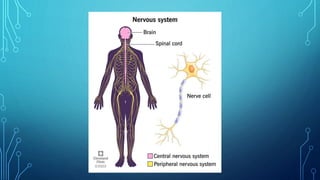
Peter is a student at the Health Care and Paramedic Science school studying radiology and imaging technology from 2024-2027. The document provides an overview of the nervous system including its main components and functions. It describes the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord which process sensory information and coordinate bodily functions. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves throughout the body which transmit signals between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. Common disorders that can affect the nervous system are also listed such as Alzheimer's disease, cancer, cerebral palsy and epilepsy.