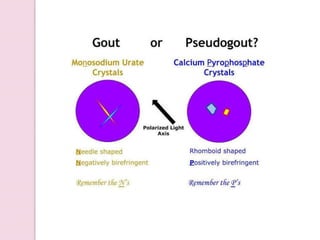
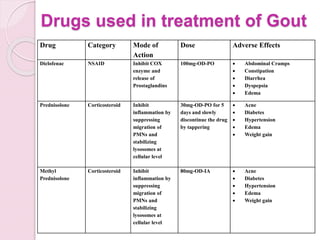
Gout is an inflammatory arthritis caused by high uric acid levels in the blood (hyperuricemia) which leads to the deposition of urate crystals in the joints. It ranges from mild asymptomatic hyperuricemia to severe chronic tophaceous gout. Risk factors include family history, diet high in purines, obesity, alcohol use, and certain medications. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, medications to reduce uric acid production like allopurinol, or increase excretion like probenecid. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids are used for acute flares while long term management focuses on normalization of uric acid levels.