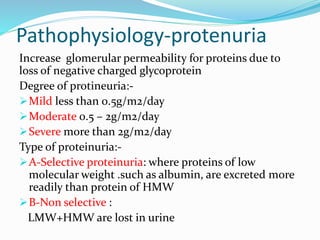
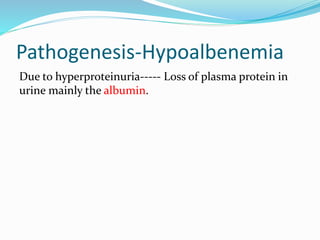
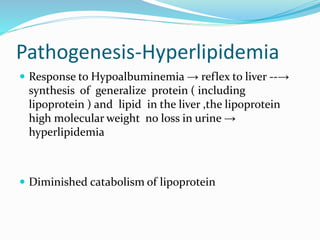
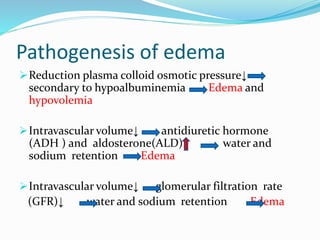
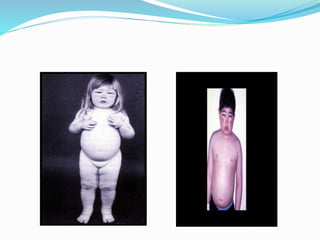
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, and edema. It results from increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane. The majority of cases are primary or idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Treatment involves corticosteroids, diet modifications to reduce proteinuria, and managing complications such as edema and infection risk. Nursing care focuses on fluid balance, nutrition, infection prevention, and family education and support.