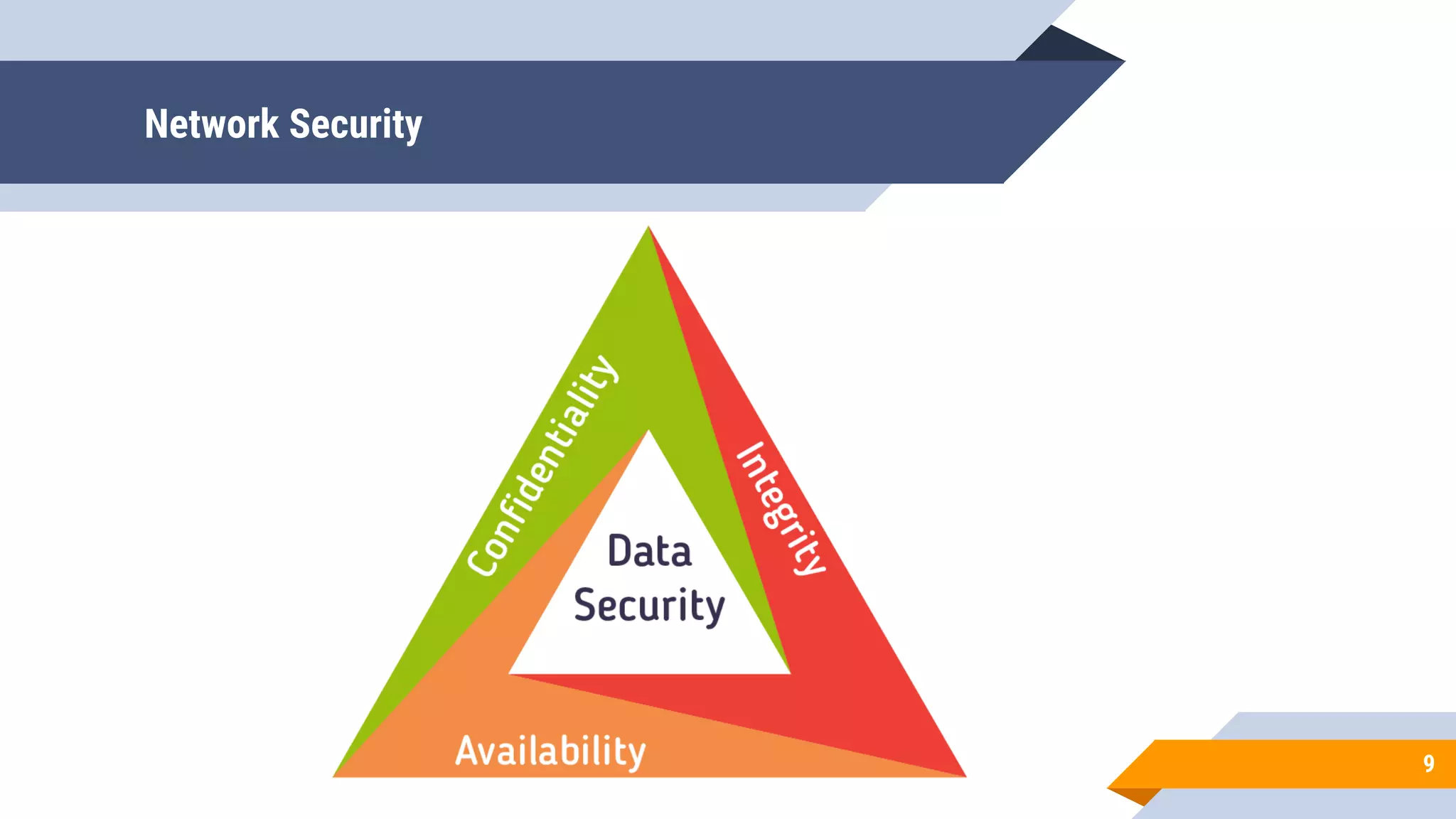
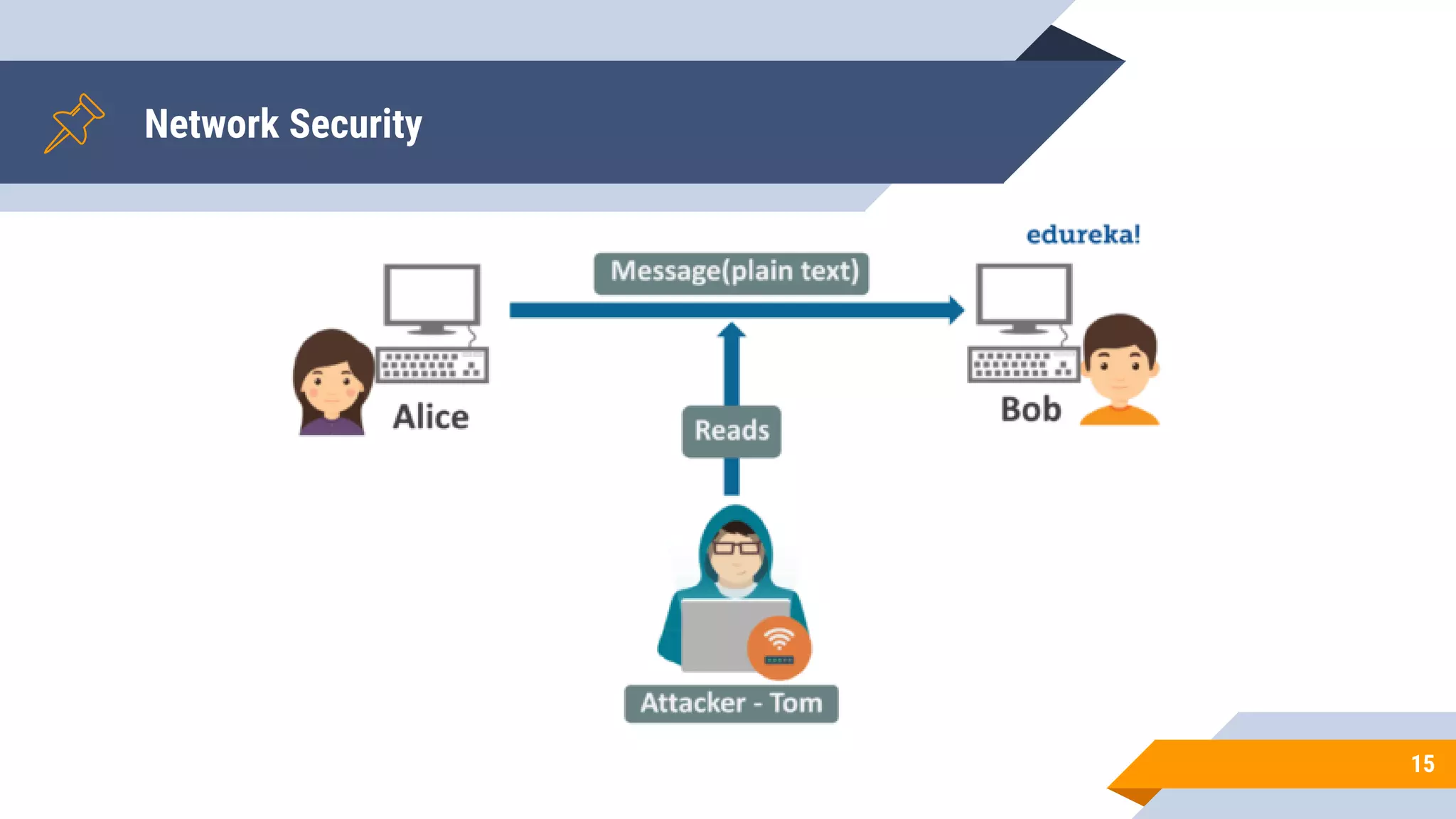
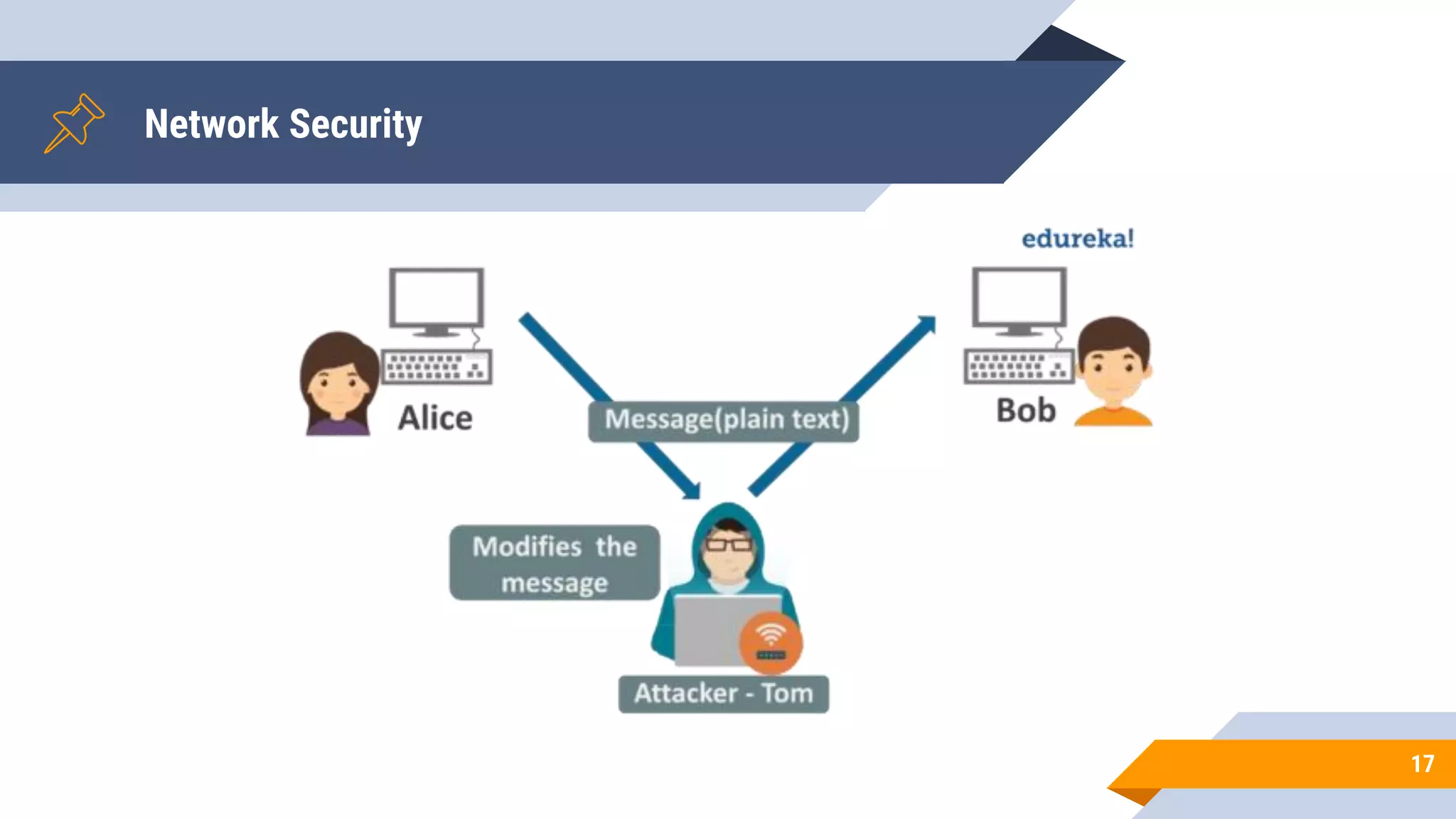
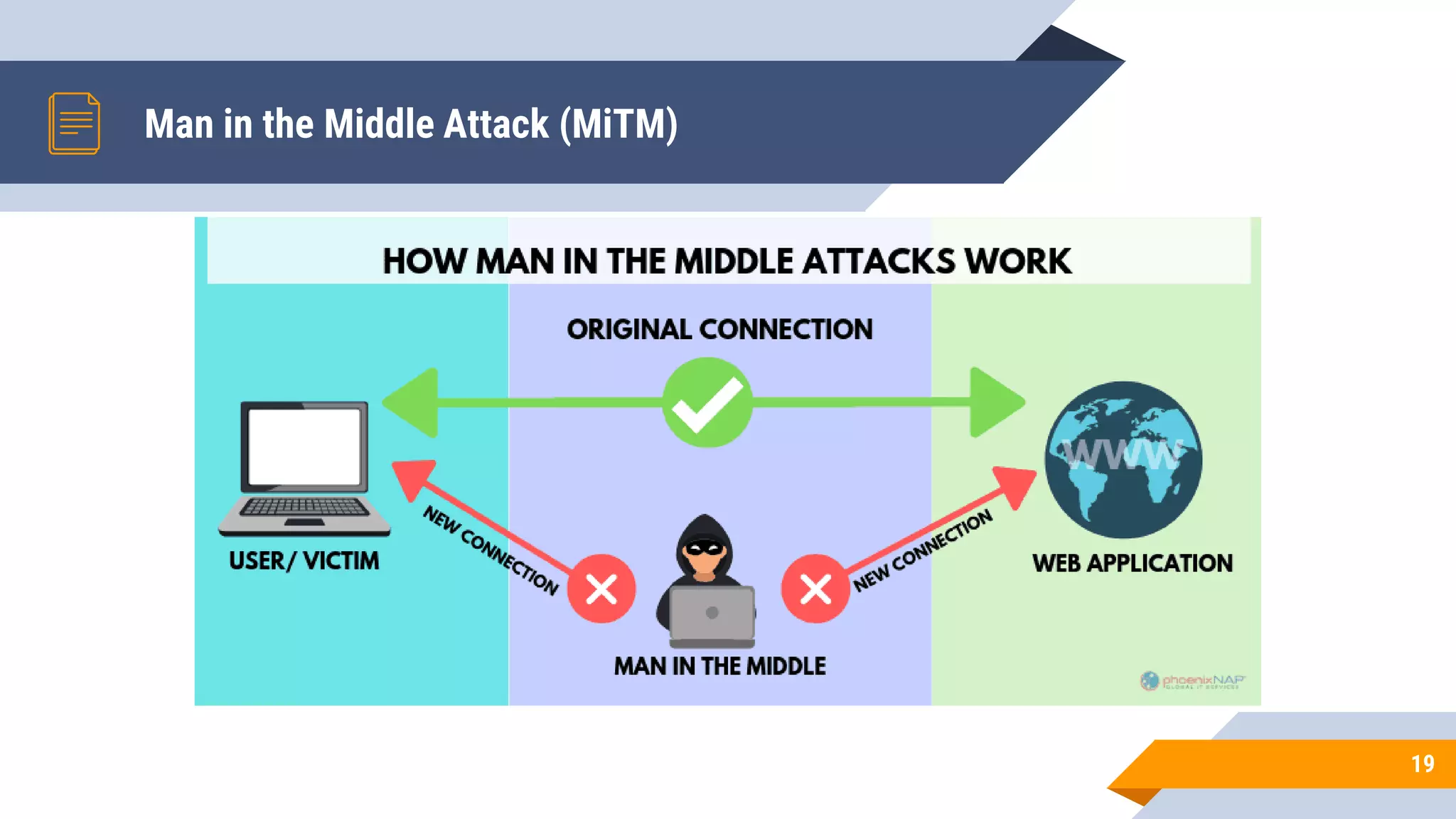
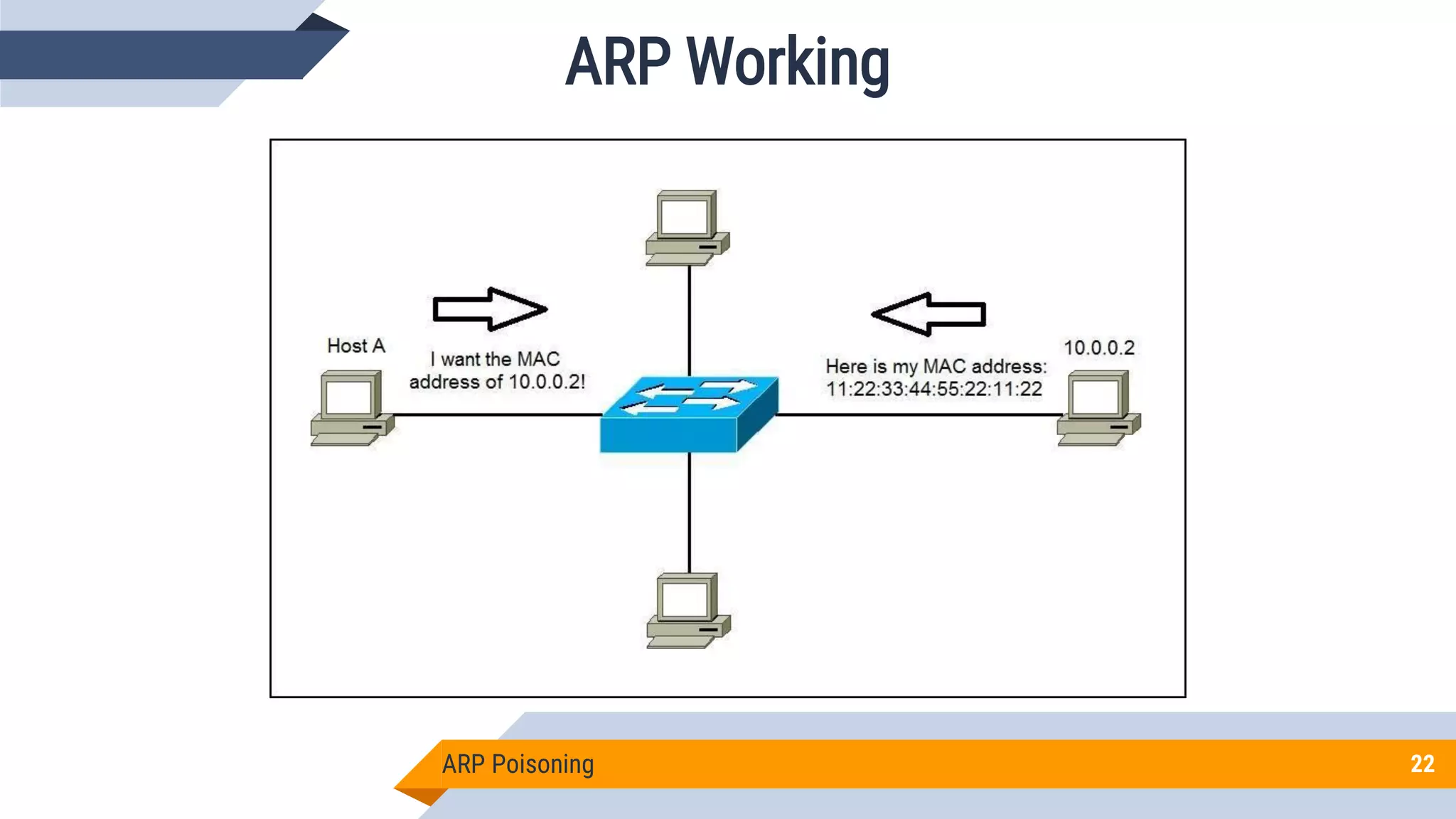
