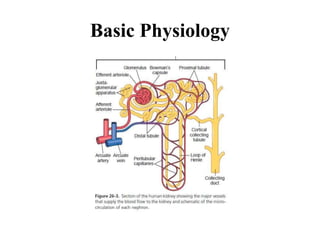
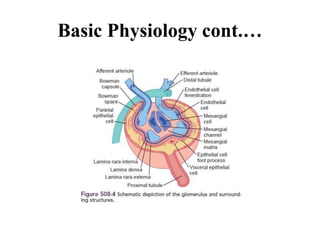
Nephrotic syndrome is defined by nephrotic range proteinuria, edema, hyperlipidemia, and hypoalbuminemia. It results from increased glomerular permeability allowing protein loss in the urine. The most common causes are minimal change disease in children and membranous nephropathy in adults. Treatment involves diuretics, albumin, steroids, and steroid-sparing immunosuppressants depending on disease severity and steroid responsiveness. Prognosis is generally good but depends on underlying pathology.