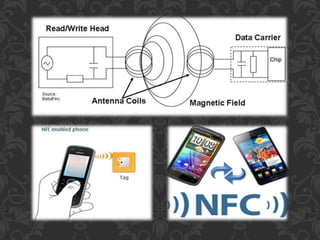
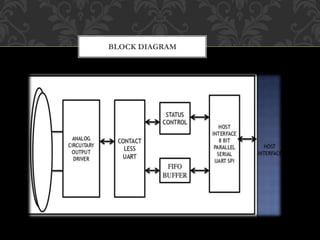
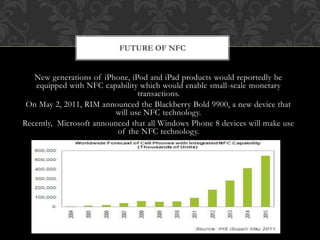
Near field communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless technology that allows data exchange between devices when they are touched or brought within close proximity of a few centimeters. It uses magnetic field induction to enable communication between electronic devices like mobile phones and readers for contactless transactions. Some key applications of NFC include touch-and-go payments, contactless ticketing/access, and data sharing by touching two NFC devices. While convenient, NFC also faces security risks like eavesdropping and data theft that require technical solutions like encryption.