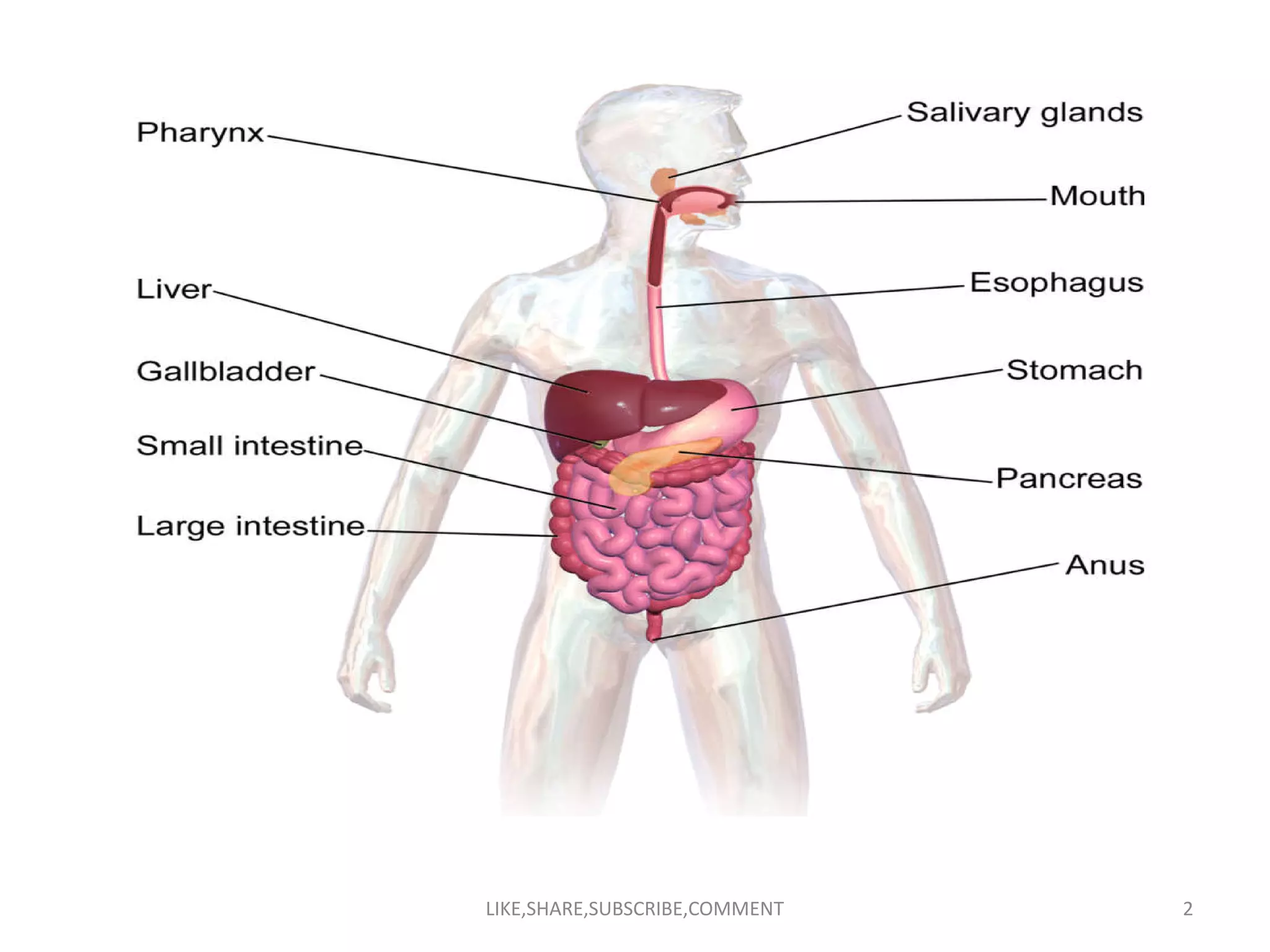
The document summarizes the human digestive system and the process of digestion. It describes the steps of digestion from ingestion to defecation. The main parts of the digestive system include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and accessory organs like the liver, pancreas and salivary glands. Digestion involves both mechanical and chemical breakdown of food by enzymes from these organs. Nutrients are then absorbed in the small intestine and transported to the liver and cells before undigested waste is excreted during defecation.