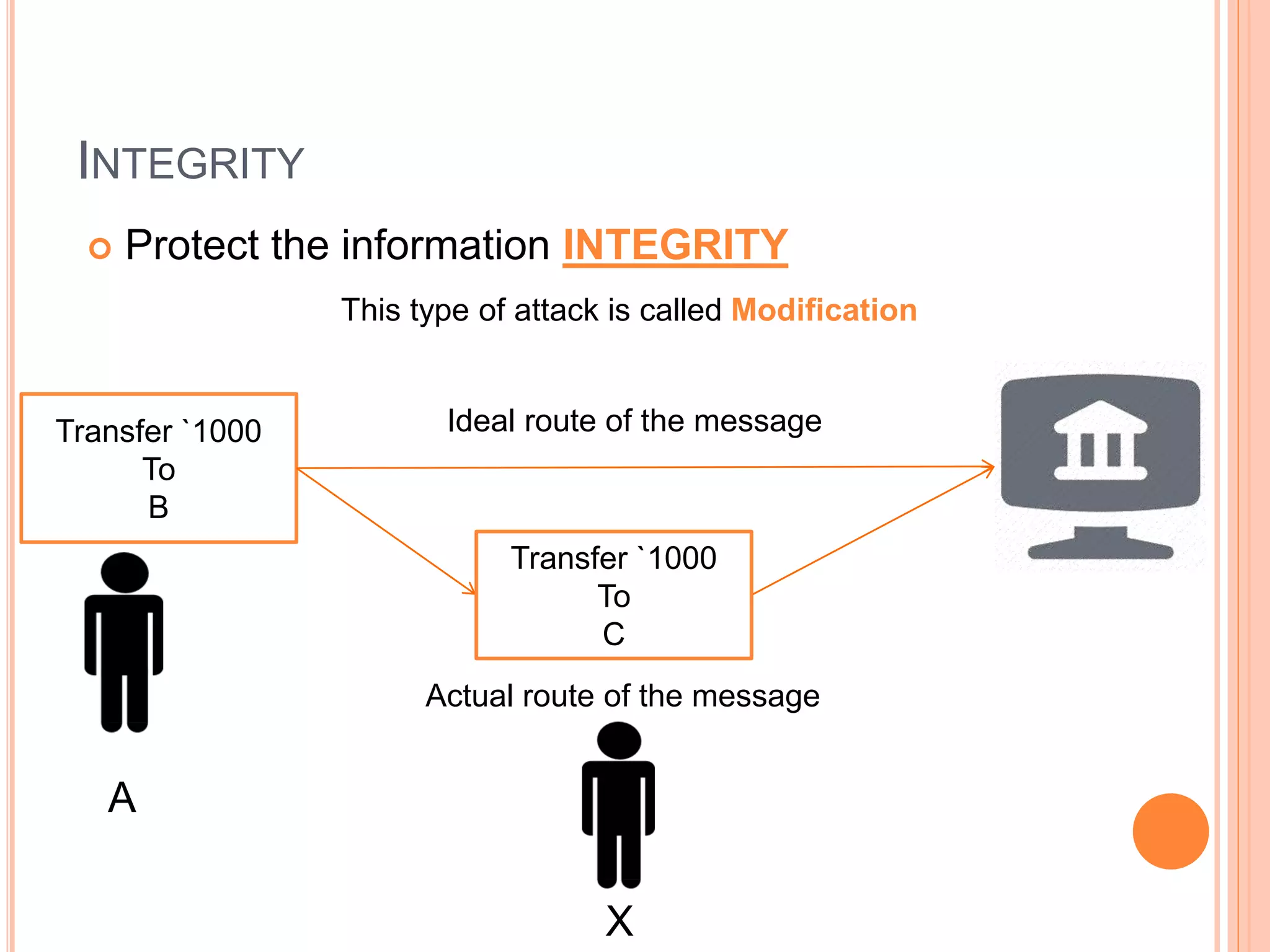
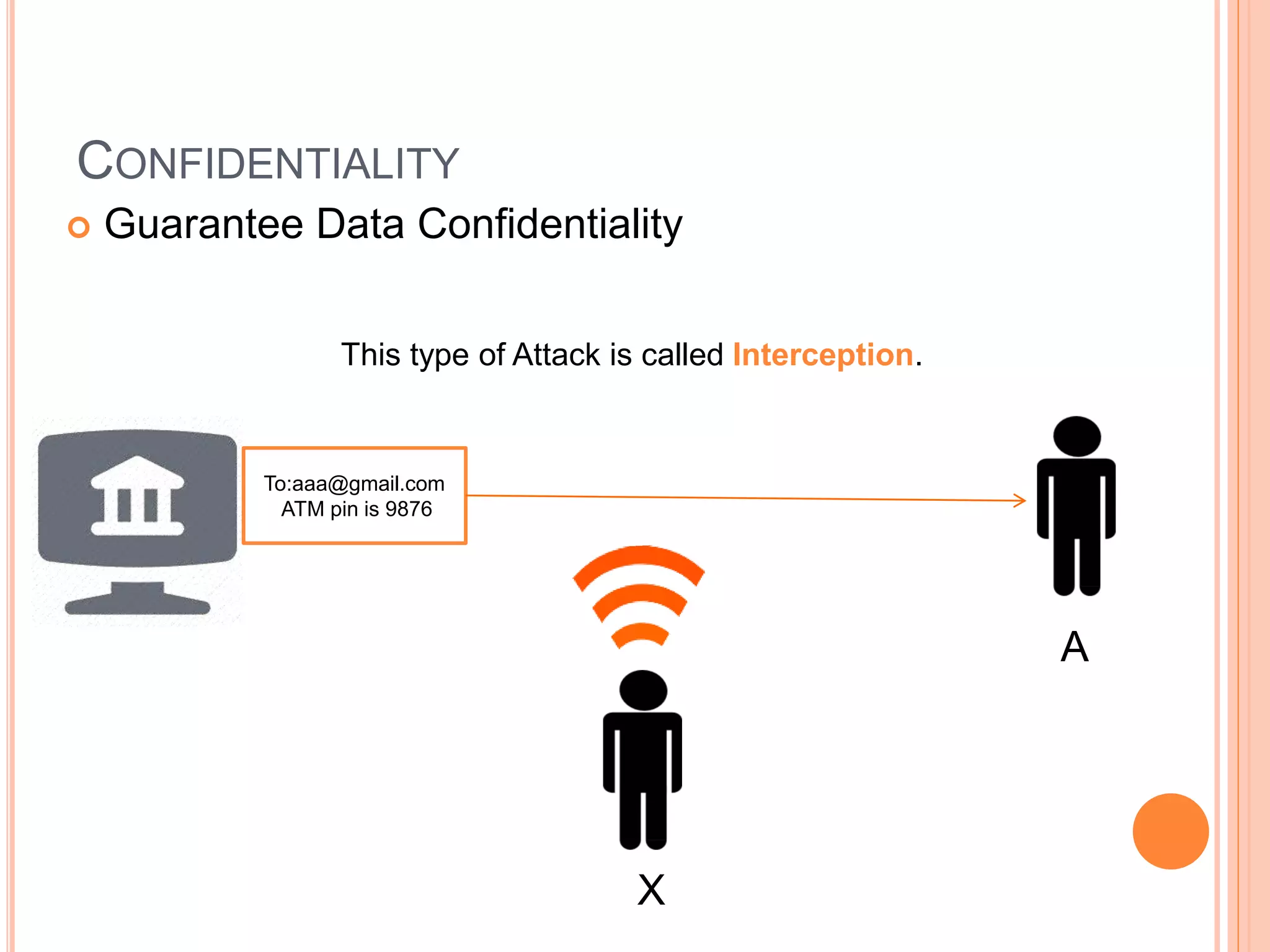
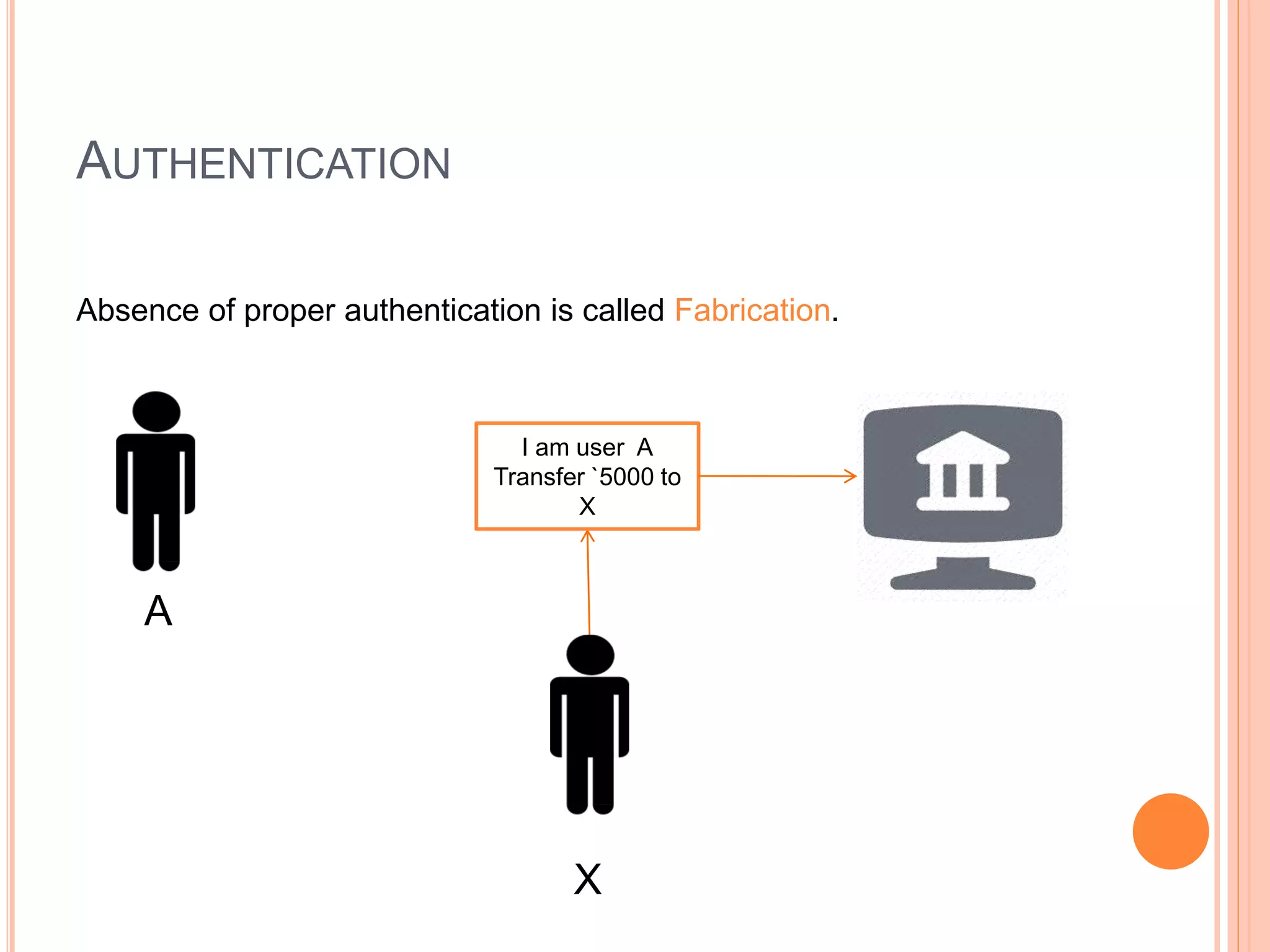
