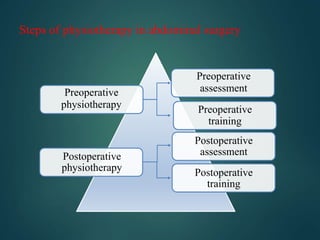
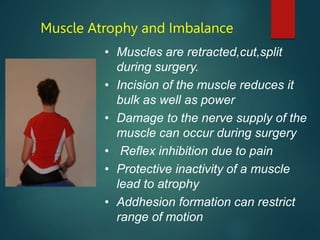
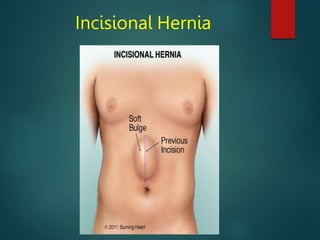
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the pre-operative and post-operative stages of abdominal surgery. In the pre-operative stage, physiotherapists assess patients' respiratory, circulatory, and functional status and provide training in breathing exercises, coughing techniques, posture, and range of motion exercises. Post-operatively, physiotherapy focuses on preventing complications like respiratory issues, blood clots, muscle wasting, and poor wound healing through techniques such as breathing exercises, early mobility, and scar management. The goal is to aid recovery and reduce hospital stay through rehabilitation.