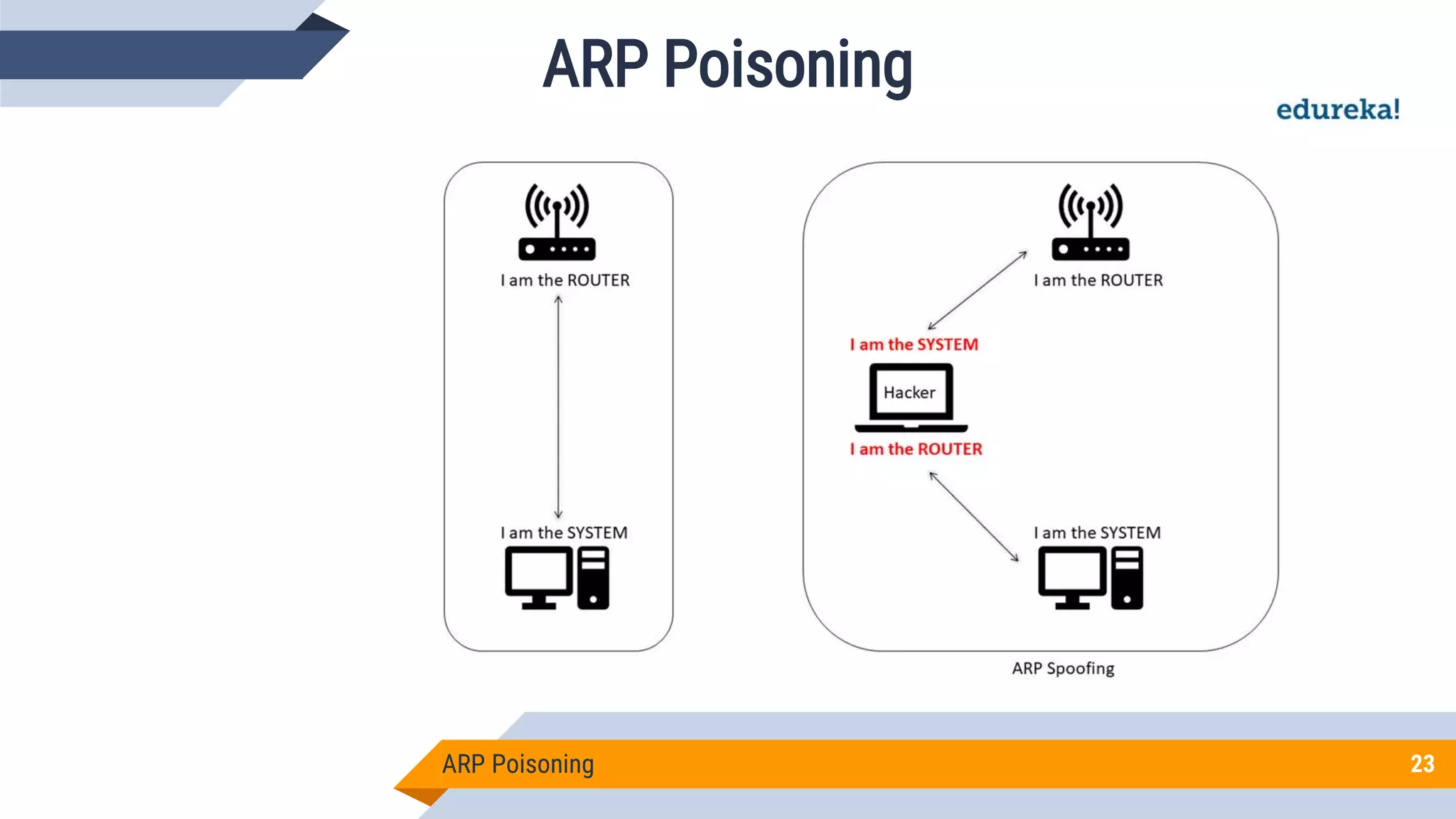
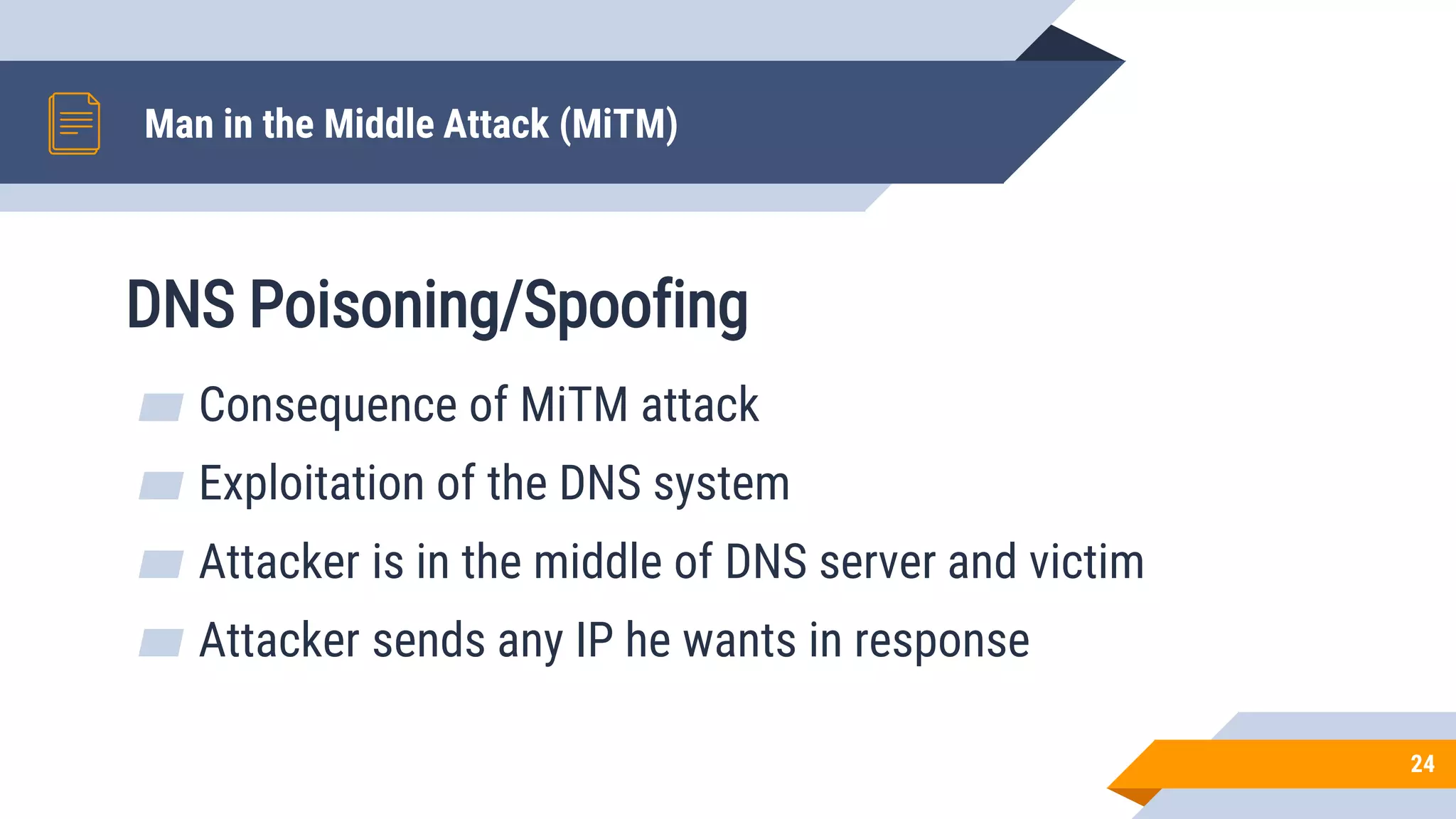
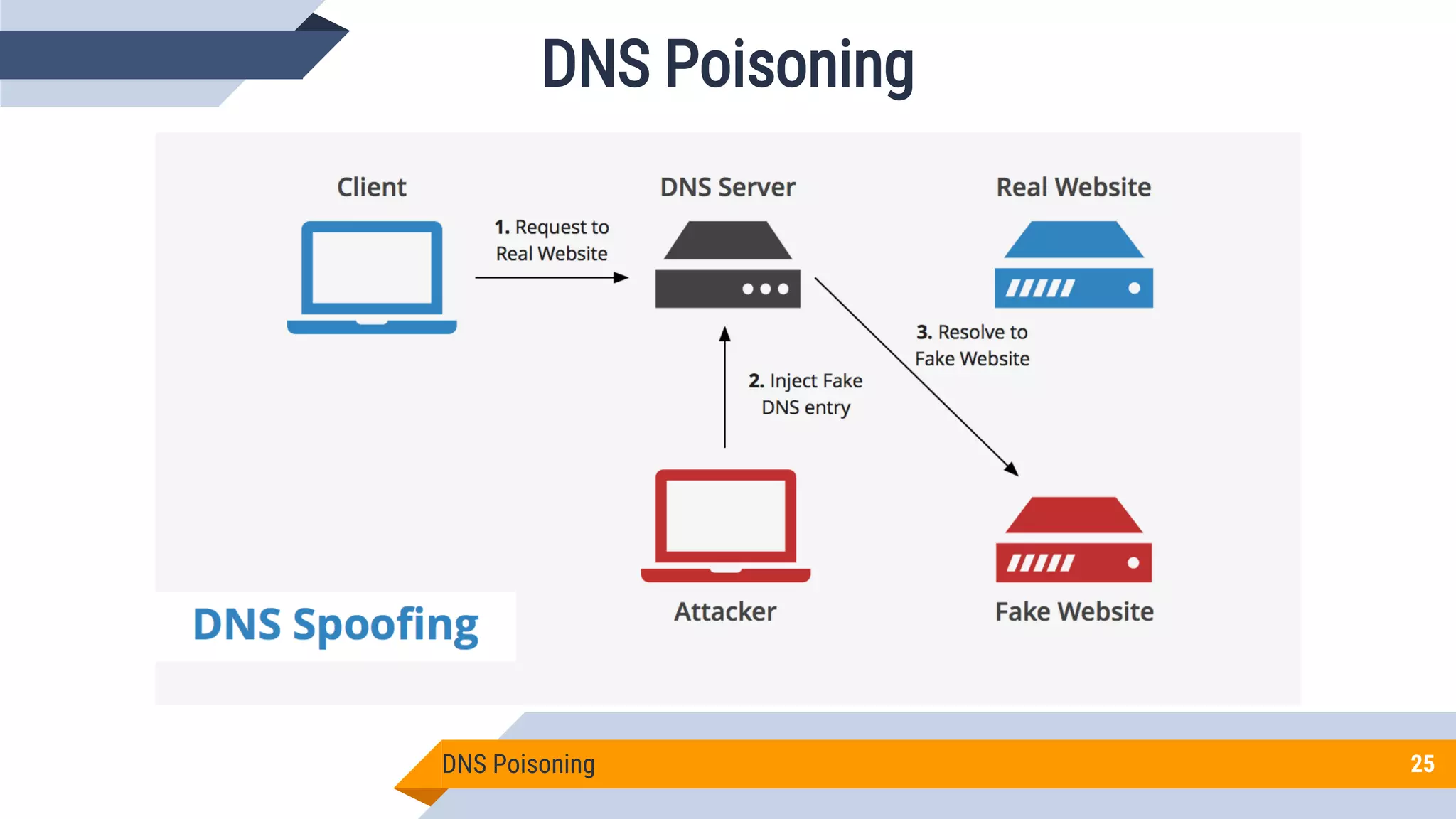
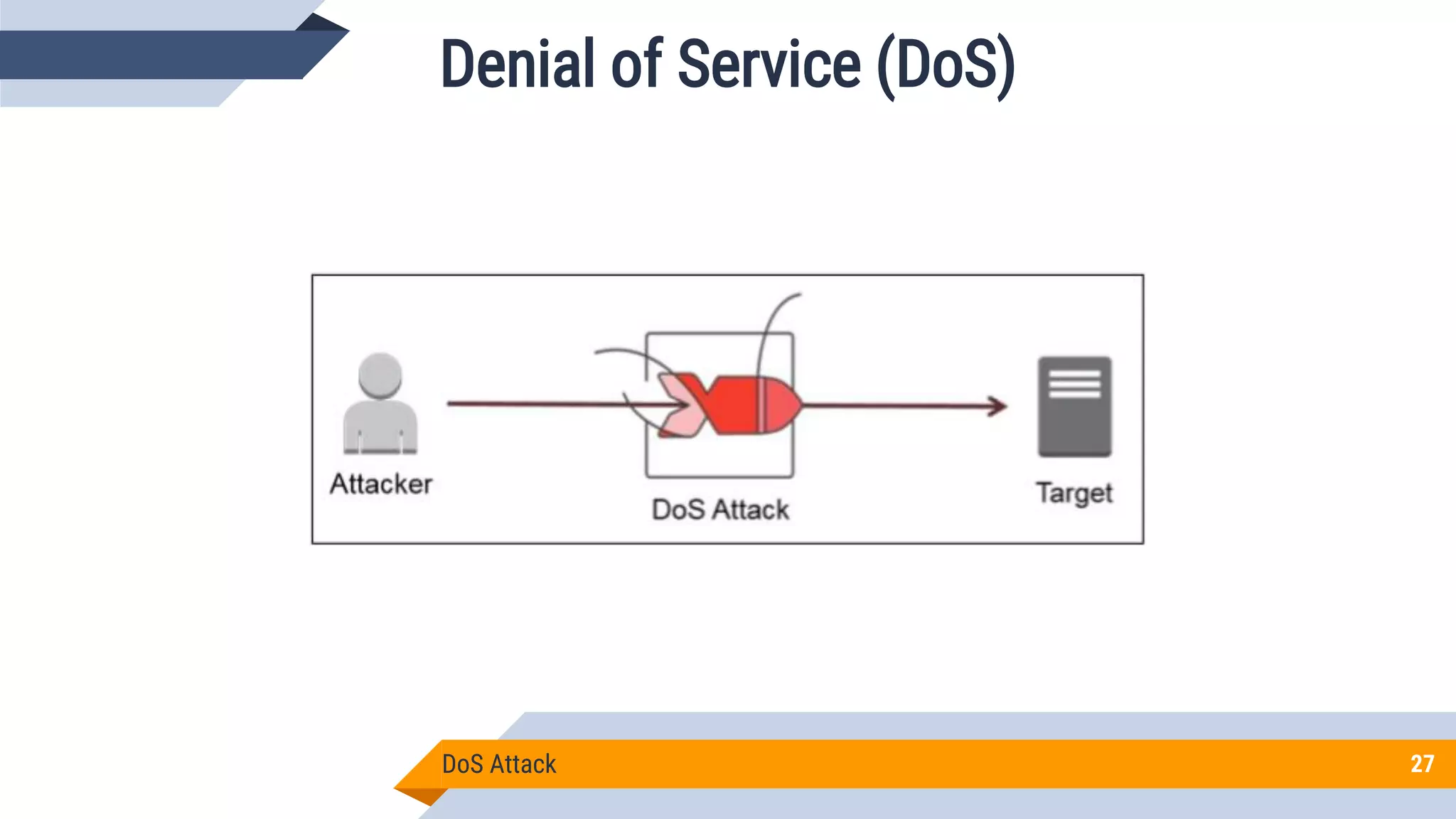
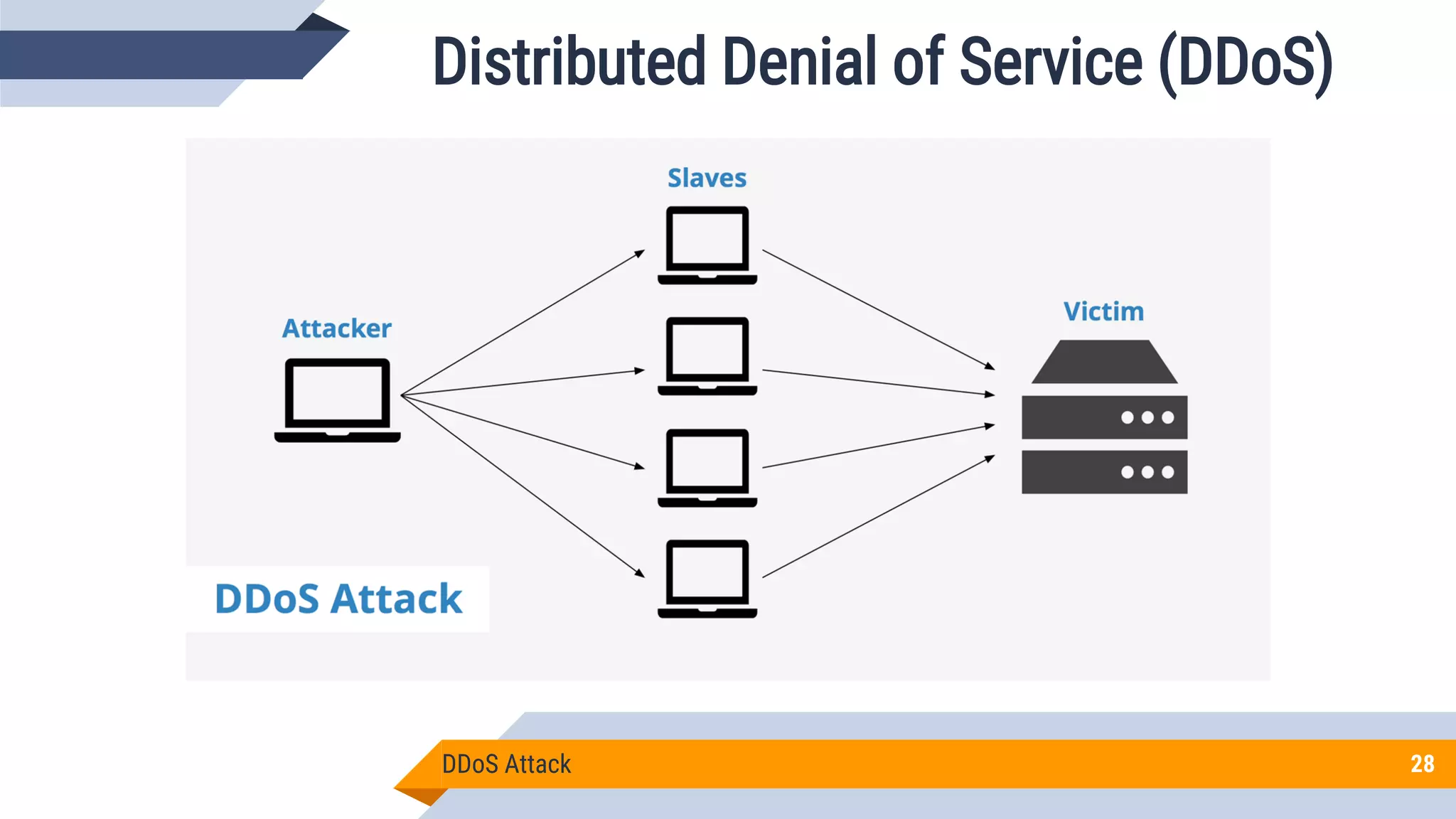
