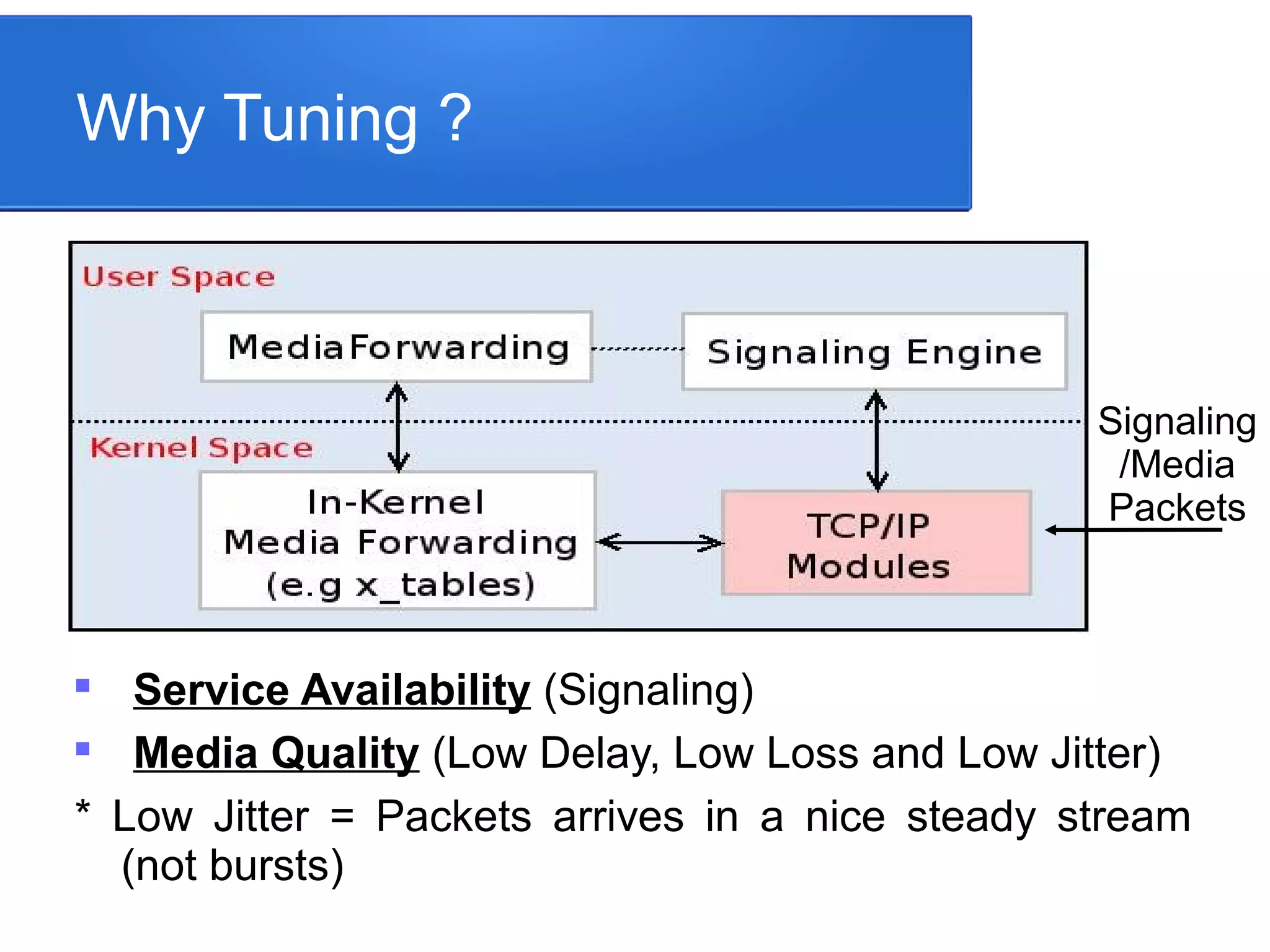
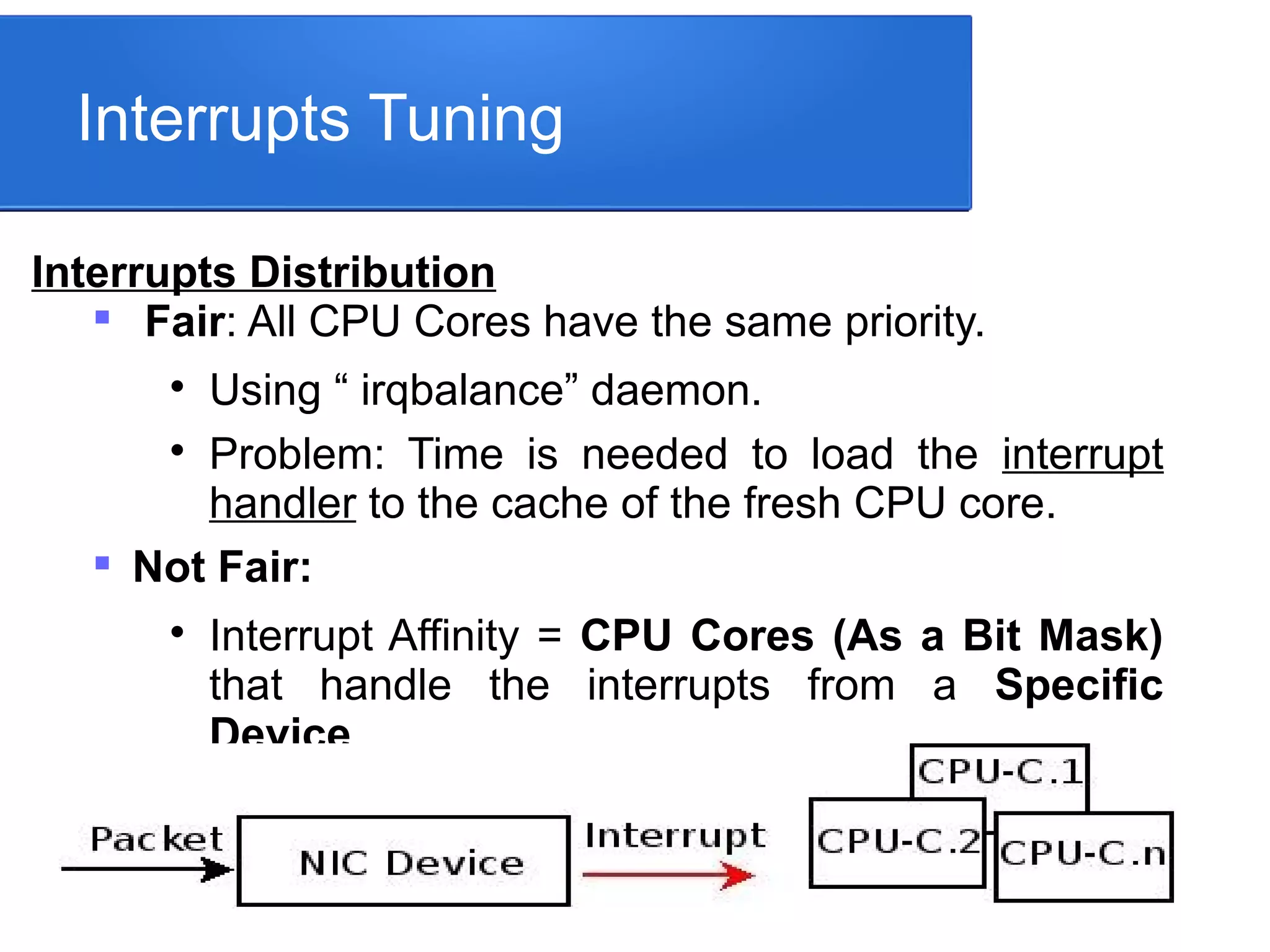
This document summarizes Linux TCP/IP tuning techniques for optimizing real-time communication. It discusses adjusting interrupts, transmission/receiving queues, socket buffer sizes, protocol parameters, port ranges, shell limits, packet marking, traffic control, connection tracking, and more. The goal is to configure these various network parameters together to ensure high availability, media quality with low delay, jitter and packet loss for signaling and media packets. Proper testing and measurement tools are also needed to validate any tuning changes.









![Kernel Connection Tracking
System
Conntrack Example:
Udp 17 20 src=192.168.1.2 dst=192.168.1.5
sport=137 dport=1025 [UNREPLIED]
src=192.168.1.5 dst=192.168.1.2 sport=1025
dport=137 use=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuning-17march-150317155702-conversion-gate01/75/Tuning-17-march-12-2048.jpg)