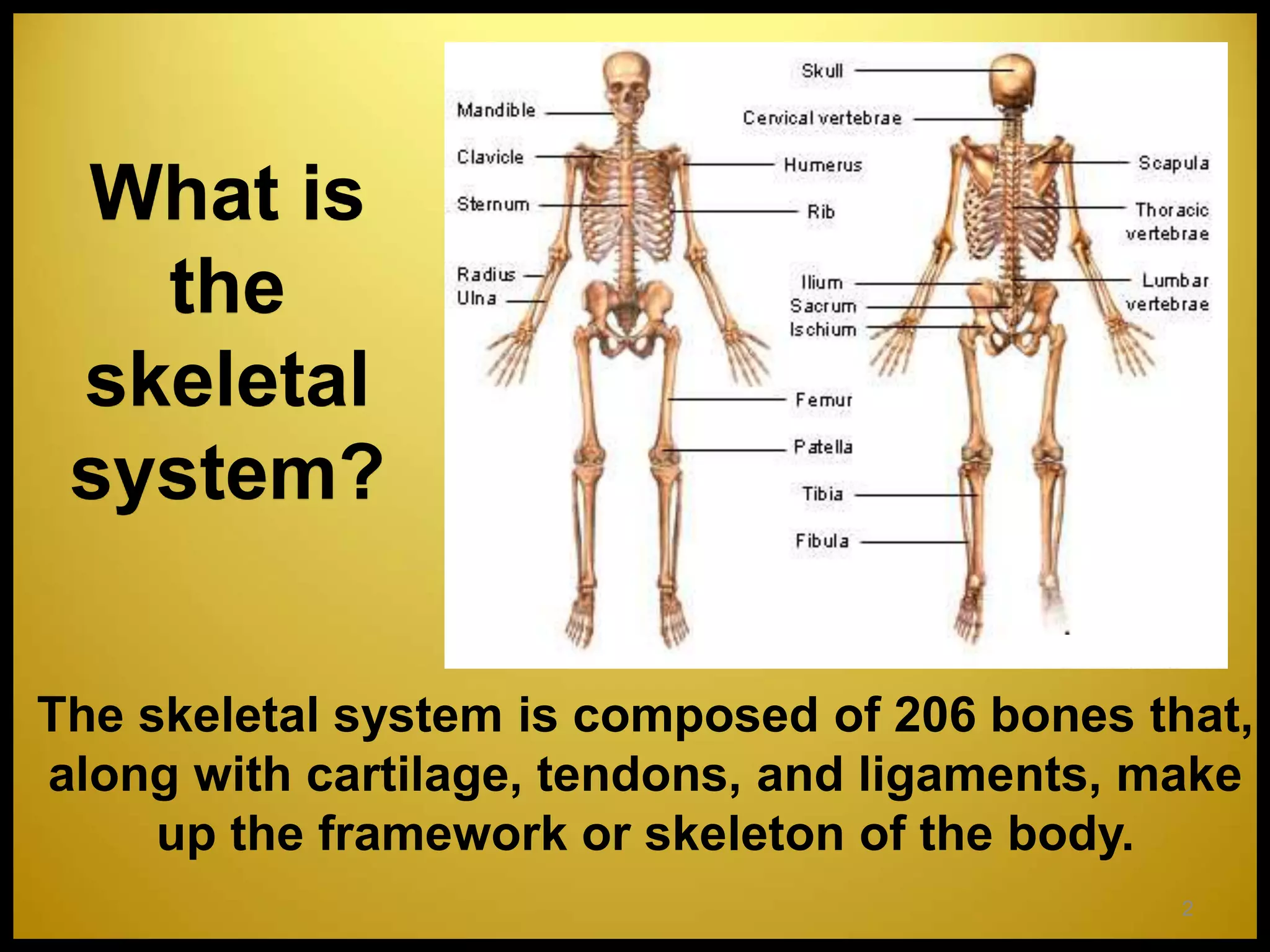
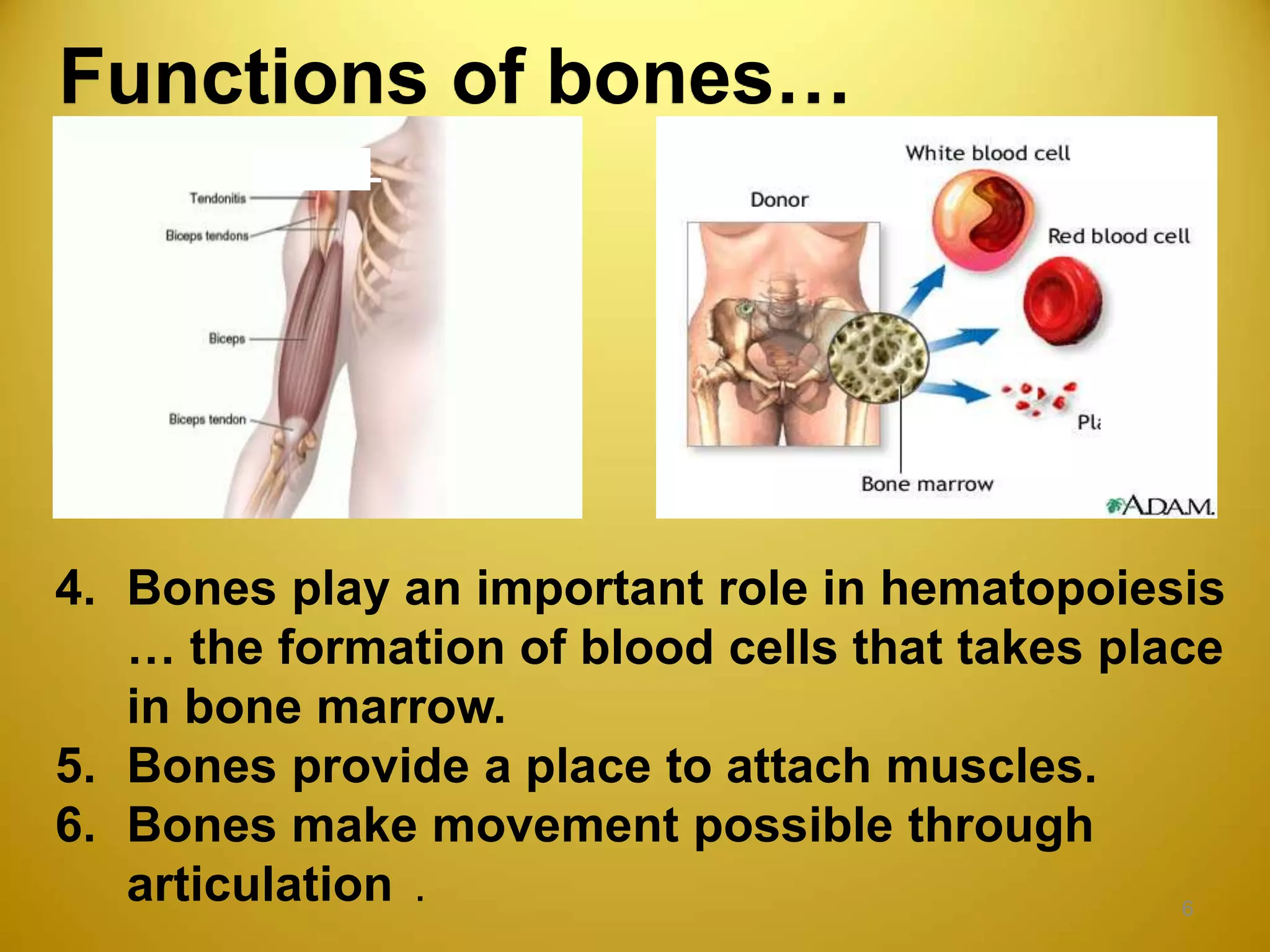
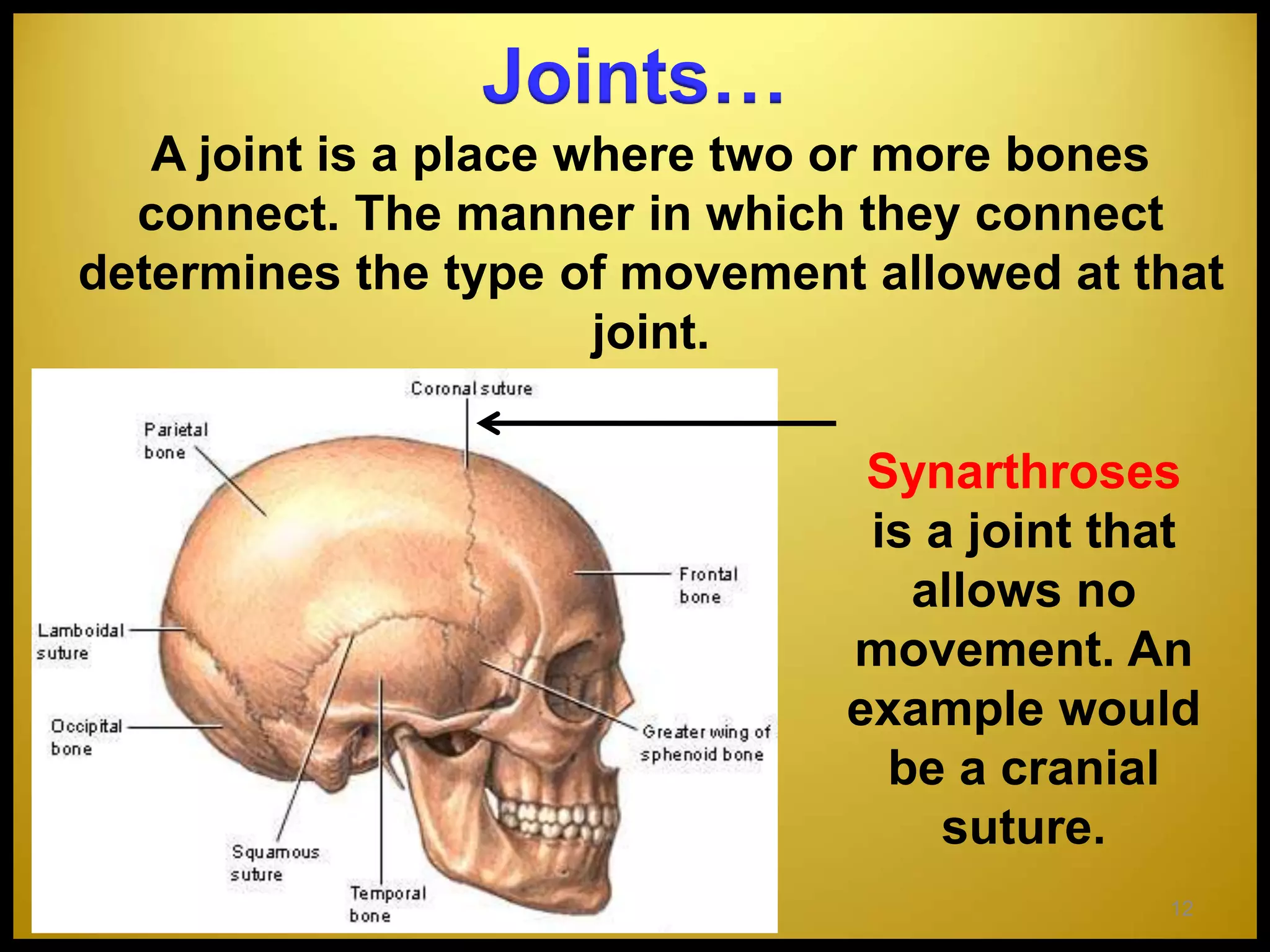
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones that make up the framework of the body, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. The skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton, with 80 bones including the skull, spine, ribs, and sternum, and the appendicular skeleton with 126 bones including the shoulders, arms, hands, pelvis, legs and feet. Bones provide structure and support to the body, protect internal organs, store minerals, allow for movement through articulation of joints, and enable muscle attachment. Bones are classified by shape as long, short, flat, or irregular. Joints like the knee and elbow allow diverse movements like flexion, extension, and rotation. The curvature of the vertebral column provides