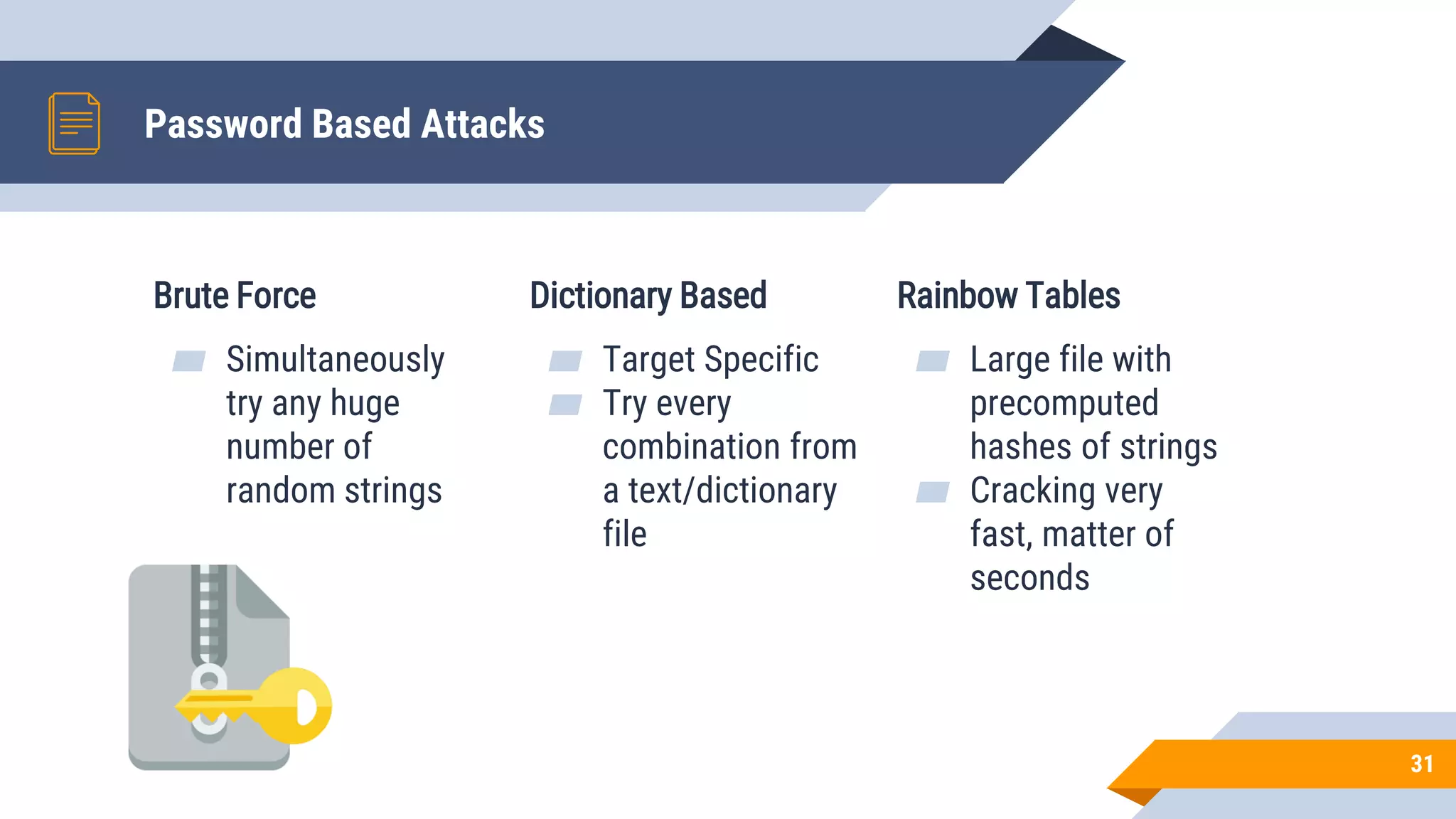
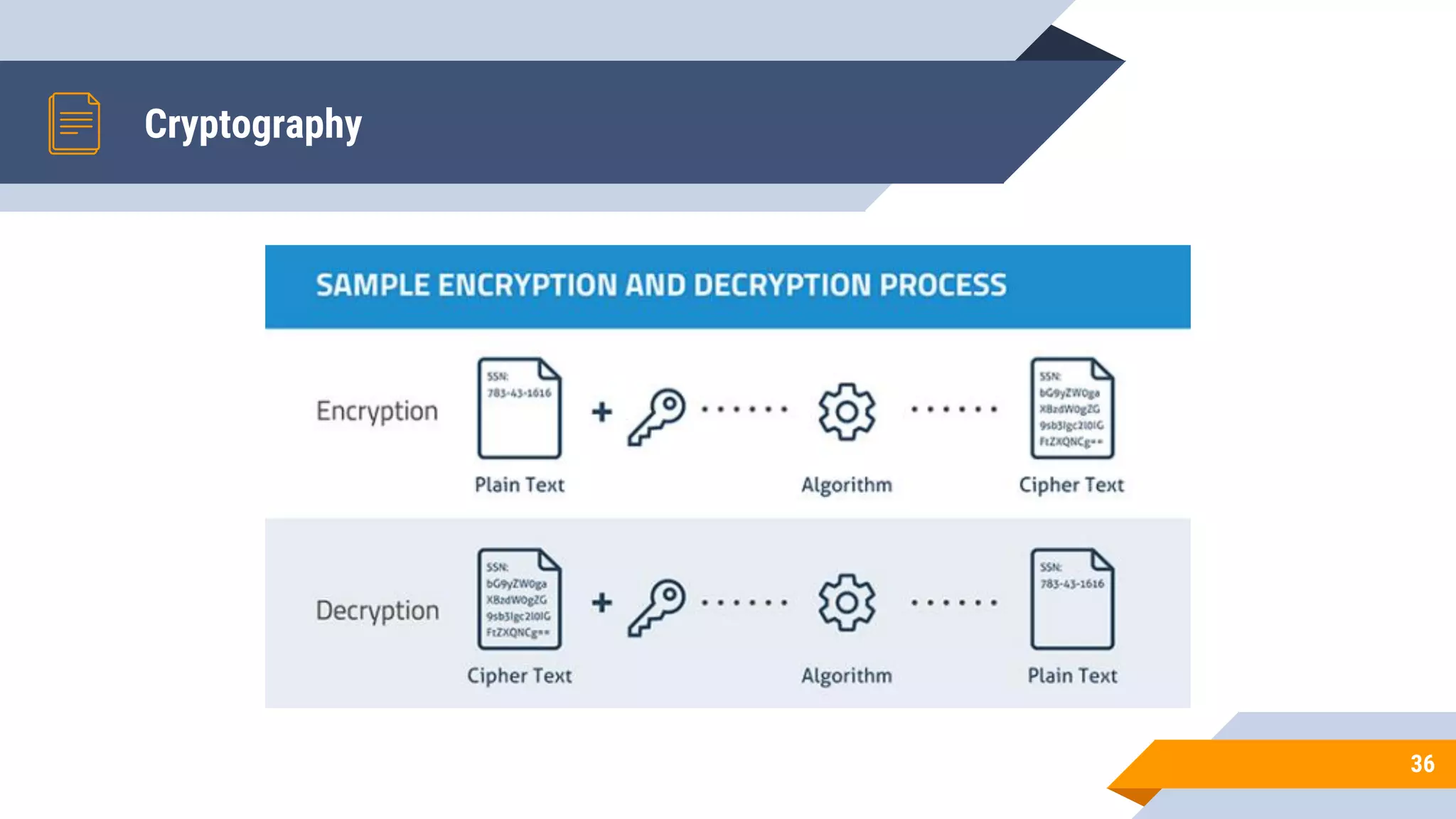
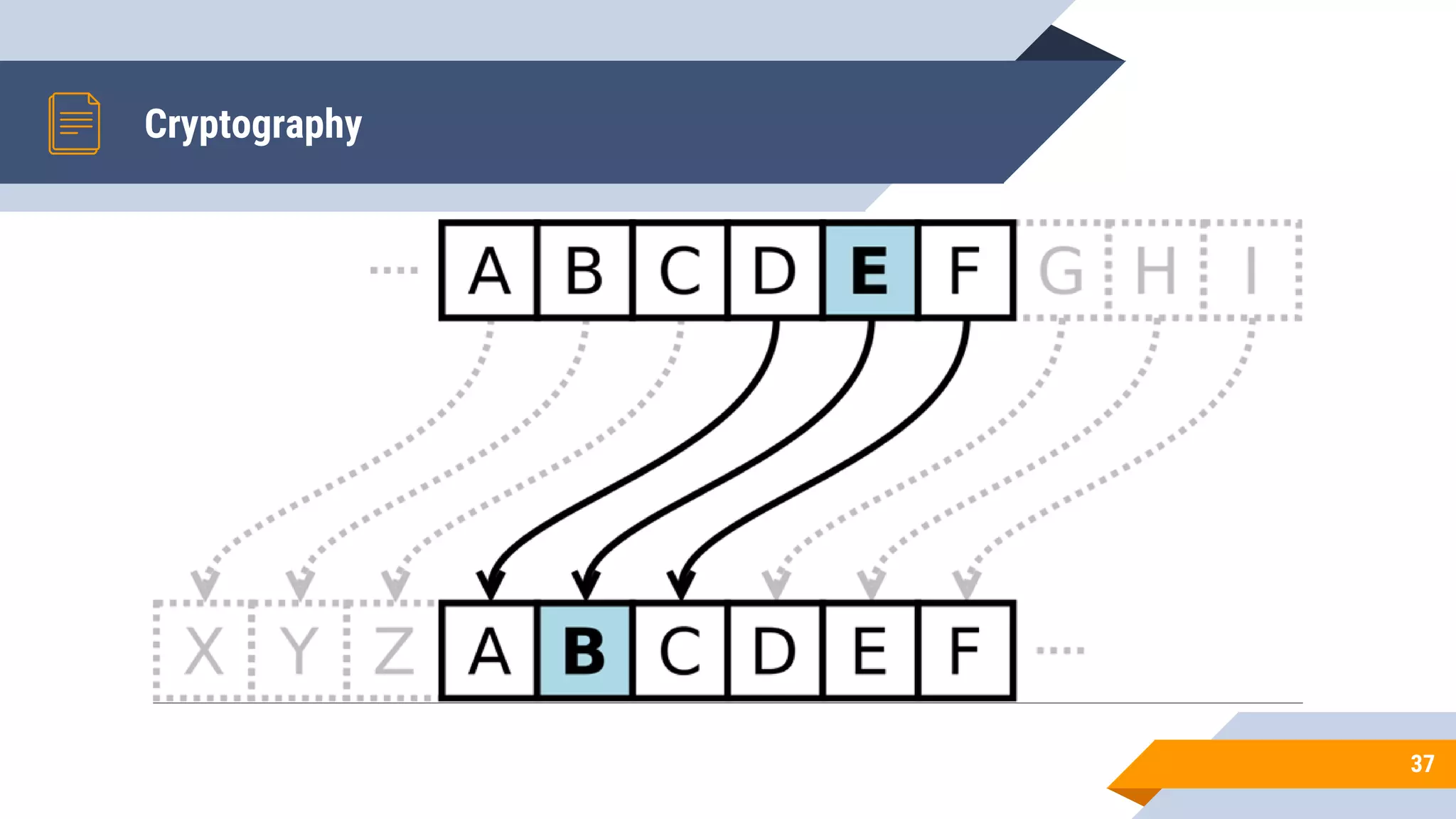
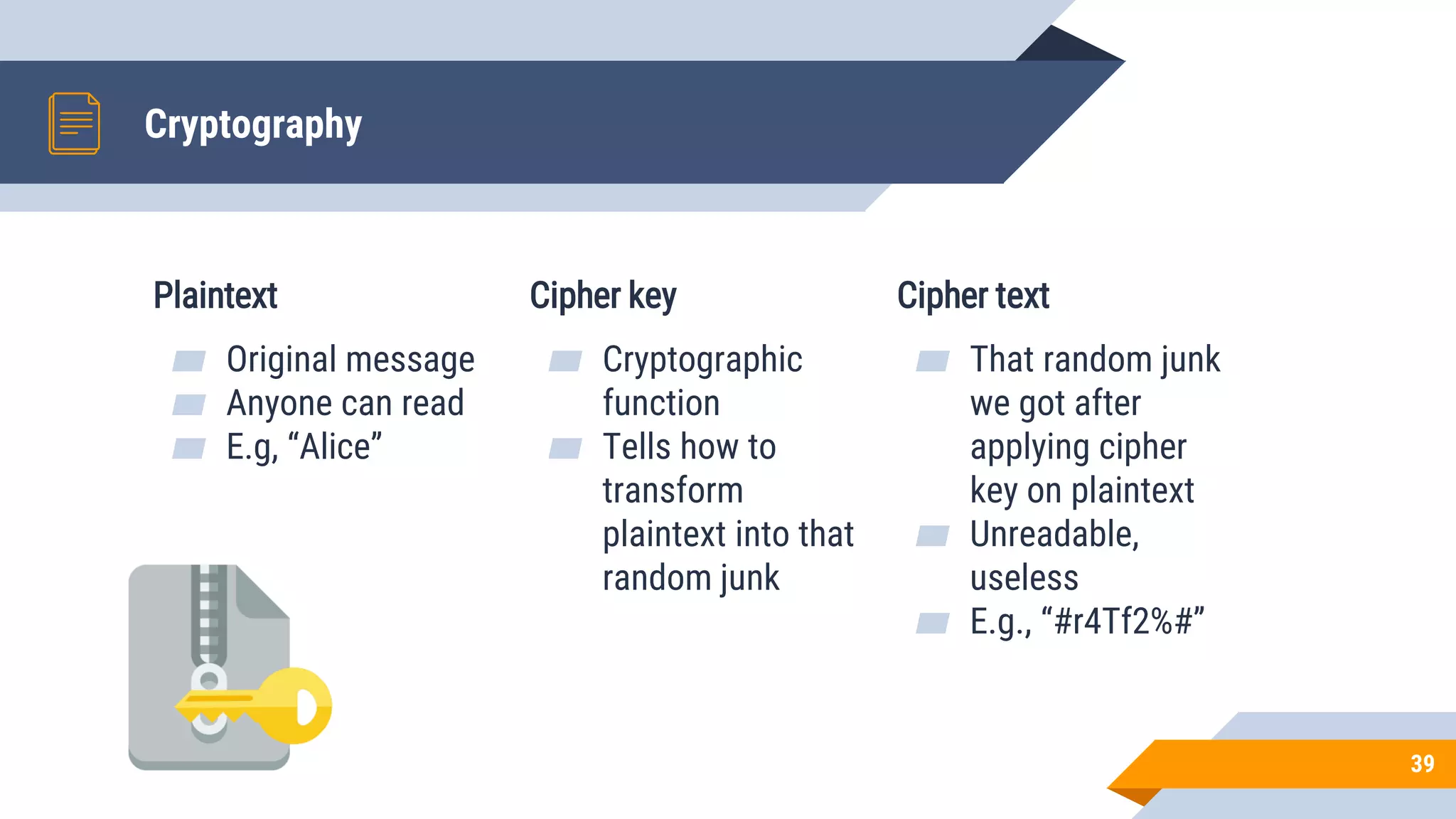
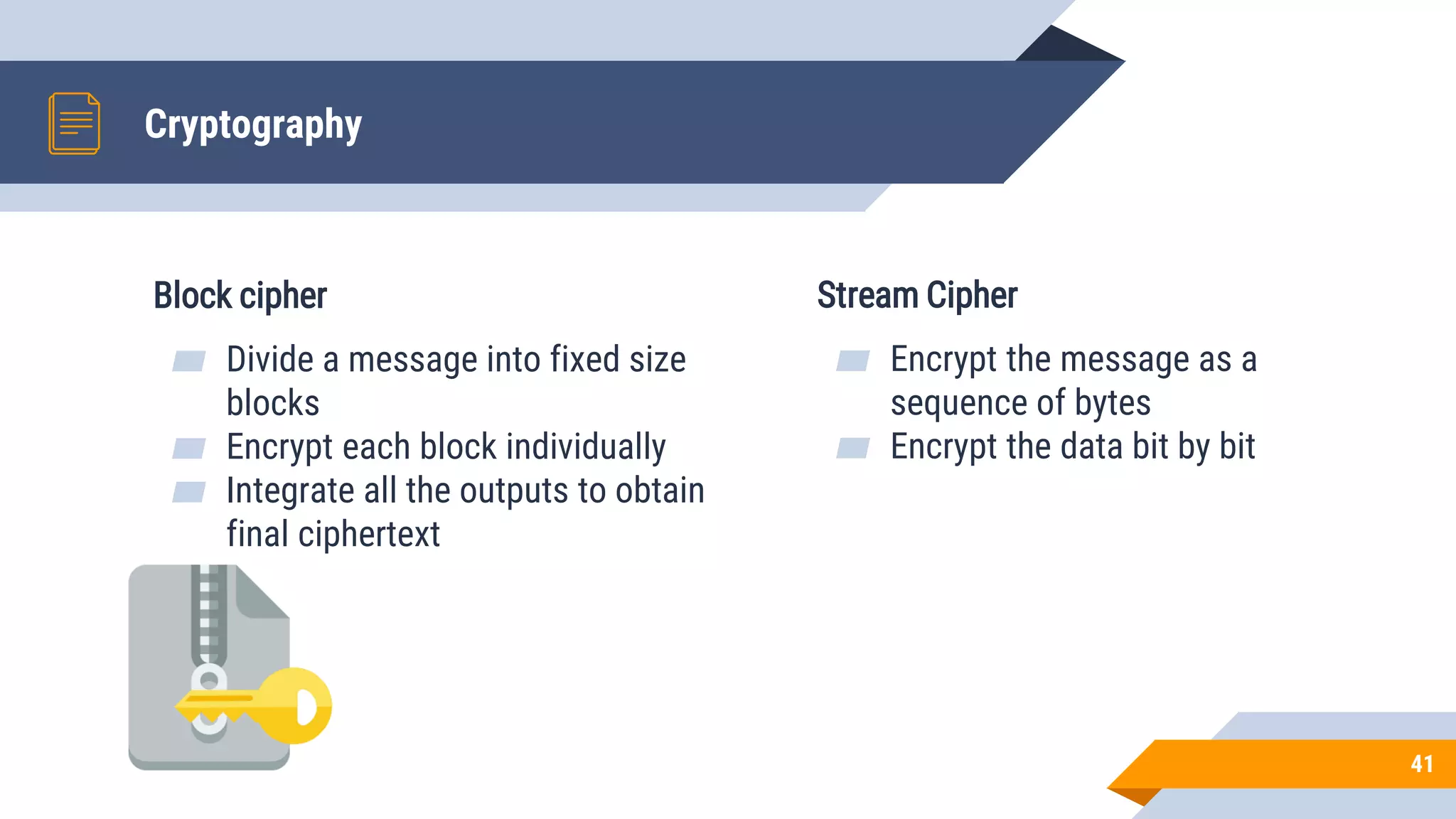
