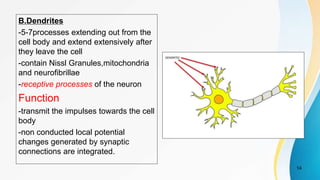
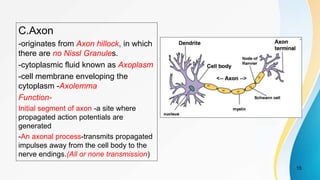
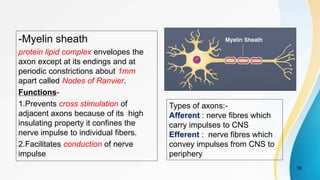
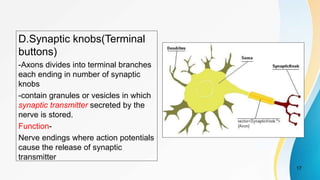
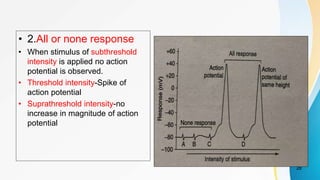
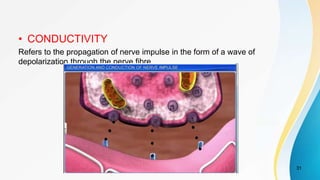
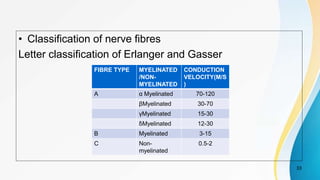
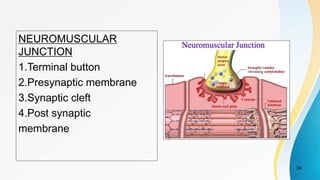
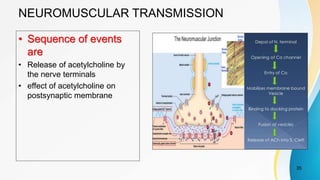
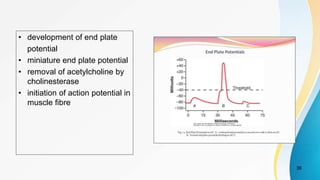
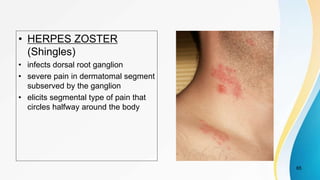
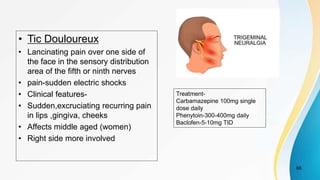
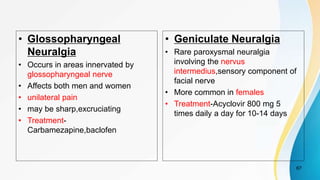
The document provides an overview of pain pathways and physiology. It discusses:
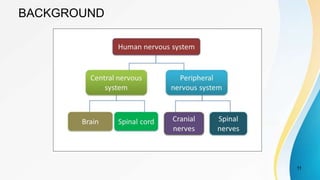
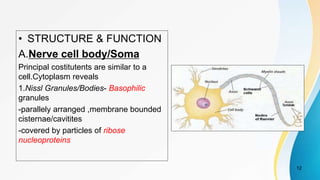
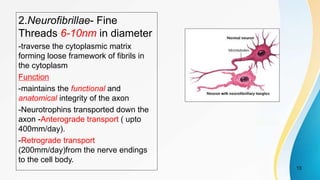
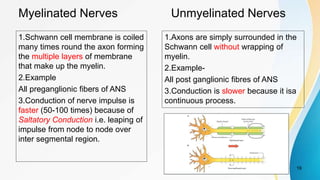
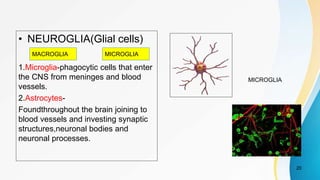
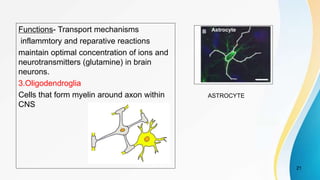
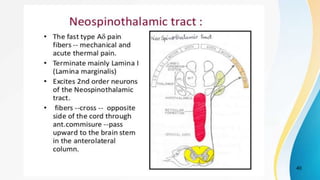
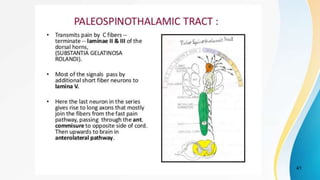
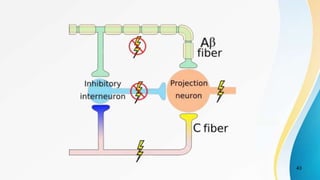
- The dual pain pathway in the spinal cord and brainstem, including the neospinothalamic and paleospinothalamic tracts.
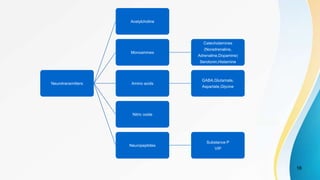
- Pain receptor types and the chemicals involved in mediating pain.
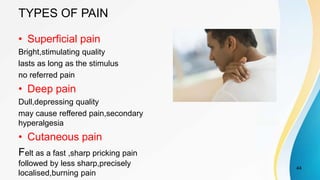
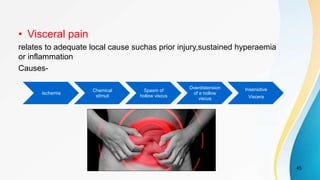
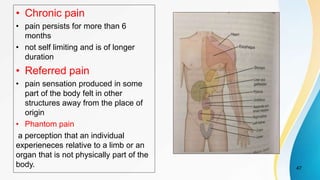
- Classification of different types of pain including somatic, visceral, acute, chronic, referred, and phantom pain.
- Theories of pain transmission including specificity theory and gate control theory.
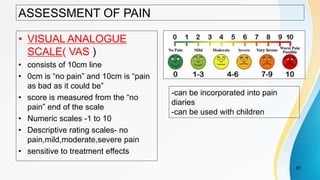
- Assessment tools for pain such as visual analogue scales and McGill Pain Questionnaire.