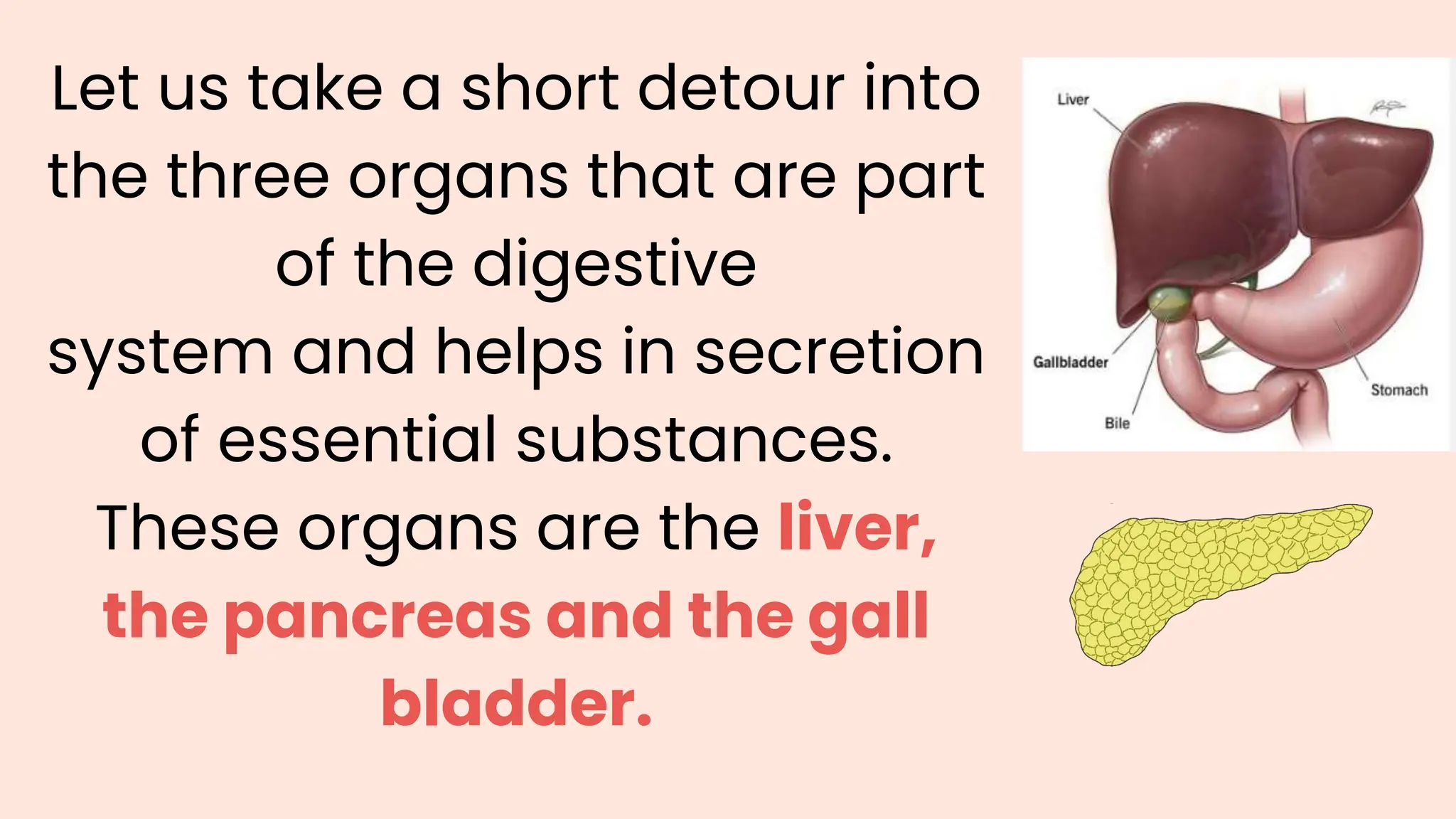
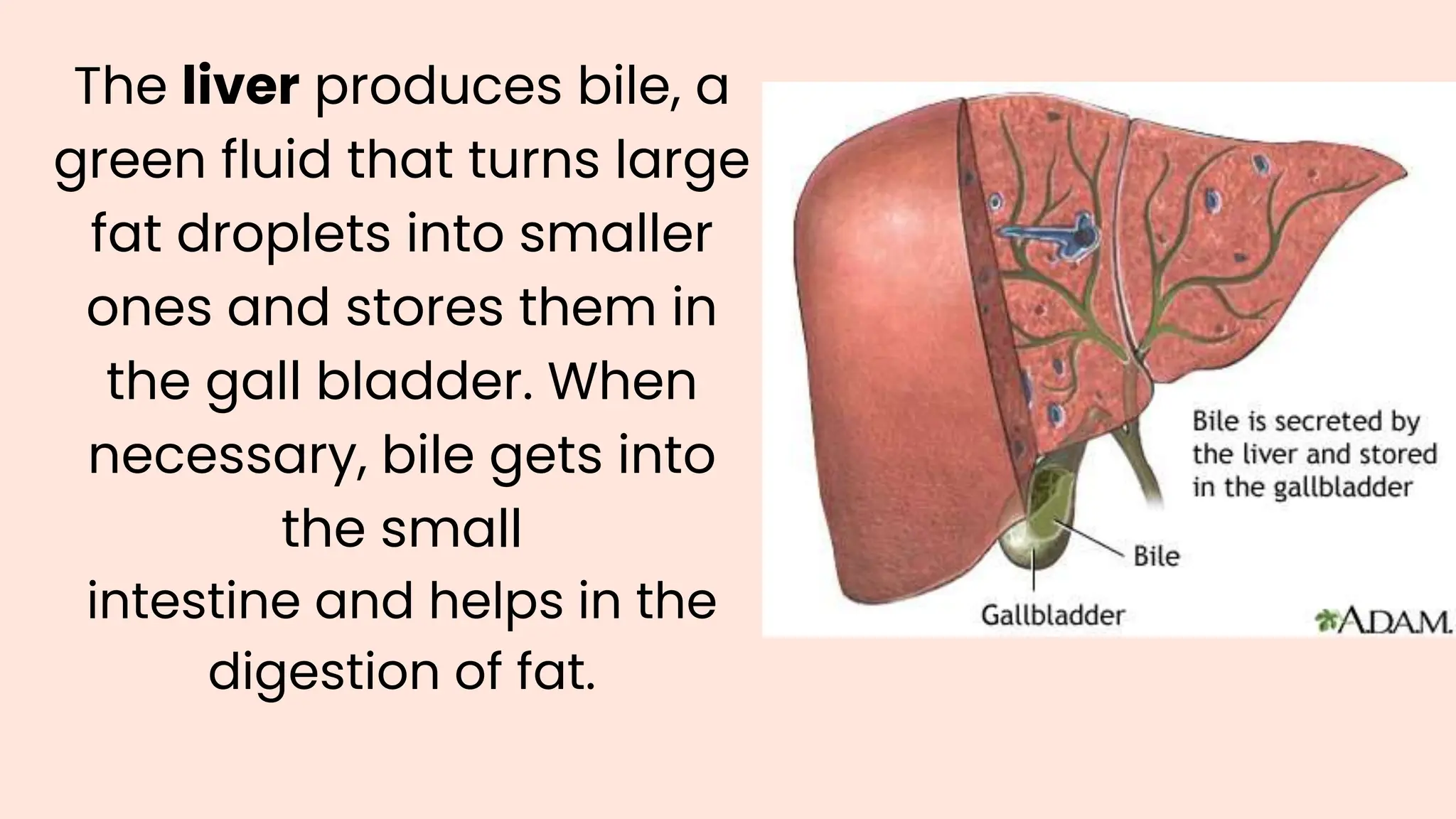
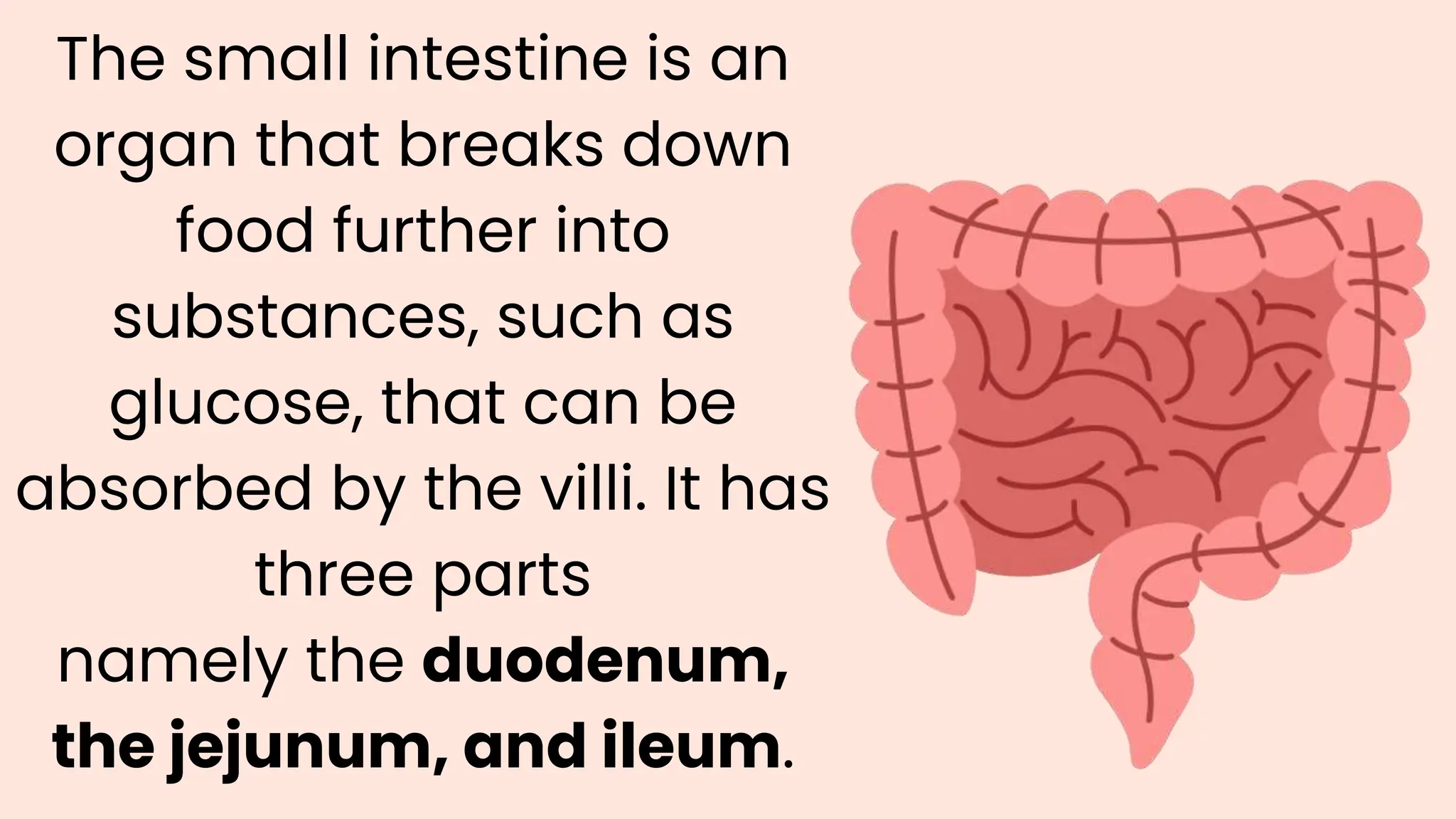
The document summarizes the key processes of the digestive system:
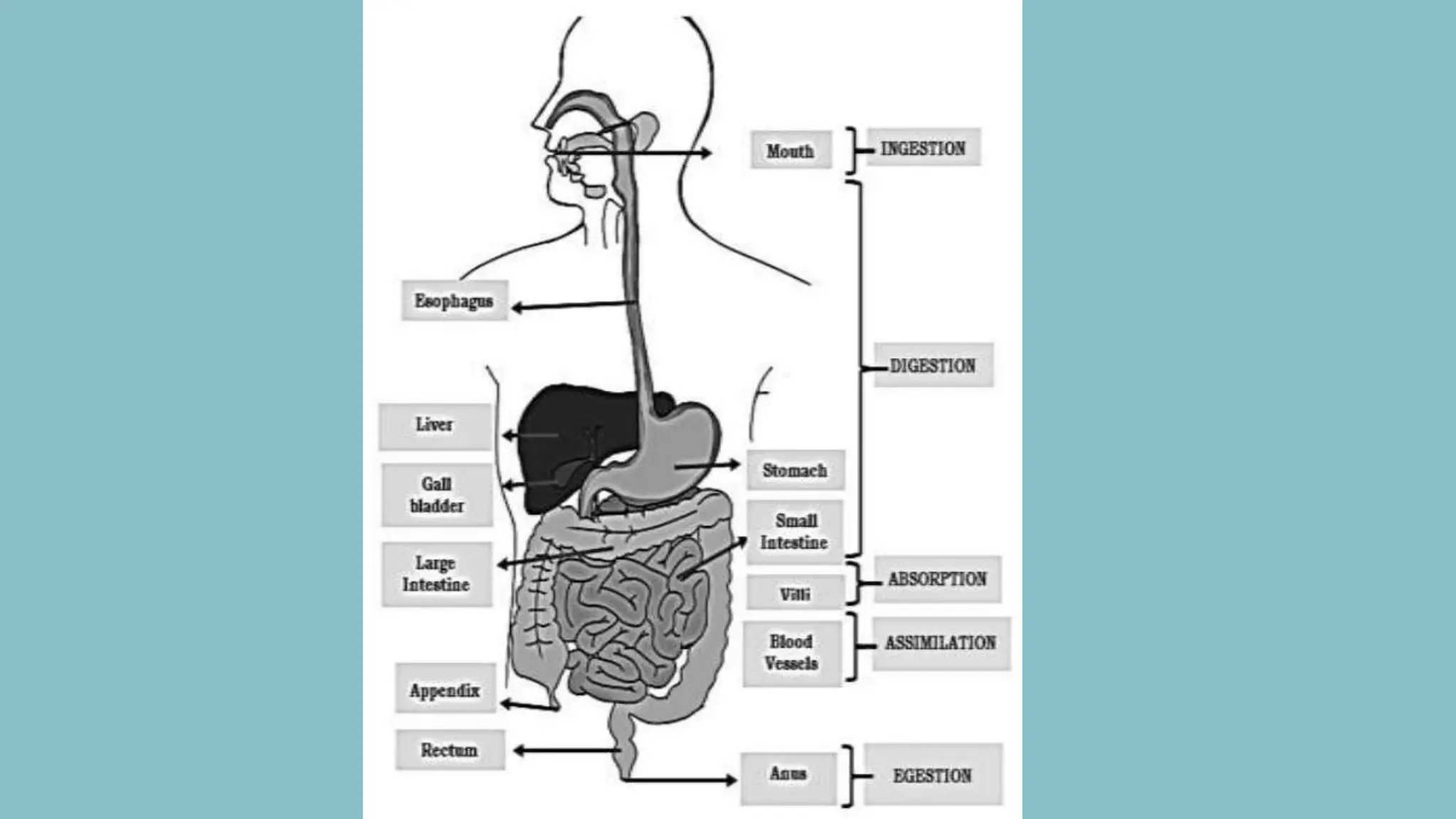
1) Ingestion is taking food into the mouth and esophagus through chewing and swallowing. Digestion then breaks down food through mechanical and chemical processes in the stomach and small intestine.
2) Absorption occurs as nutrients pass from the small intestine into blood vessels.
3) Assimilation involves moving digested nutrients into body cells to be used for energy, growth, and cell repair.
4) Undigested waste is eliminated as feces through egestion. The five main processes are ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.