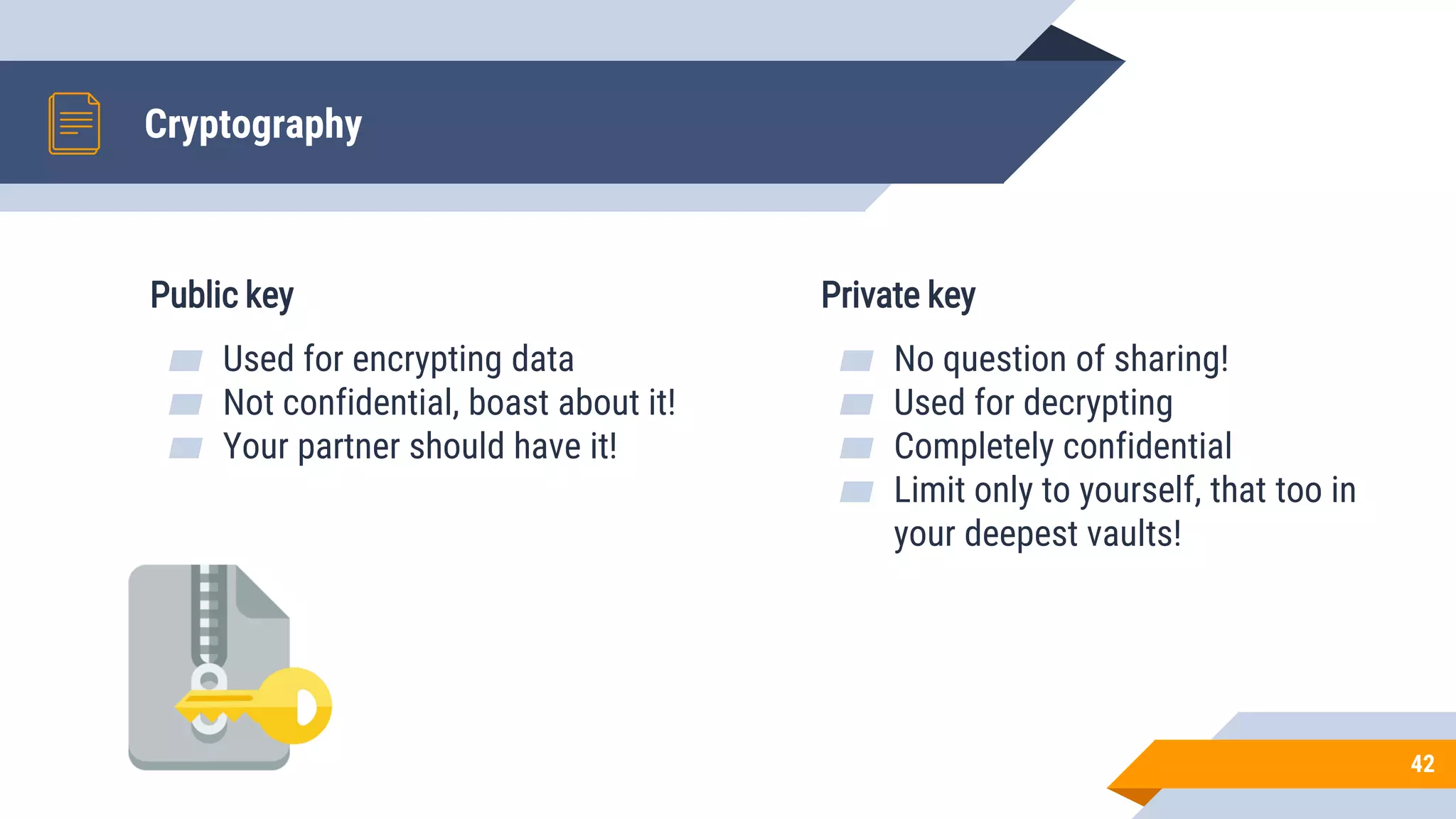
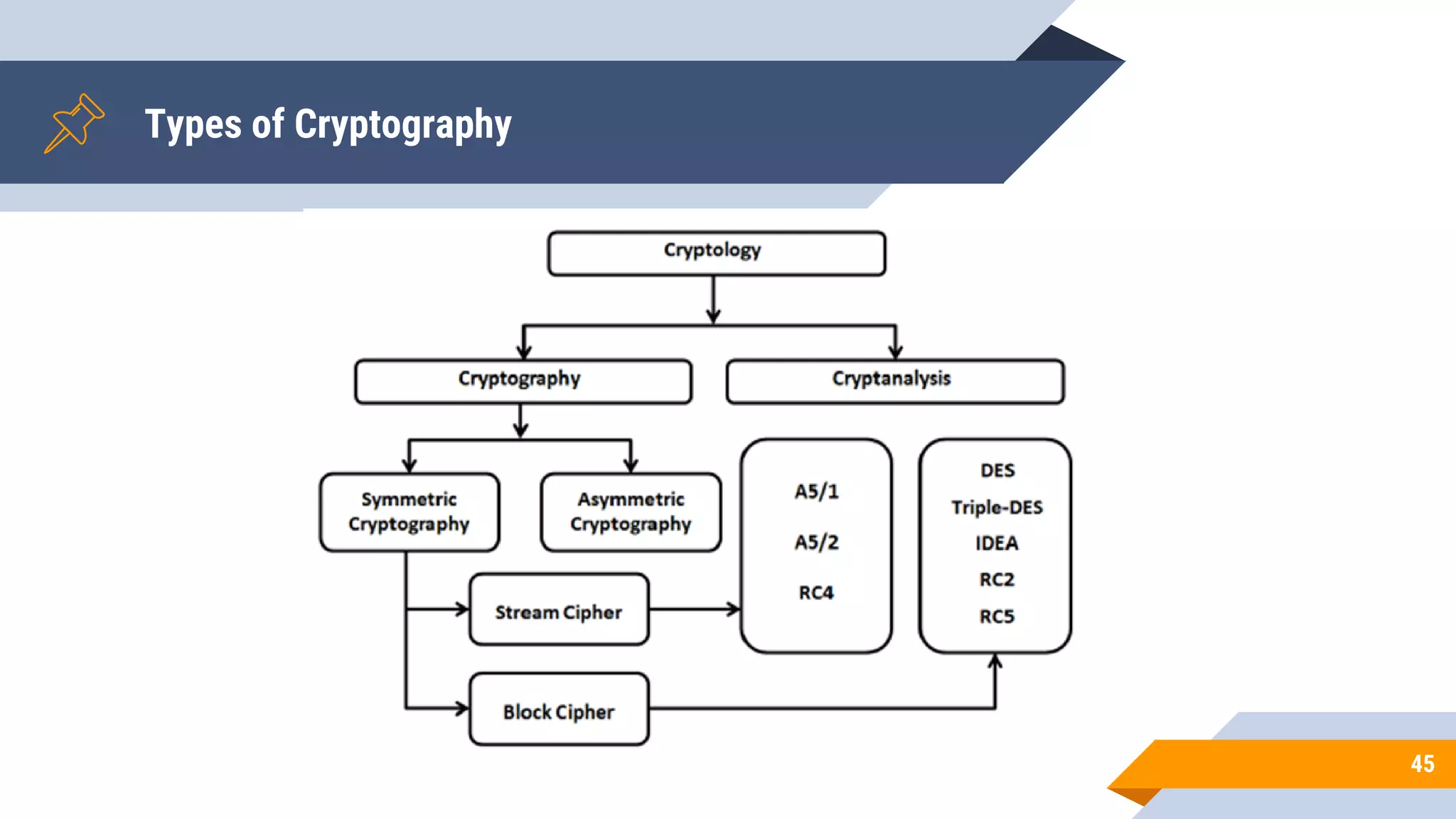
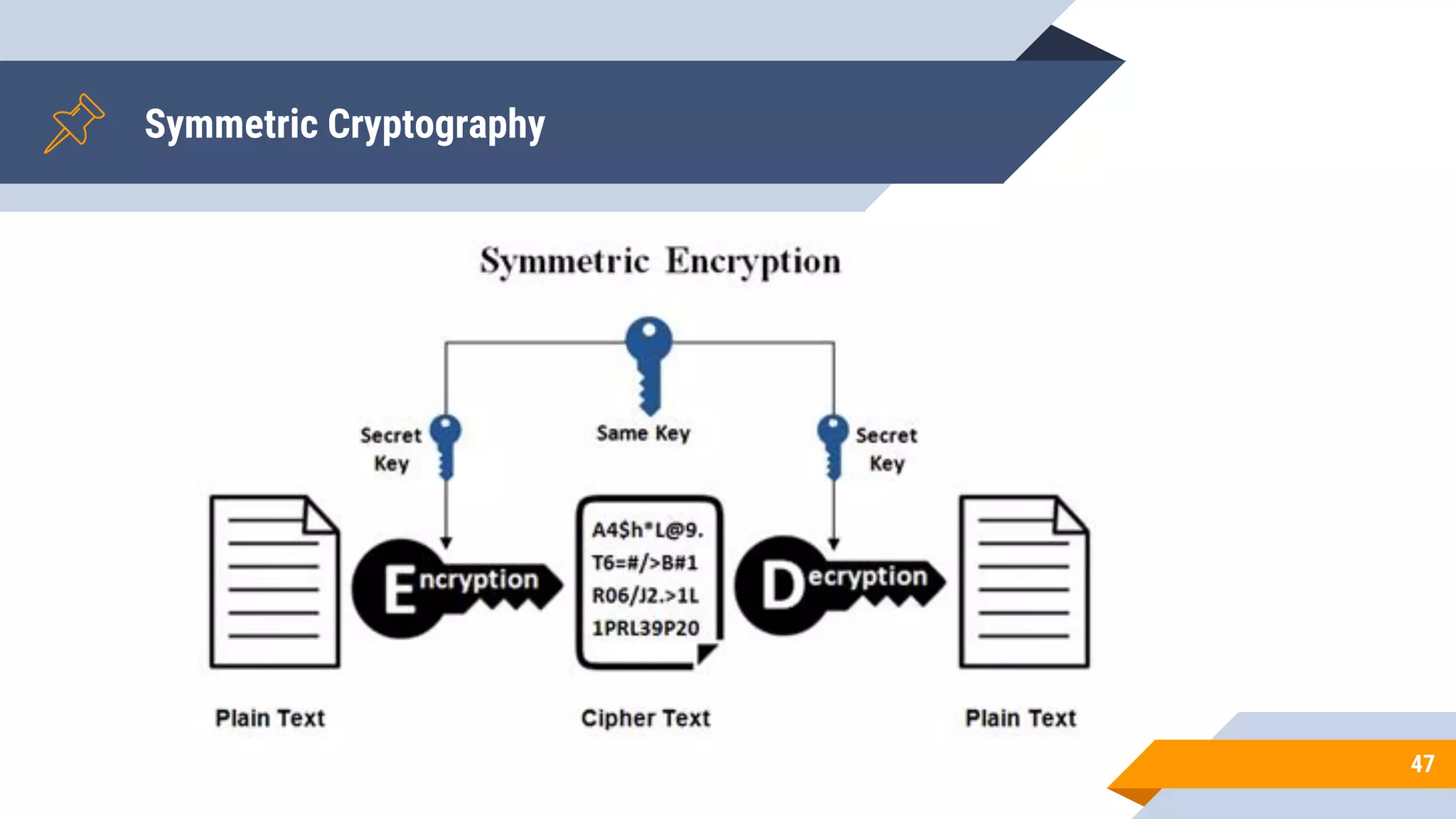
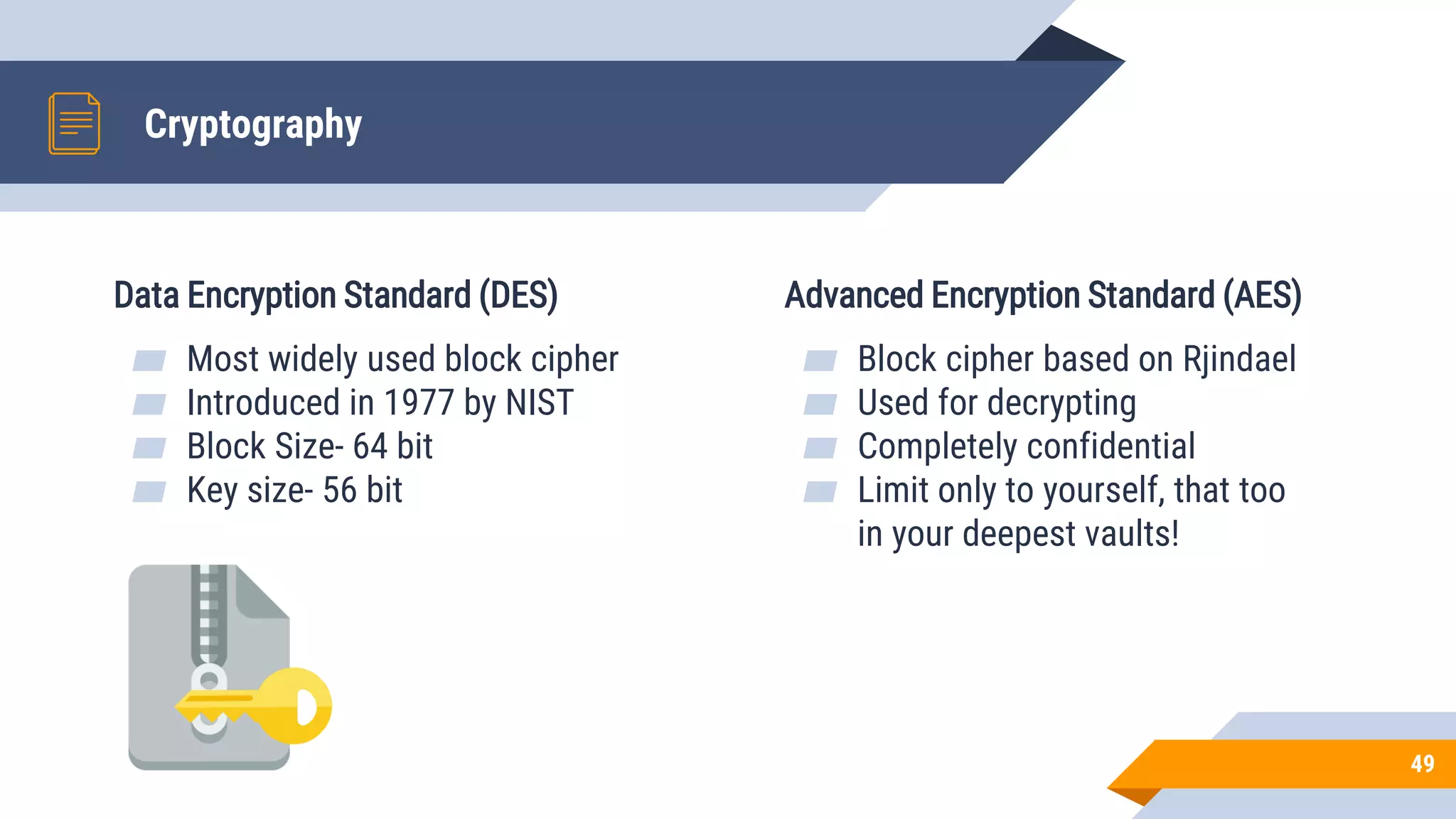
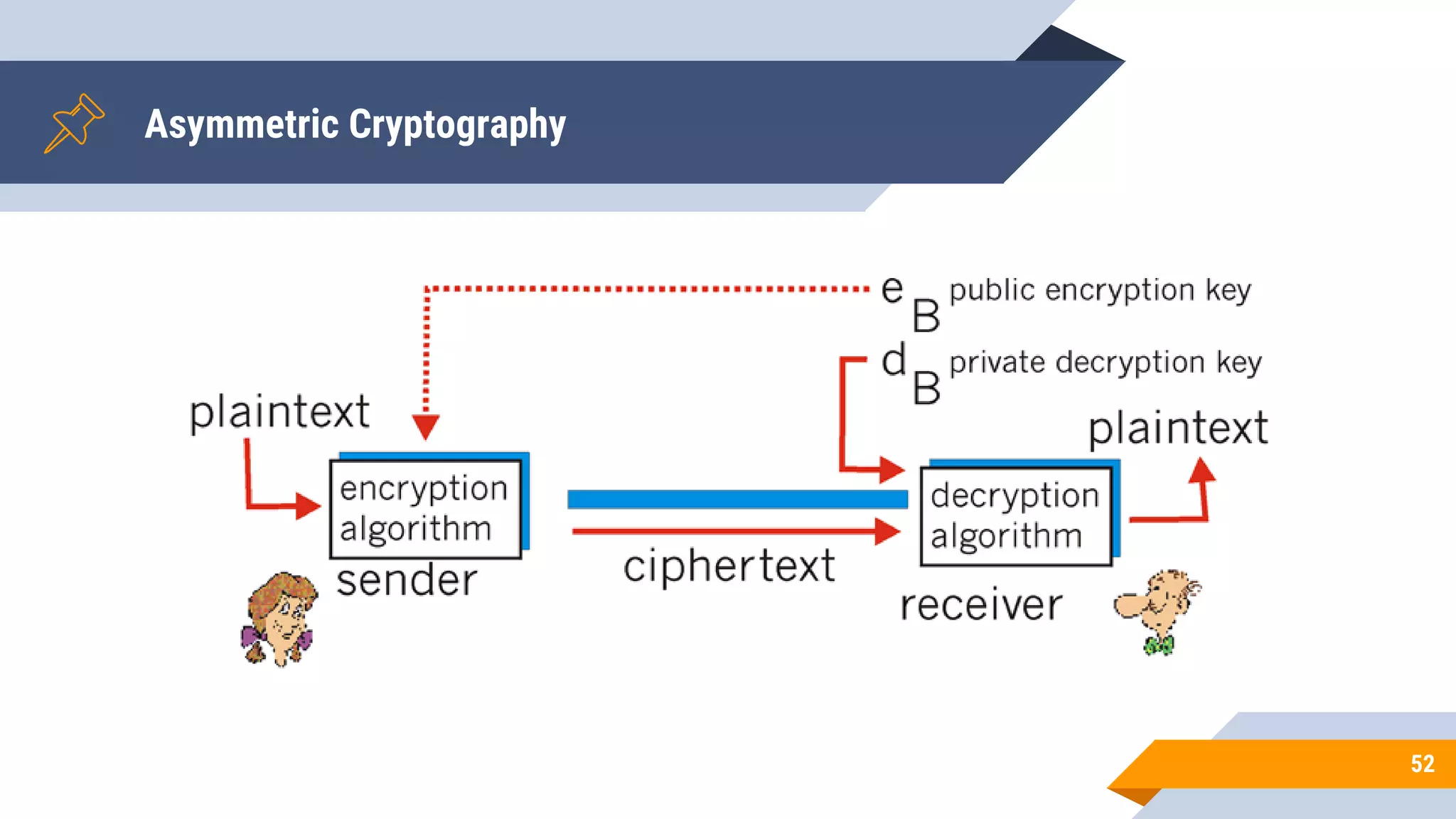