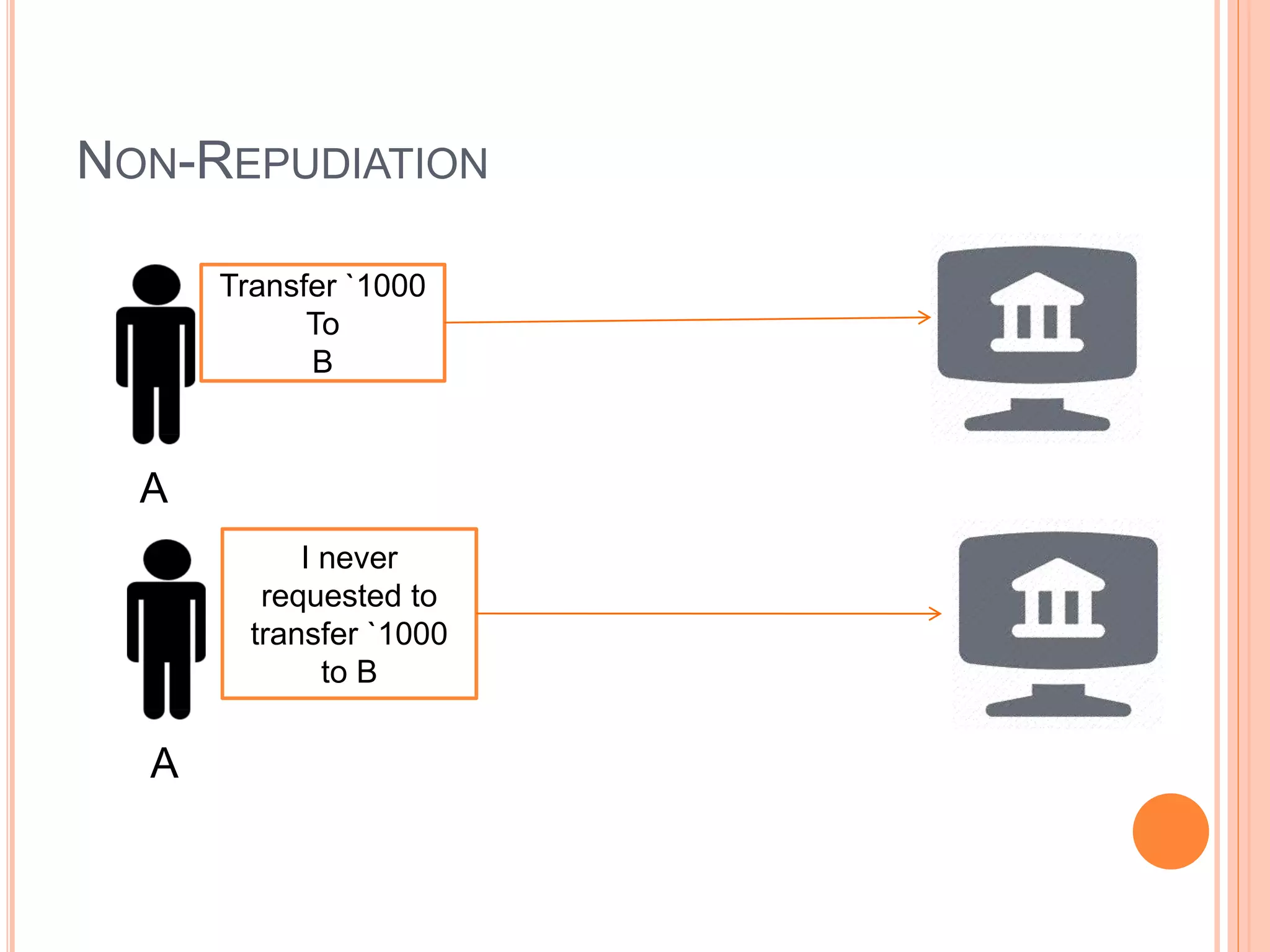
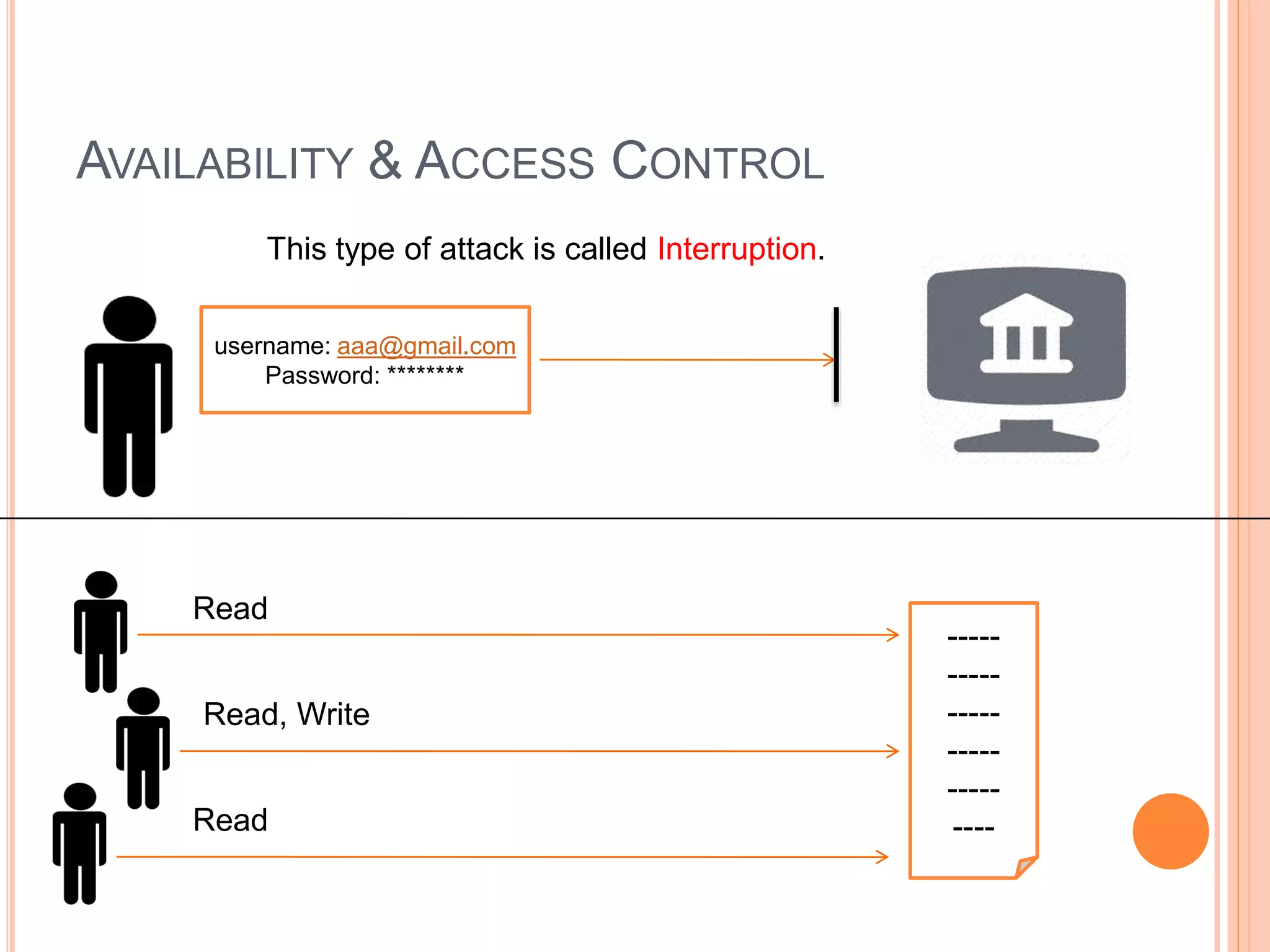
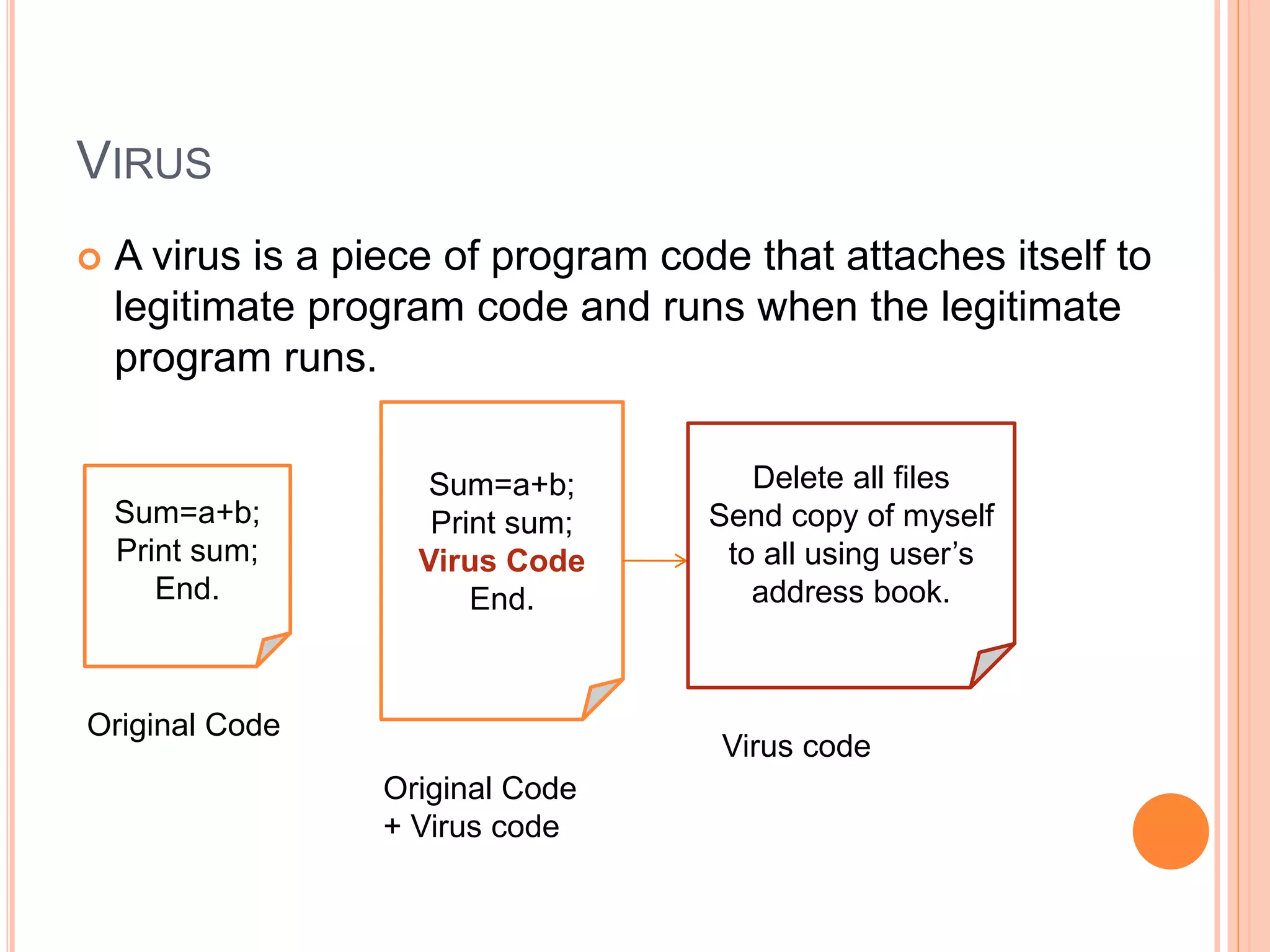
