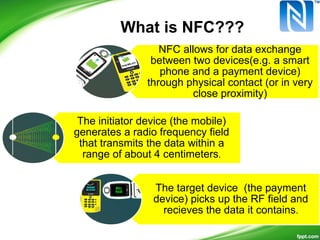
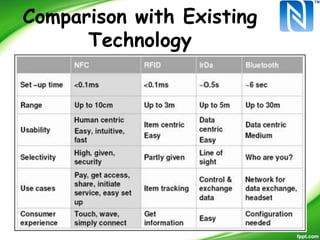
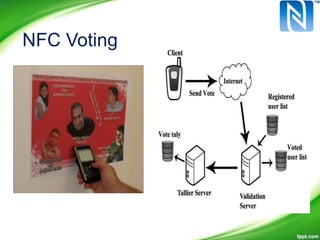
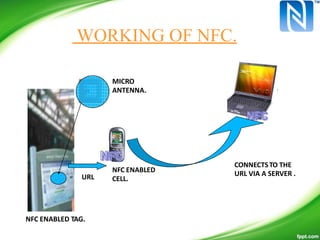
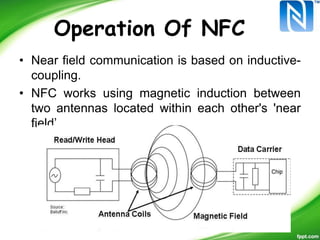
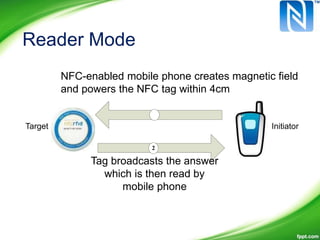
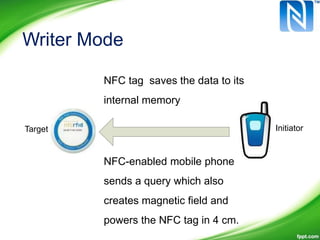
Near-Field Communication (NFC) allows contactless data exchange between devices within close proximity. NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and has a maximum range of about 4 cm. It can be used for applications such as contactless payment, ticketing, and data sharing when two NFC devices are tapped together. NFC has three operating modes - reader/writer mode where an NFC device can read from and write to tags, card emulation mode where a phone acts like a card, and peer-to-peer mode for data transfer between two NFC phones. NFC integration with mobile devices has potential for new opportunities but has limitations such as short range and low data transfer rates.