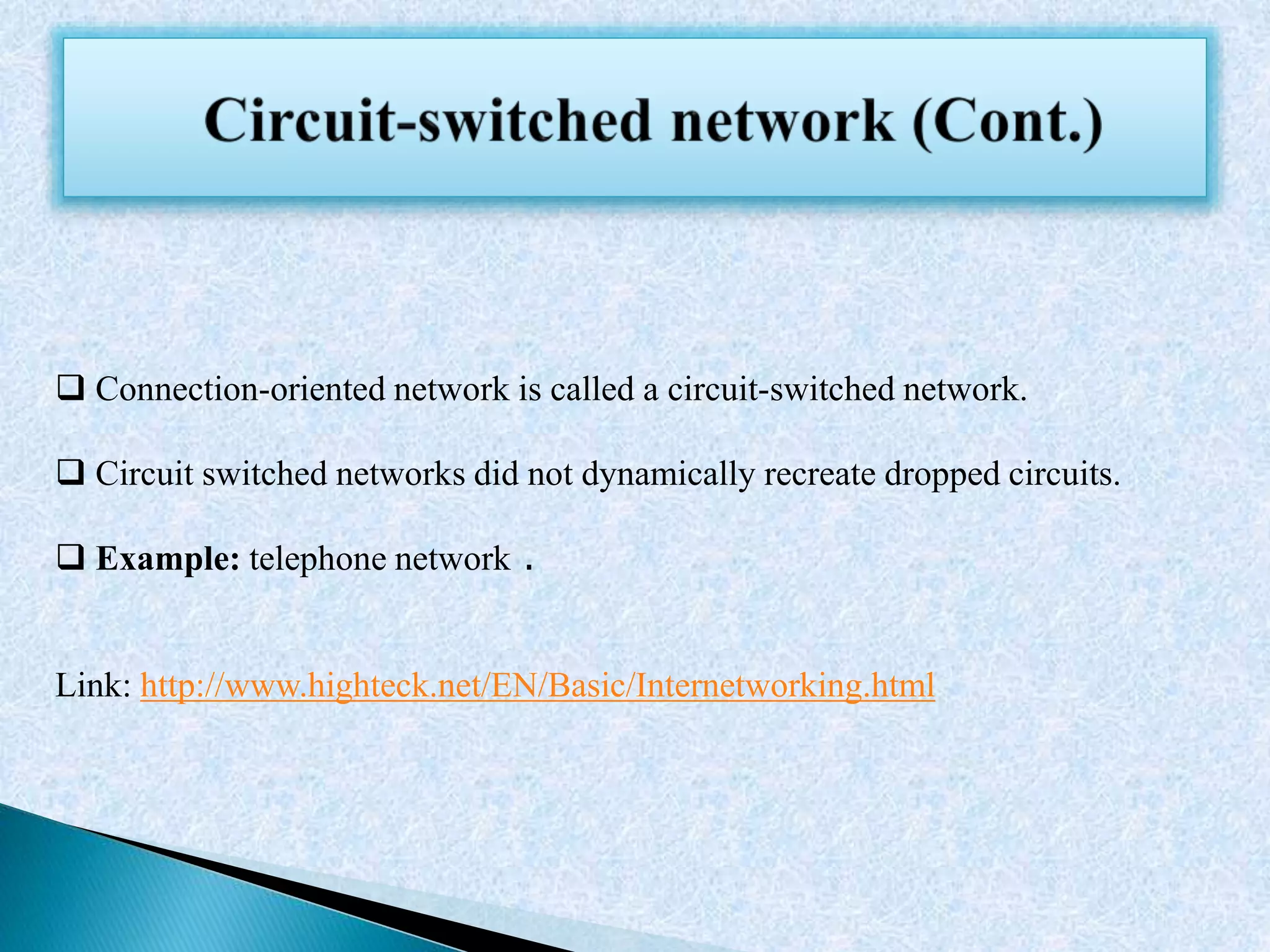
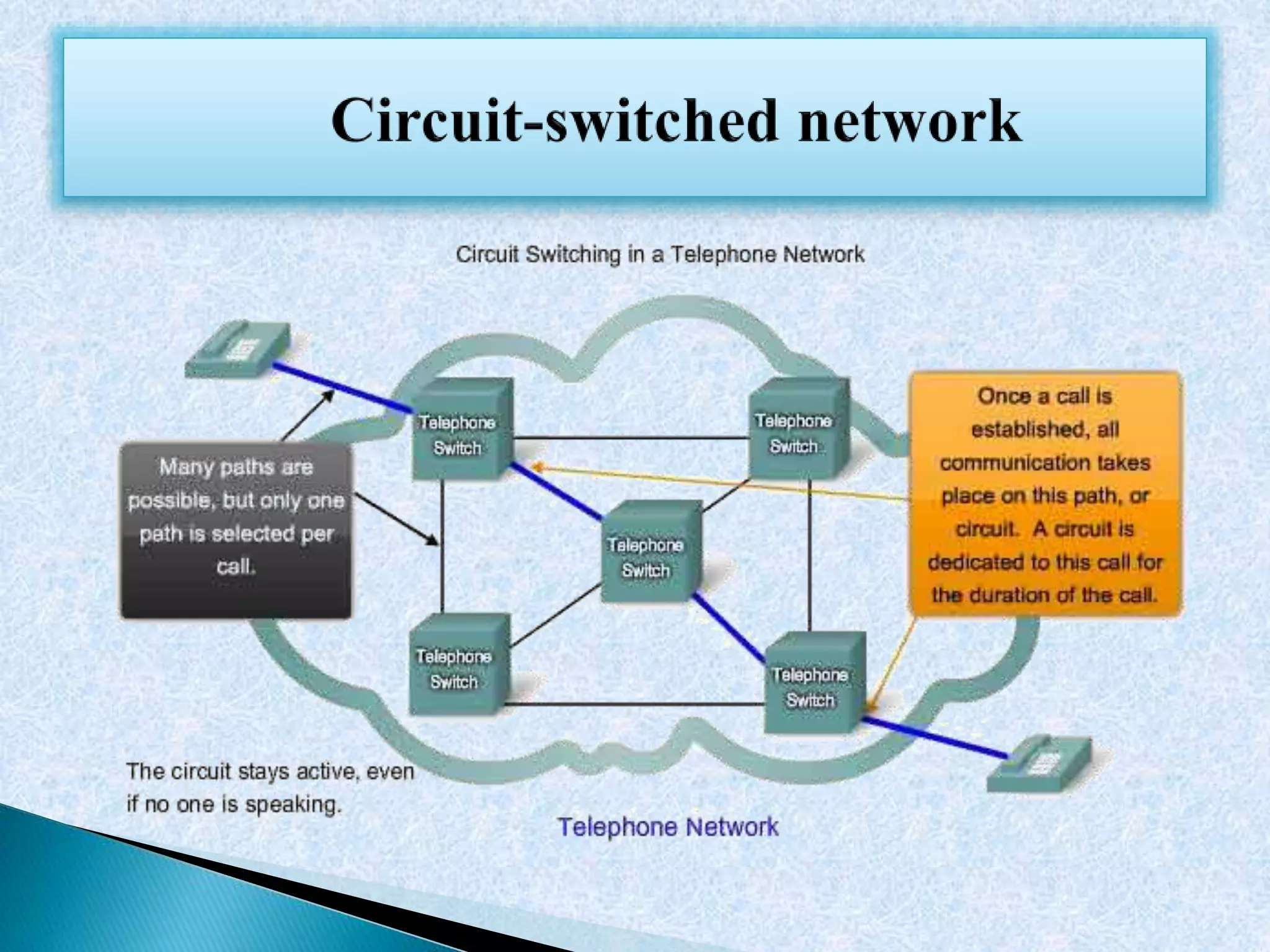
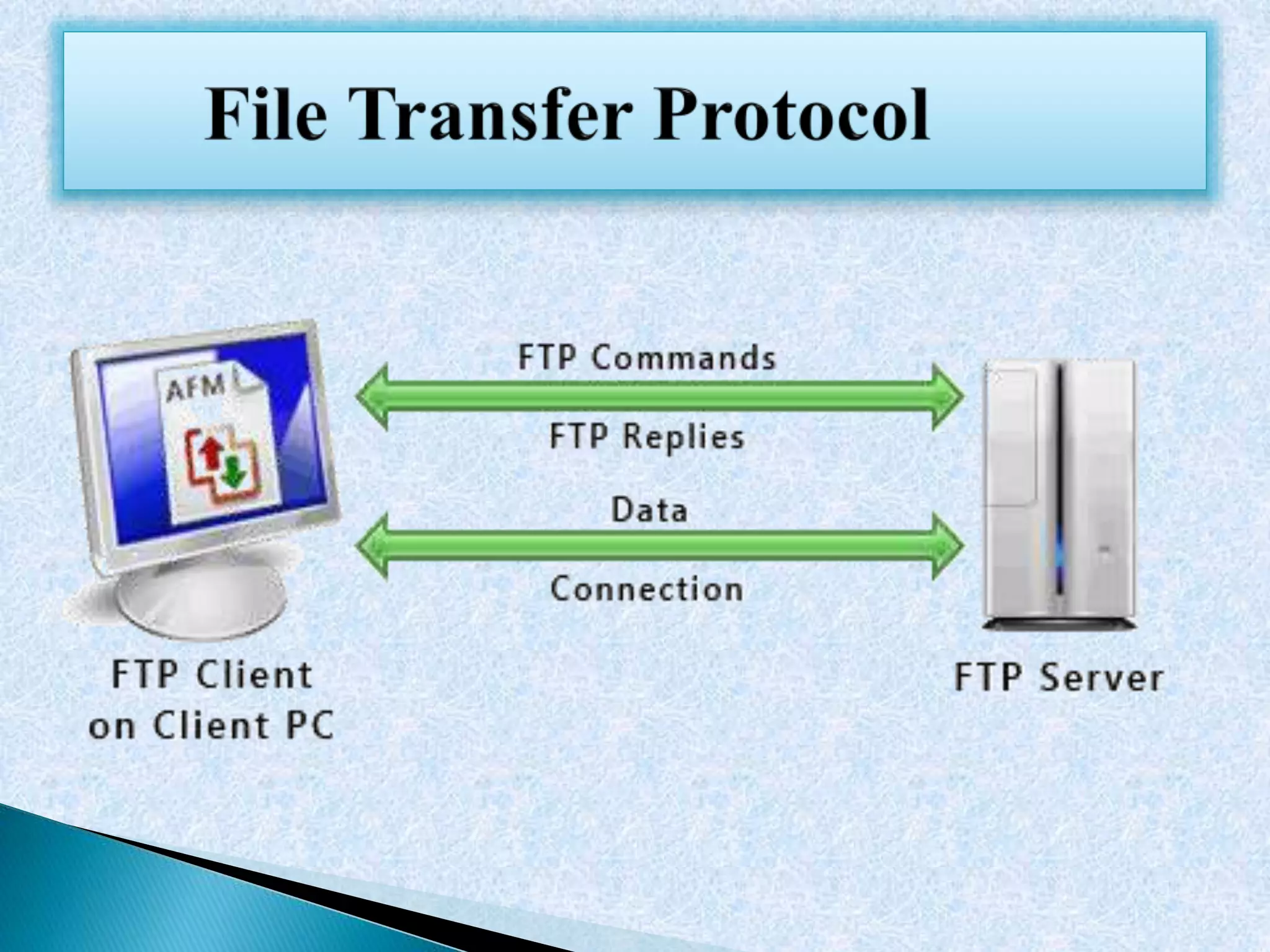
