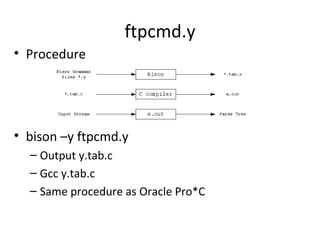
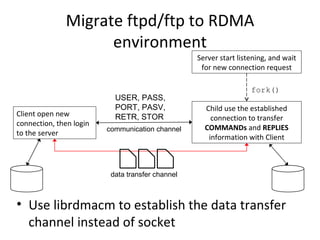
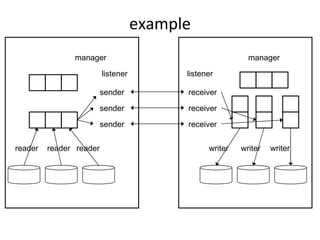
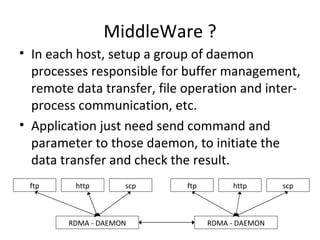
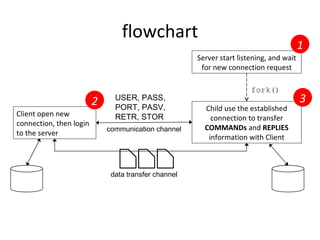
The document summarizes the netkit ftpd/ftp migration to use RDMA for data transfer instead of sockets. It describes using librdmacm to establish RDMA channels for transferring commands/replies and data. It also discusses making transfers more efficient by reading data directly into memory regions to avoid copies, using parallel channels, and separating execution from memory management.



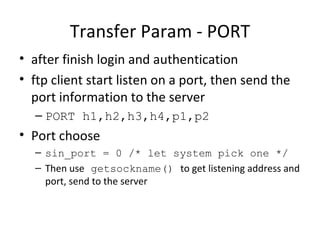
![Transfer Param - PASV ftp client send PASV command to the server, server listening on a port and waiting for connection Choose a port in [40000, 44999] Random sin_port = 0 /* let system pick one */ Then use getsockname() to get listening address and port, send to the client](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/netkitmig-100909213912-phpapp01/85/Netkitmig-6-320.jpg)