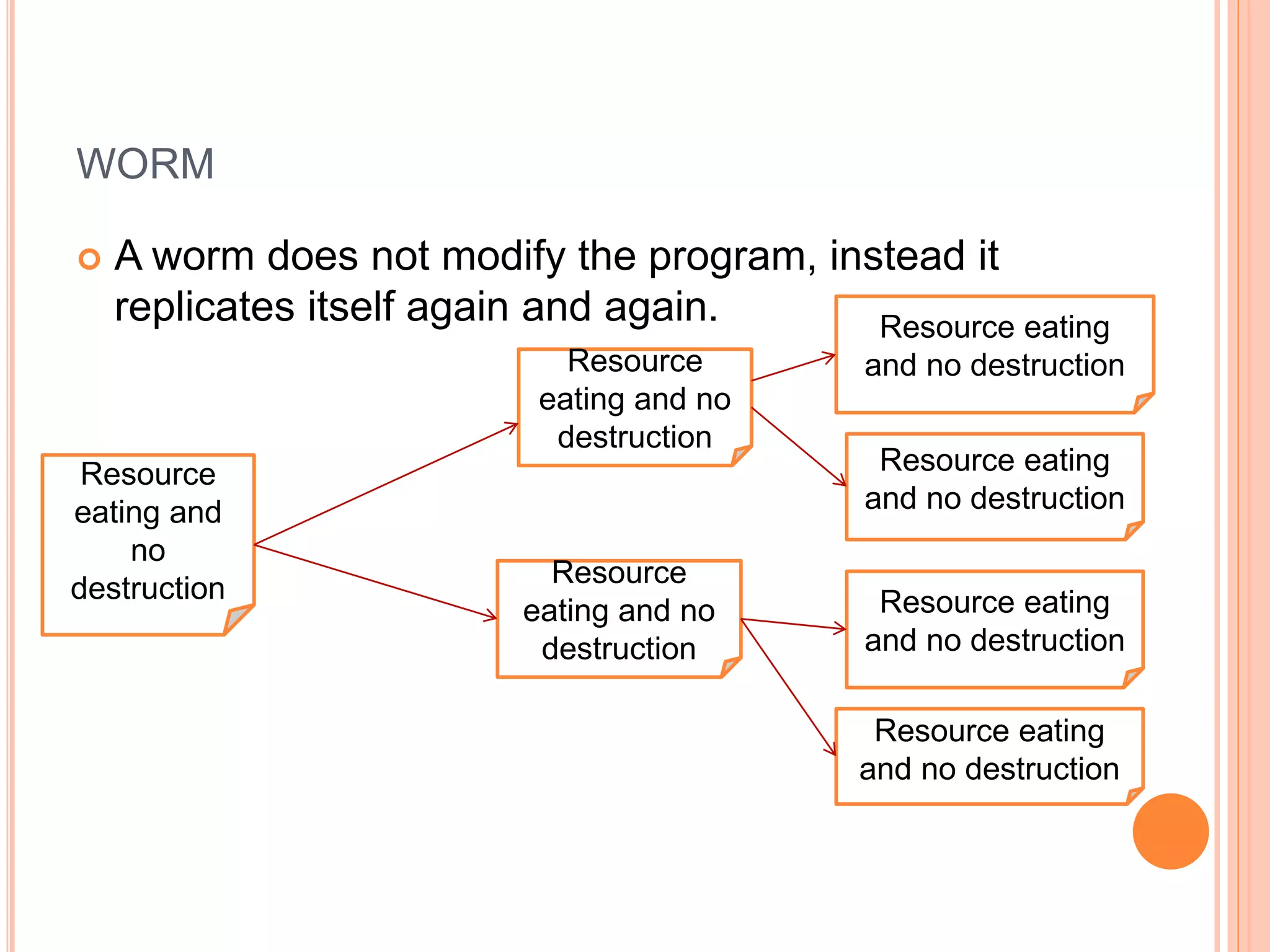
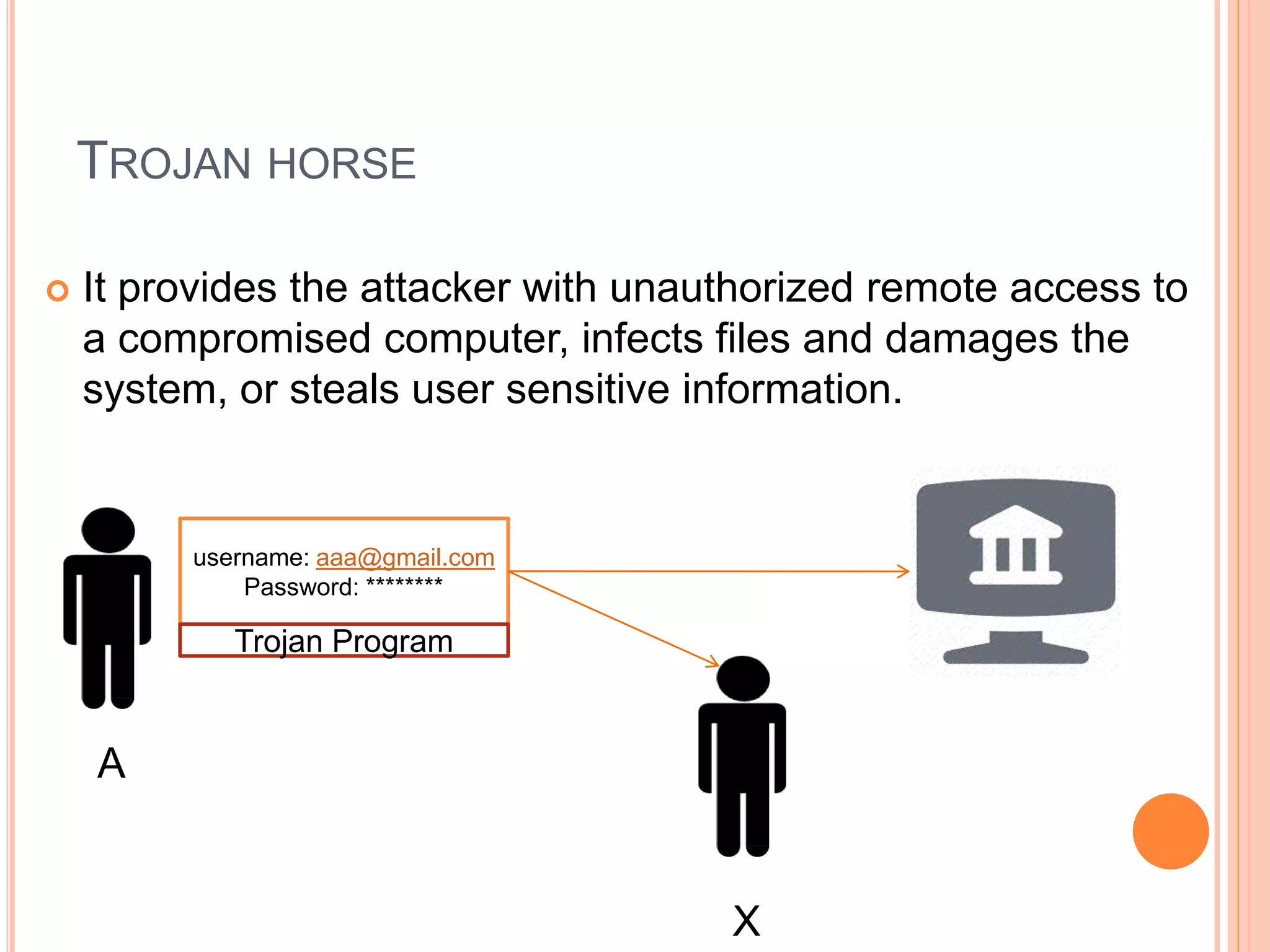
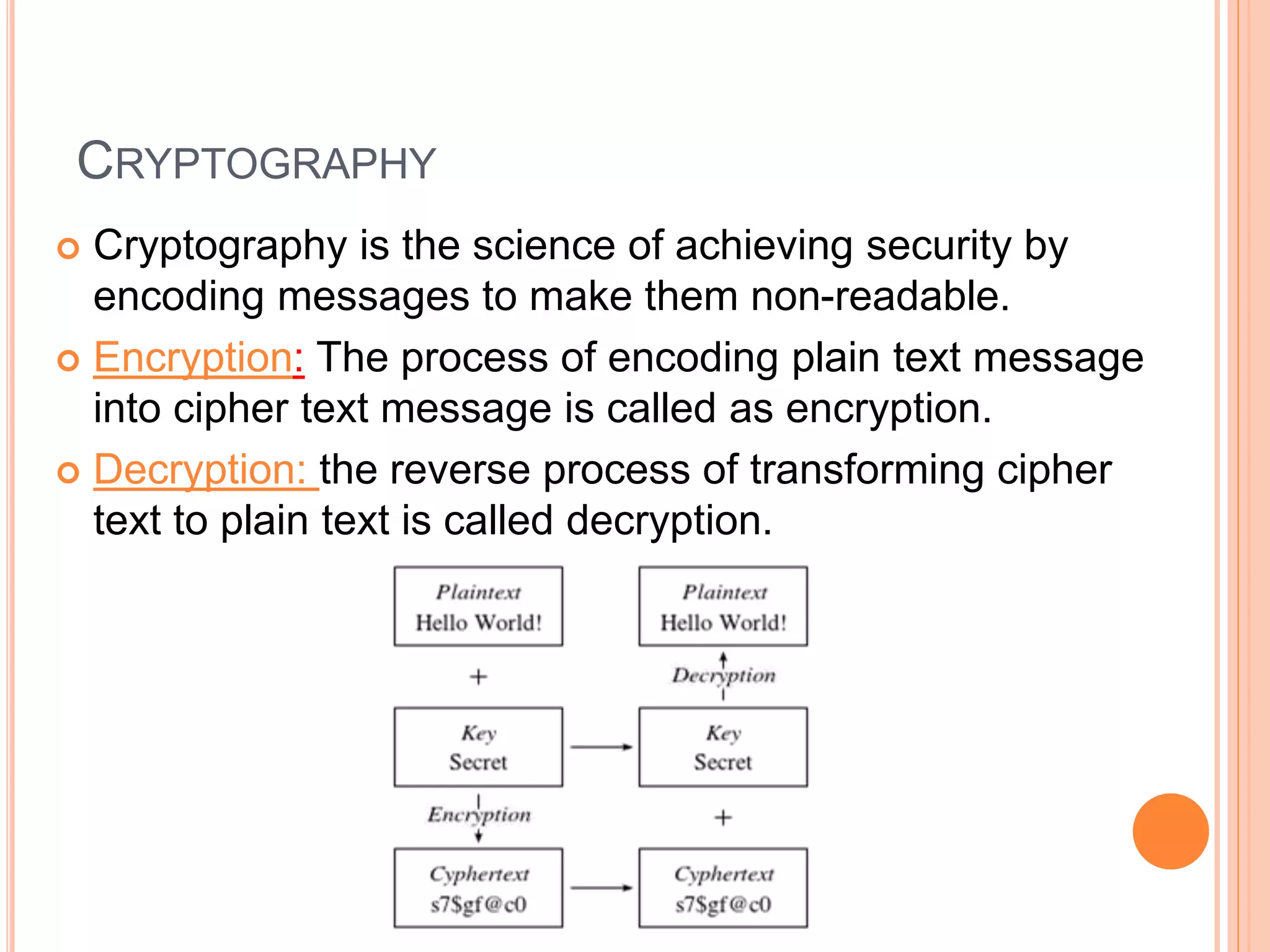