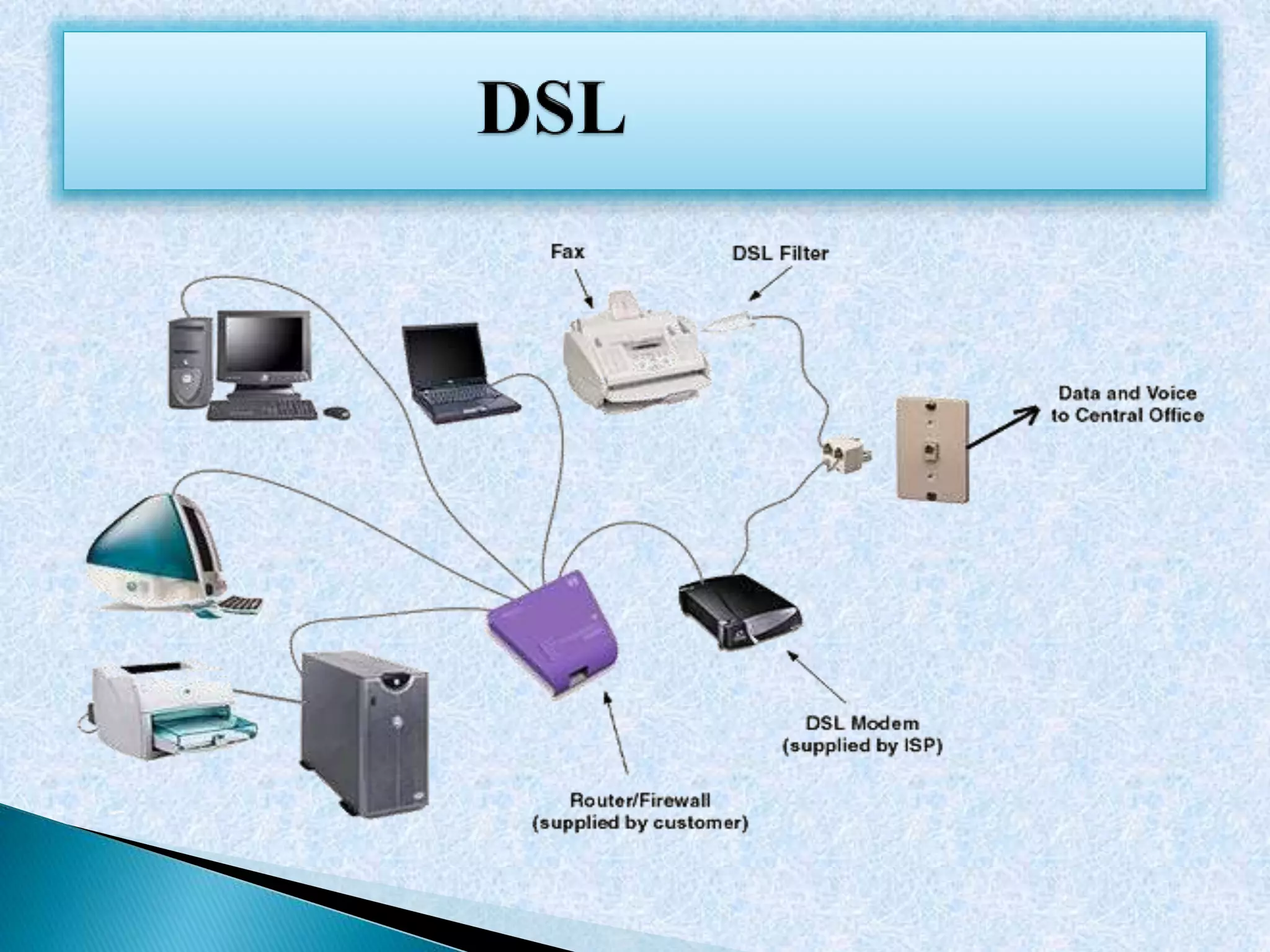
This document discusses various topics in networking and telecommunications including cellular networks, half and full duplex communication, circuit switched networks, radio communication, HTTP, FTP, NAT, DNS, SMTP, and DSL. It provides definitions and examples for each topic with links to additional online resources for further information.