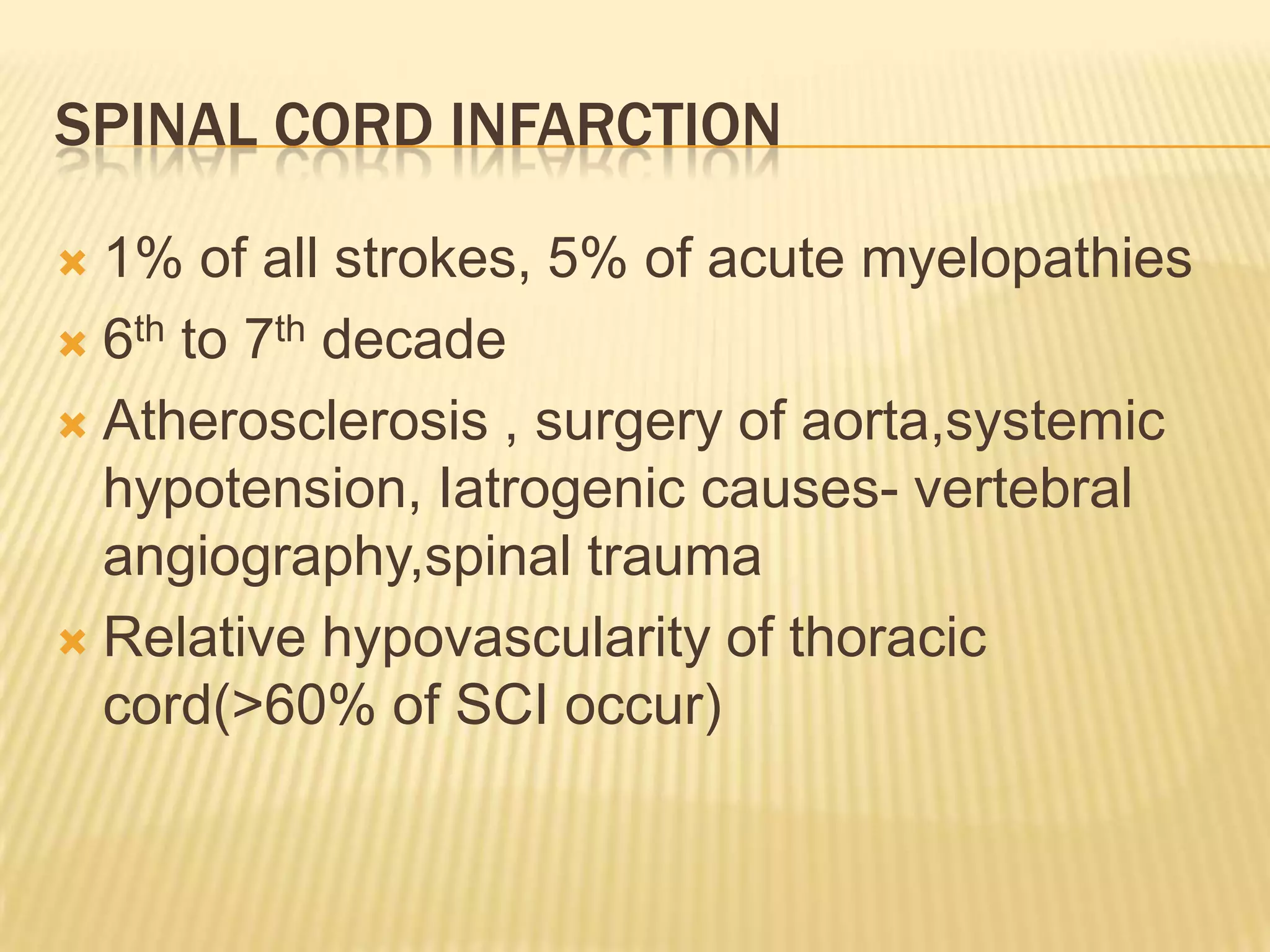
The document provides an overview of non-compressive myelopathy, detailing its evaluation, diagnosis, and management, including classifications such as infectious and non-infectious myelitis, metabolic myelopathies, and associated clinical features. It discusses the epidemiology and diagnosis of transverse myelitis, emphasizing the need for MRI and CSF analysis, along with treatment options like high-dose steroids and plasmapheresis. Additionally, it explores prognostic factors and complications, linking various myelopathies to potential underlying causes, including nutritional deficiencies and autoimmune disorders.