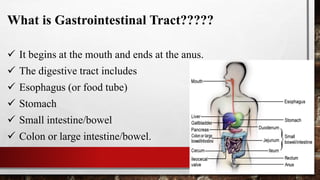
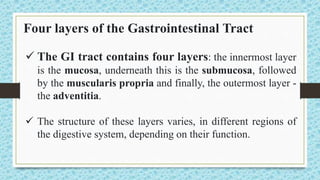
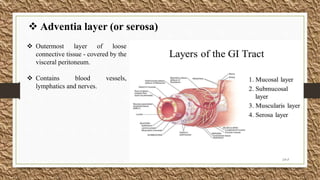
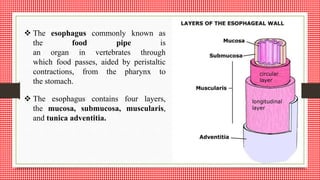
The document discusses the gastrointestinal tract and motility. It begins with defining the GI tract and its parts. It then discusses GI motility including peristalsis and segmentation contractions that move food through the digestive system. It details the layers of the stomach and small intestine walls and their roles in digestion. It concludes with describing motility and movement of food through the specific parts of the GI tract.