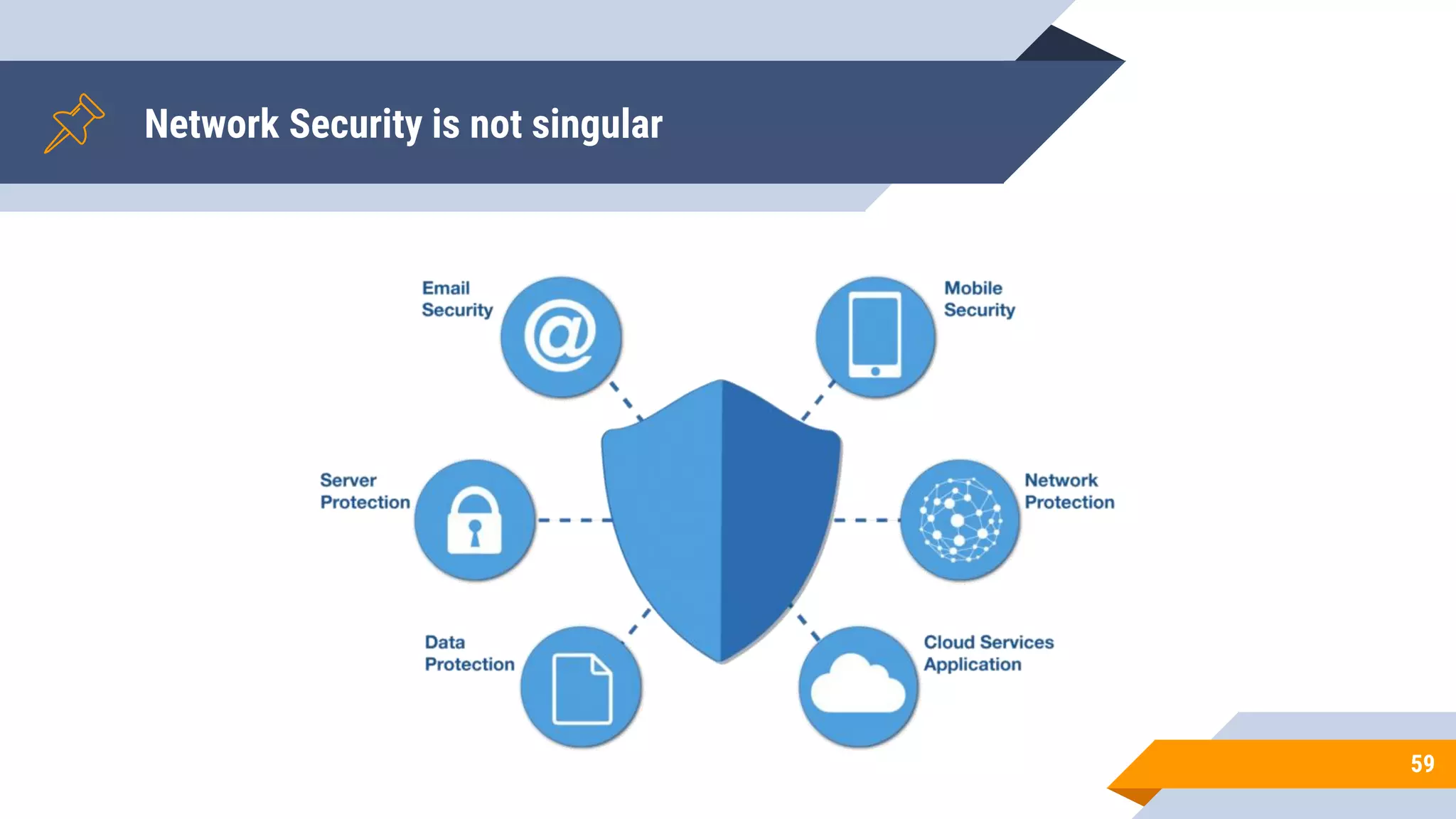
This document discusses network security and cryptography. It begins by defining network security principles like confidentiality, integrity and availability. It then describes common network security attacks such as man-in-the-middle attacks, denial-of-service attacks, password attacks and social engineering. The document introduces cryptography as a way to provide secure communications and explains cryptographic techniques like encryption, hashing, and digital signatures. It discusses symmetric and asymmetric encryption standards and their applications to secure communications and protecting stored data. The document emphasizes the importance of security updates, firewalls, intrusion detection systems and having expertise in cyber security.