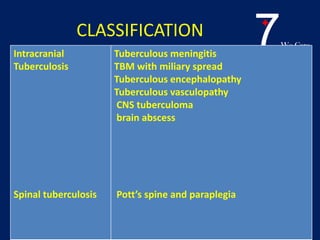
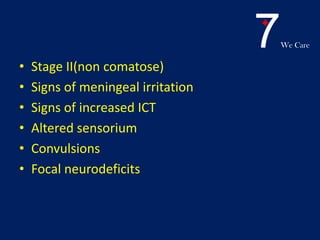
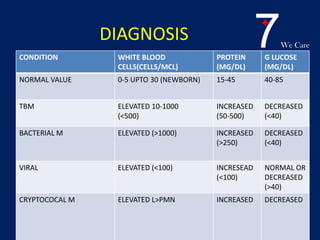
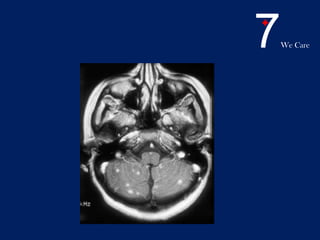
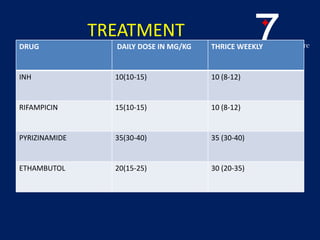
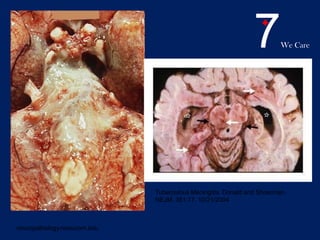
Central nervous system tuberculosis (CNS TB) is a severe form of TB infection that can affect the brain and spinal cord. It is most common in children under 5 years old. Left untreated, CNS TB has an almost 100% fatality rate and can cause permanent neurological damage even with treatment. Diagnosis involves examination of cerebrospinal fluid which shows increased white blood cells and protein with low glucose. Brain imaging also helps with diagnosis. Treatment requires a multi-drug regimen administered over 9-12 months. Adjunctive steroids are also often used to reduce inflammation and complications. Even with treatment, CNS TB has poor outcomes with only one third of patients fully recovering neurologically.