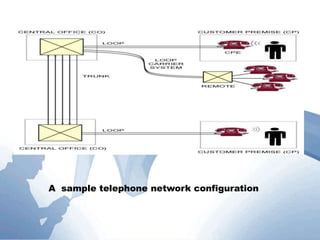
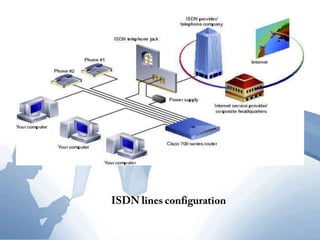
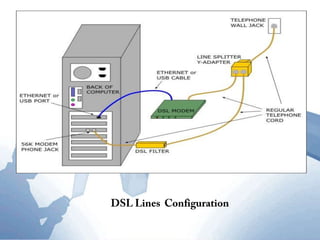
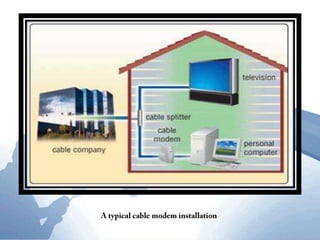
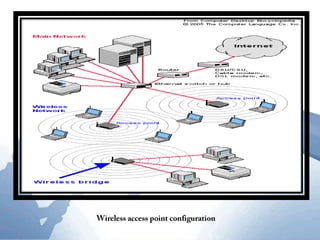
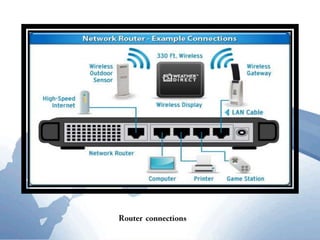
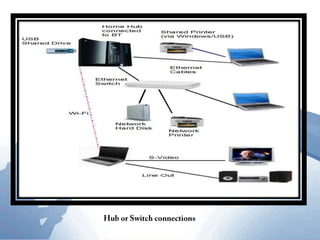
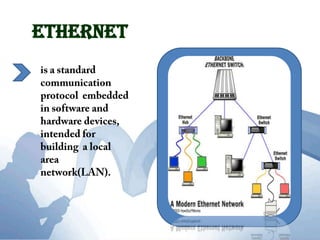
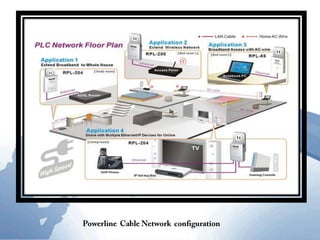
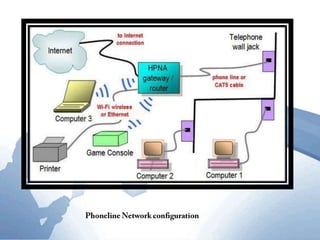
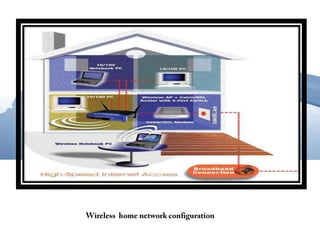
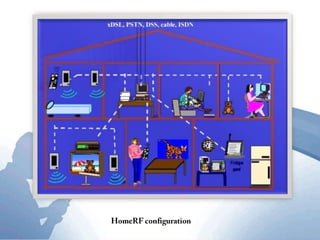
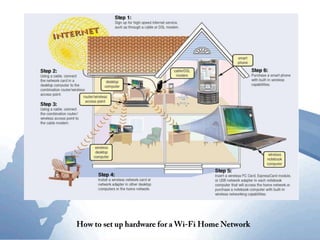
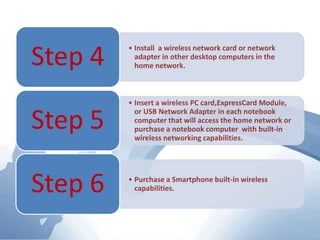
This document discusses communication networks and their components. It describes the public switched telephone network and examples of telephone network configurations including dial-up and dedicated lines. It then covers different types of digital dedicated lines such as ISDN, DSL, FTTH/FTTB, T-carrier, and ATM lines. Various communication devices are also outlined including modems, network cards, wireless access points, hubs/switches, and routers. Finally, it discusses communication channels, transmission media such as twisted pair cable, coaxial cable and fiber optic cable.