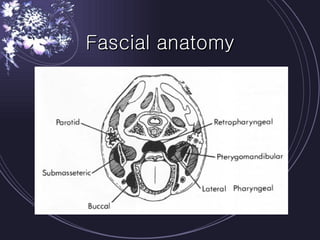
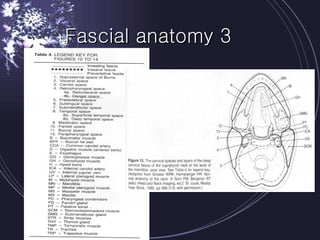
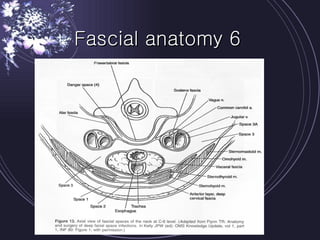
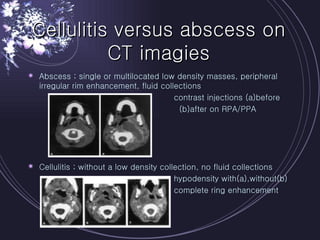
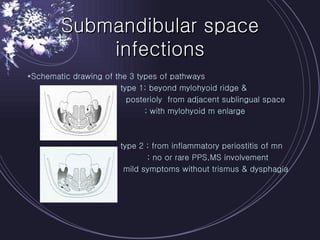
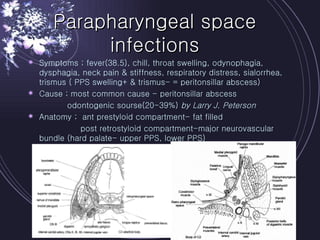
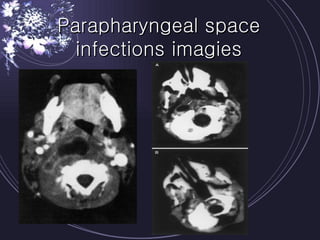
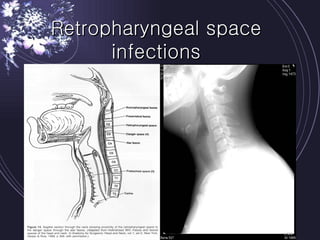
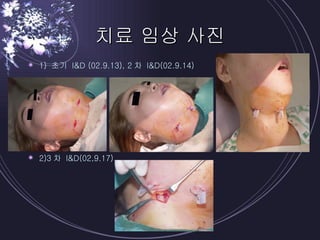
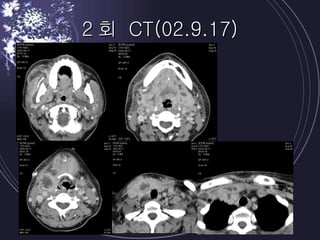
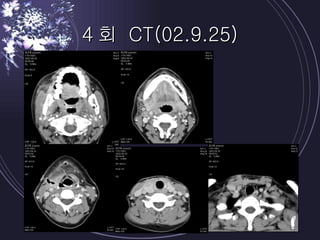
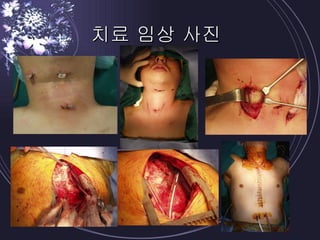
Deep neck infections can be life threatening if not properly treated. Early diagnosis using imaging tests like CT scans is important to identify the infected spaces. Aggressive treatment involving broad-spectrum antibiotics, surgical drainage of abscesses if present, and airway management is usually needed. Close monitoring is required as infections can spread rapidly between fascial spaces in the neck. Proper treatment combining medical and surgical approaches is needed to resolve the infection while preventing complications like descending necrotizing mediastinitis.