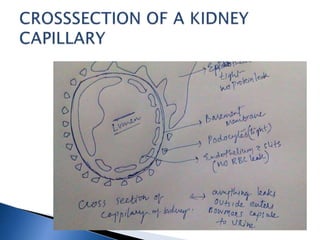
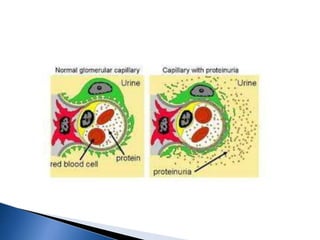
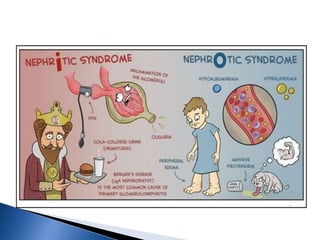
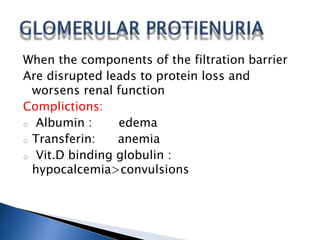
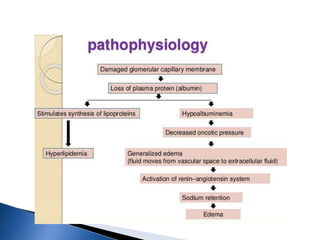
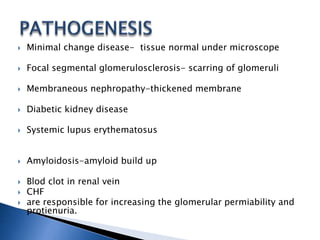
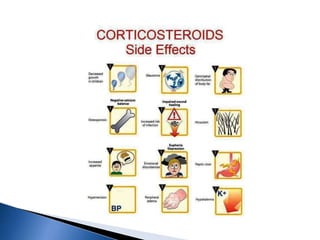
A 6-year-old male child was admitted to the pediatric ward with complaints of cough for 2 days, facial swelling for 10 days, and abdominal distension for 10 days. Laboratory tests found proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, and decreased urine output. The child was diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome and treated with antibiotics, a salt-restricted diet, diuretics, and steroids. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, edema, and hypoalbuminemia. The causes include minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and diabetic nephropathy. Treatment focuses on managing edema, replacing protein loss, lowering lipids, and in some cases using st