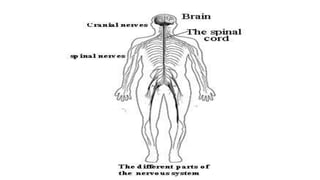
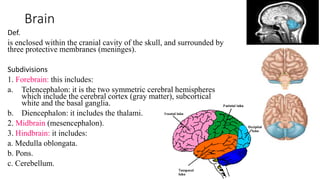
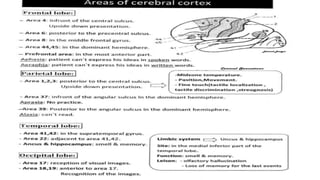
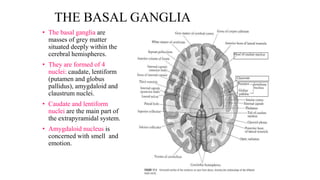
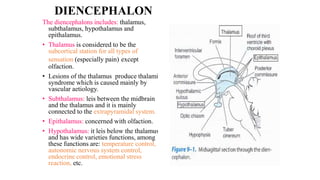
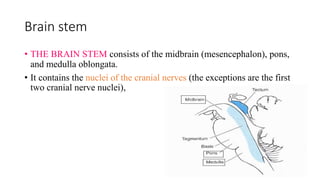
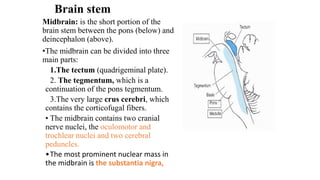
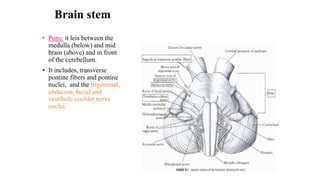
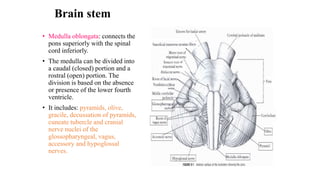
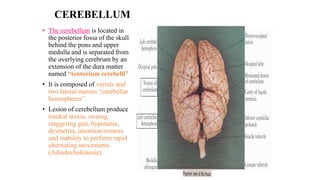
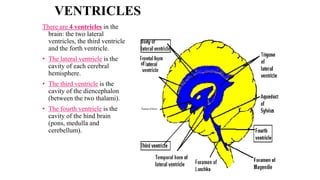
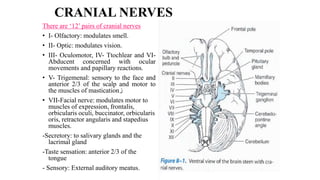
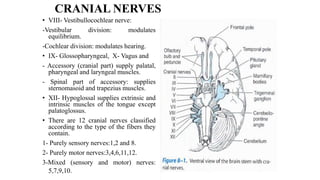
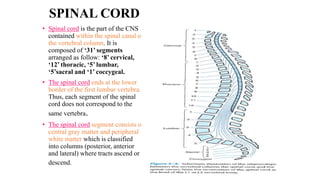
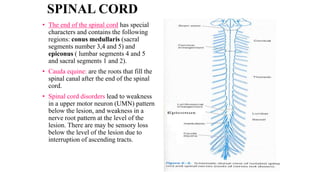
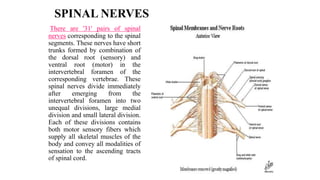
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain includes the cerebral hemispheres which are divided into lobes that control motor, sensory, auditory, visual, and higher cognitive functions. The basal ganglia help control movement. Lesions in specific areas of the brain can cause deficits like weakness, sensory loss, or language problems depending on the area affected. The spinal cord has segments that innervate parts of the body and carry motor and sensory information between the brain and body.