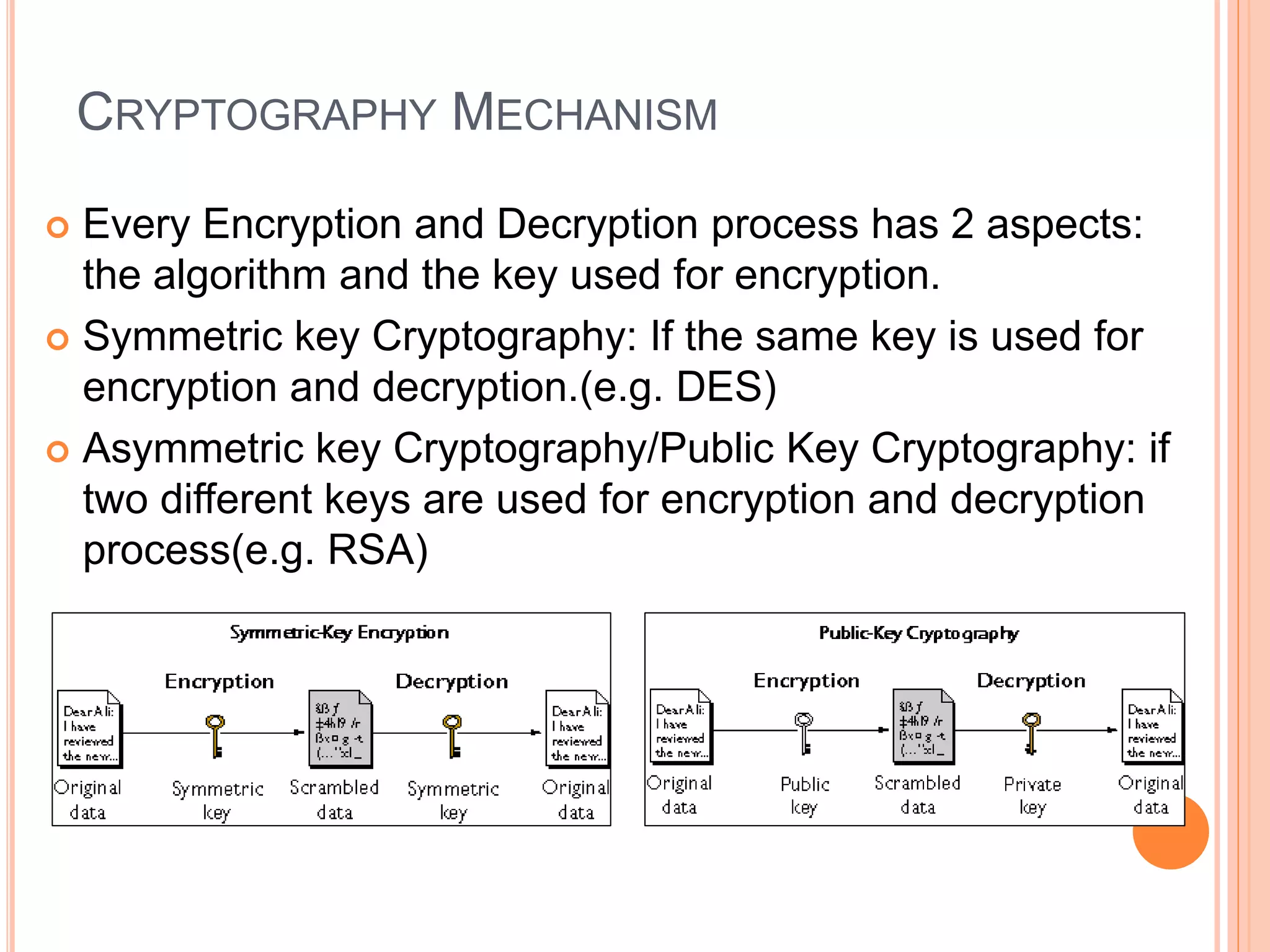
This document discusses network security. It covers the need for security, goals of security like integrity, confidentiality, authentication, non-repudiation and availability. It then discusses famous malware types like viruses, worms and trojan horses. Viruses attach to programs and run when the program runs, worms replicate endlessly without causing harm, and trojan horses provide unauthorized access. The document also covers phishing scams and cryptography techniques like encryption, decryption, symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography.