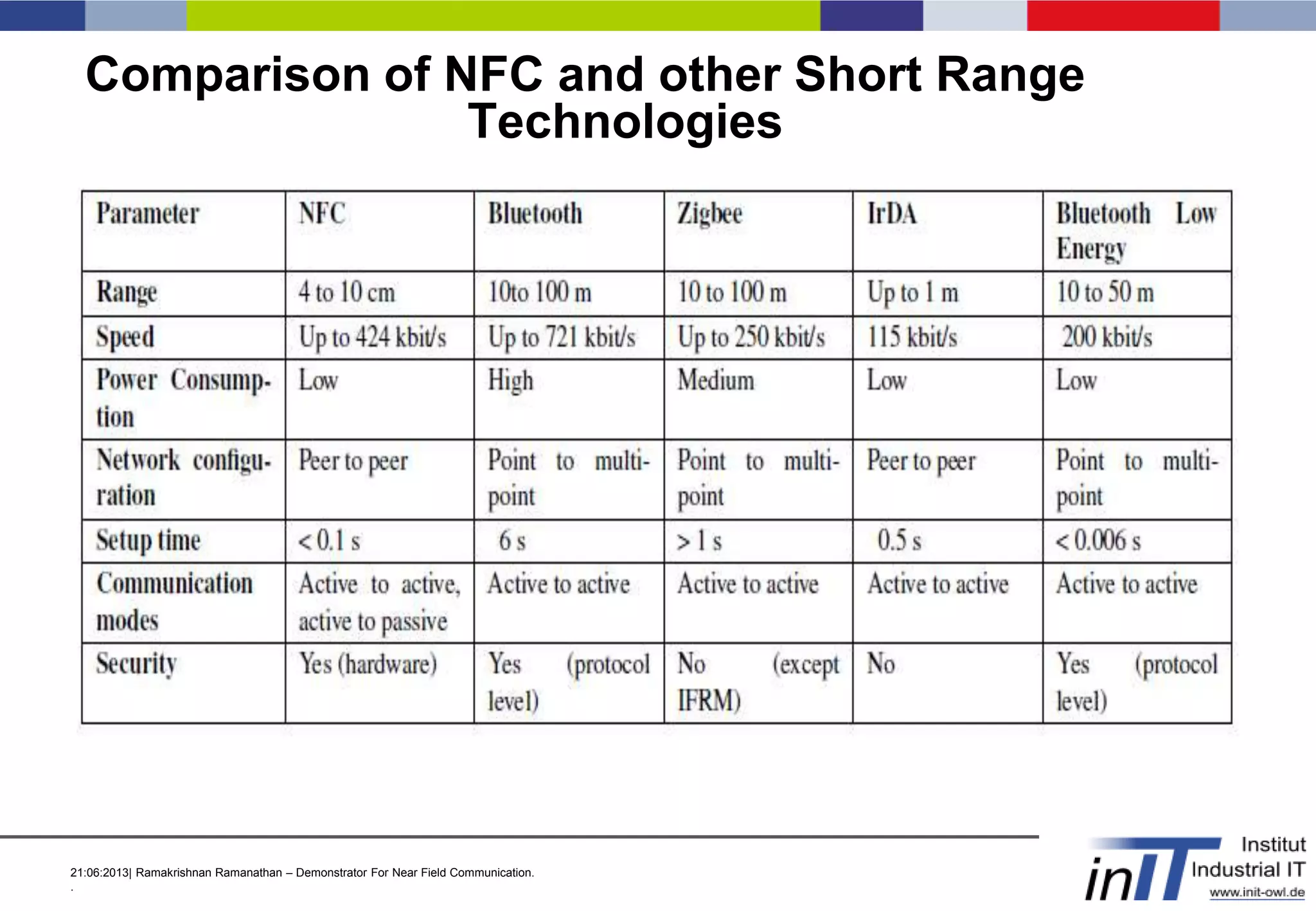
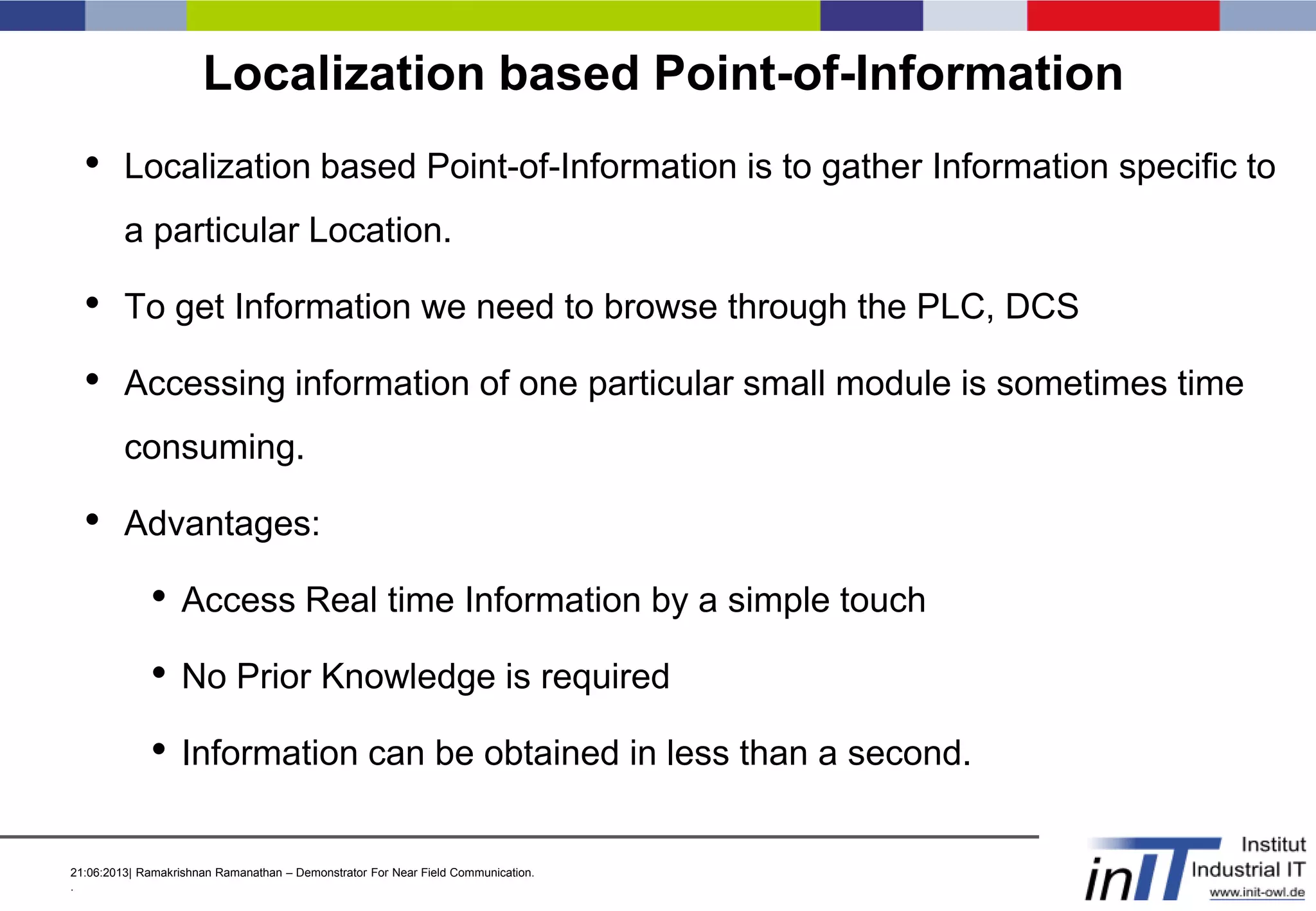
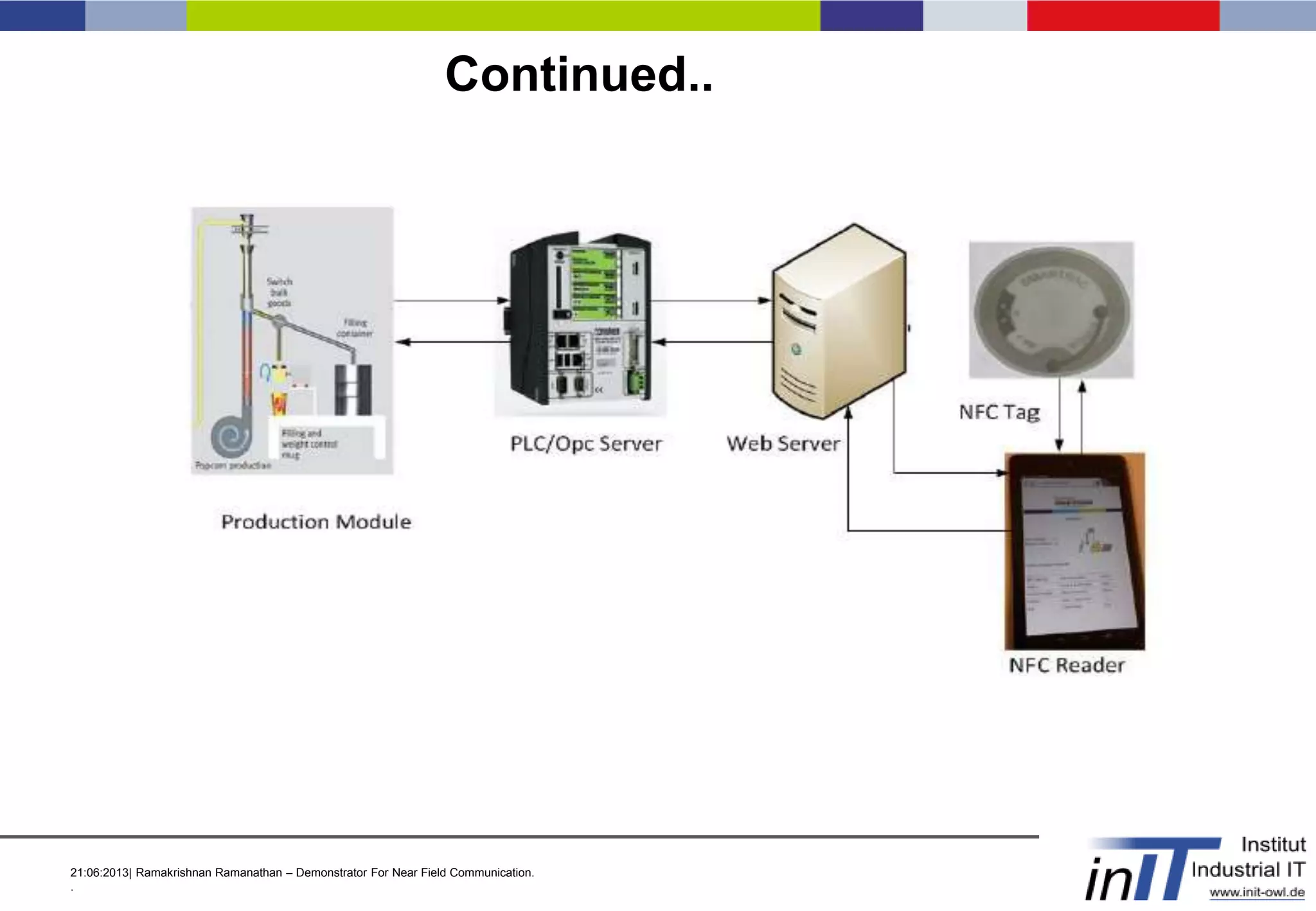
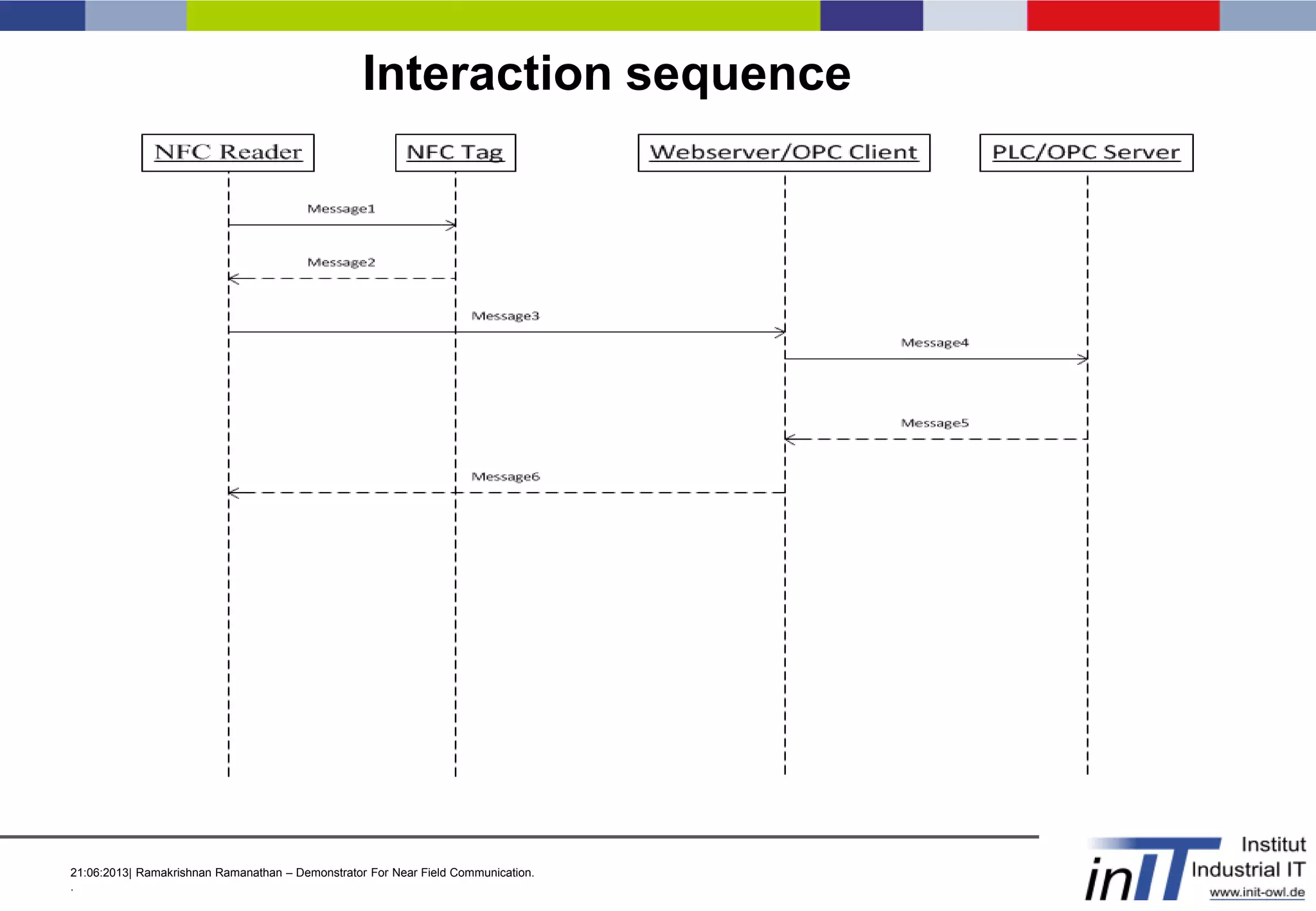
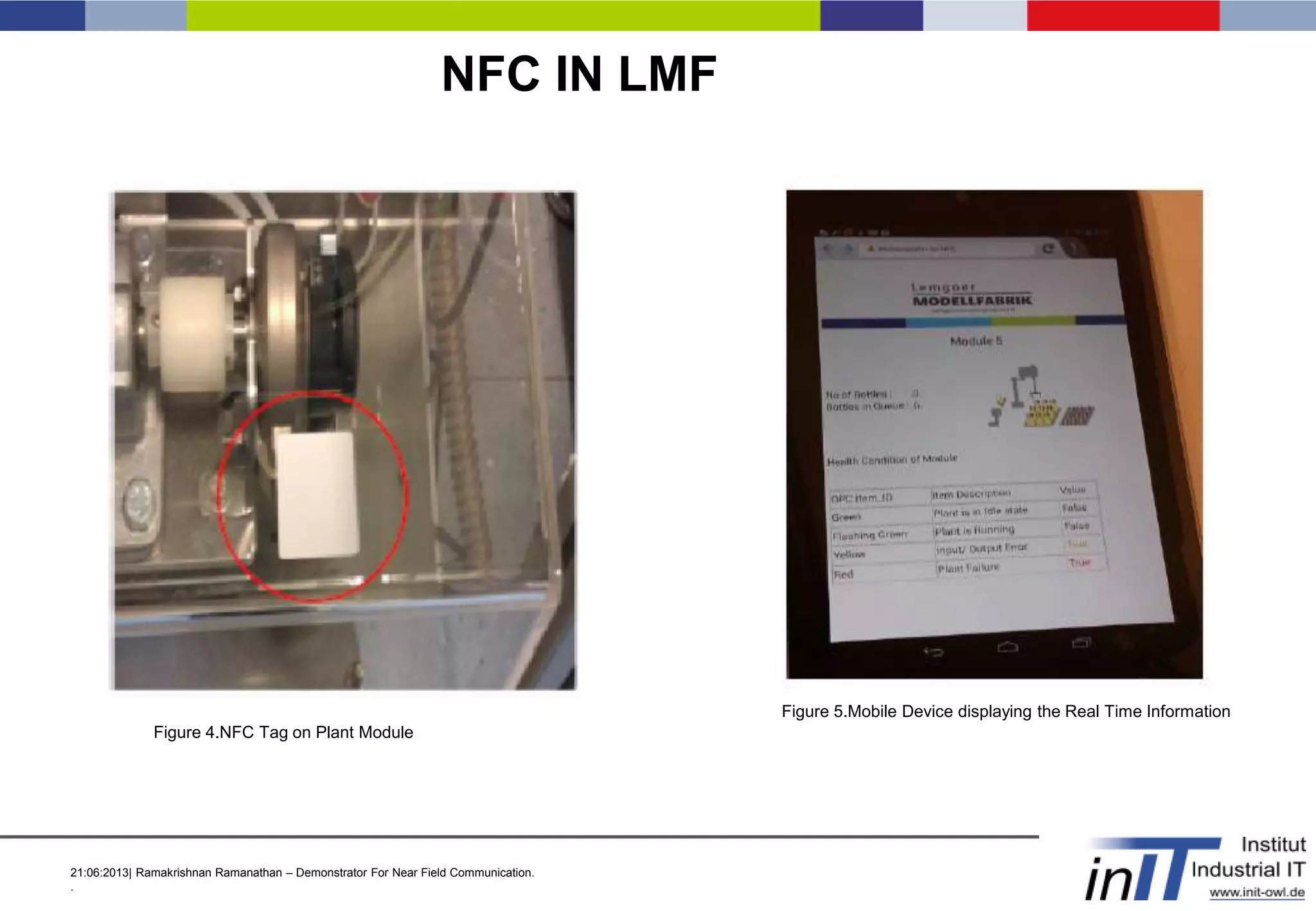
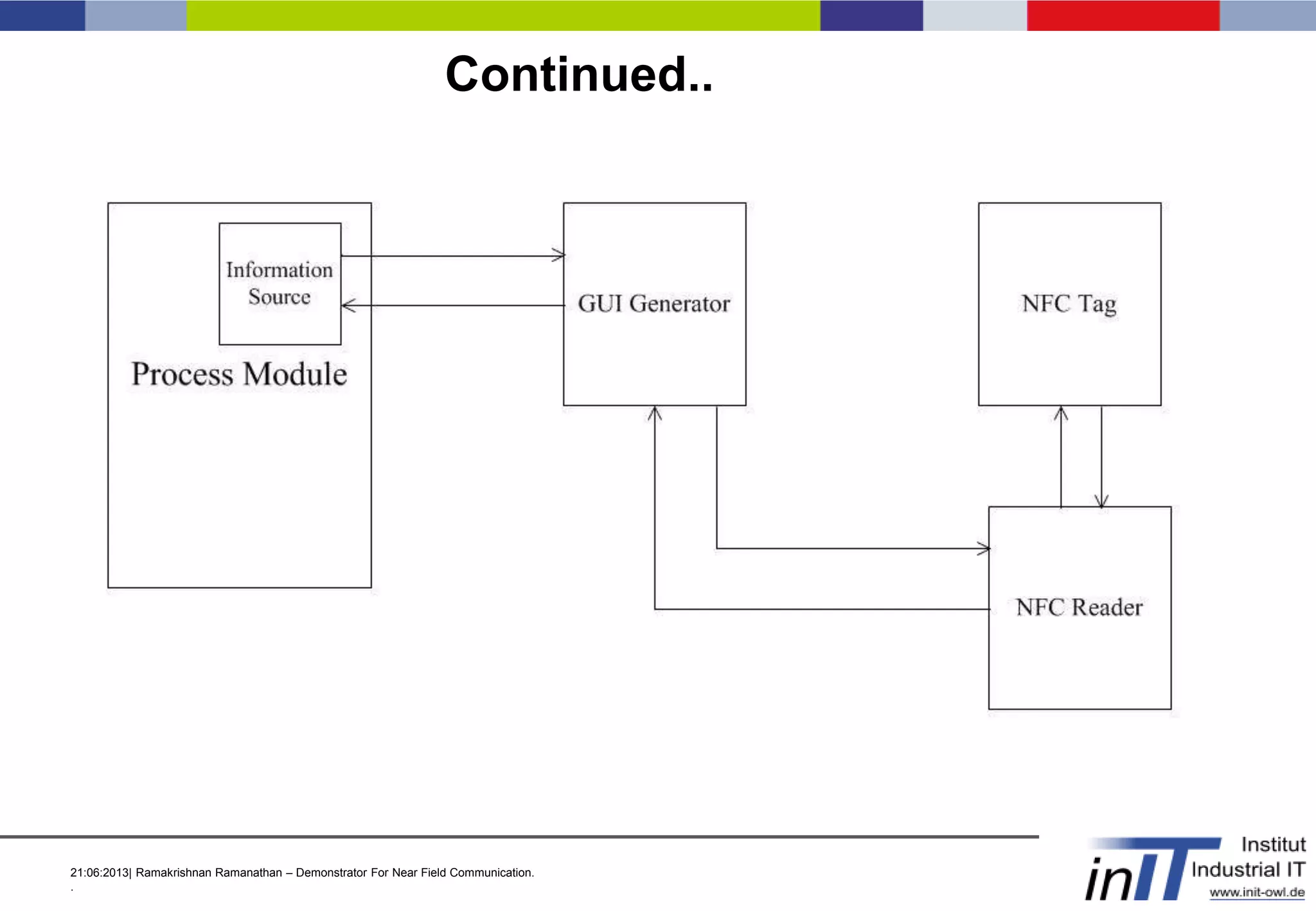
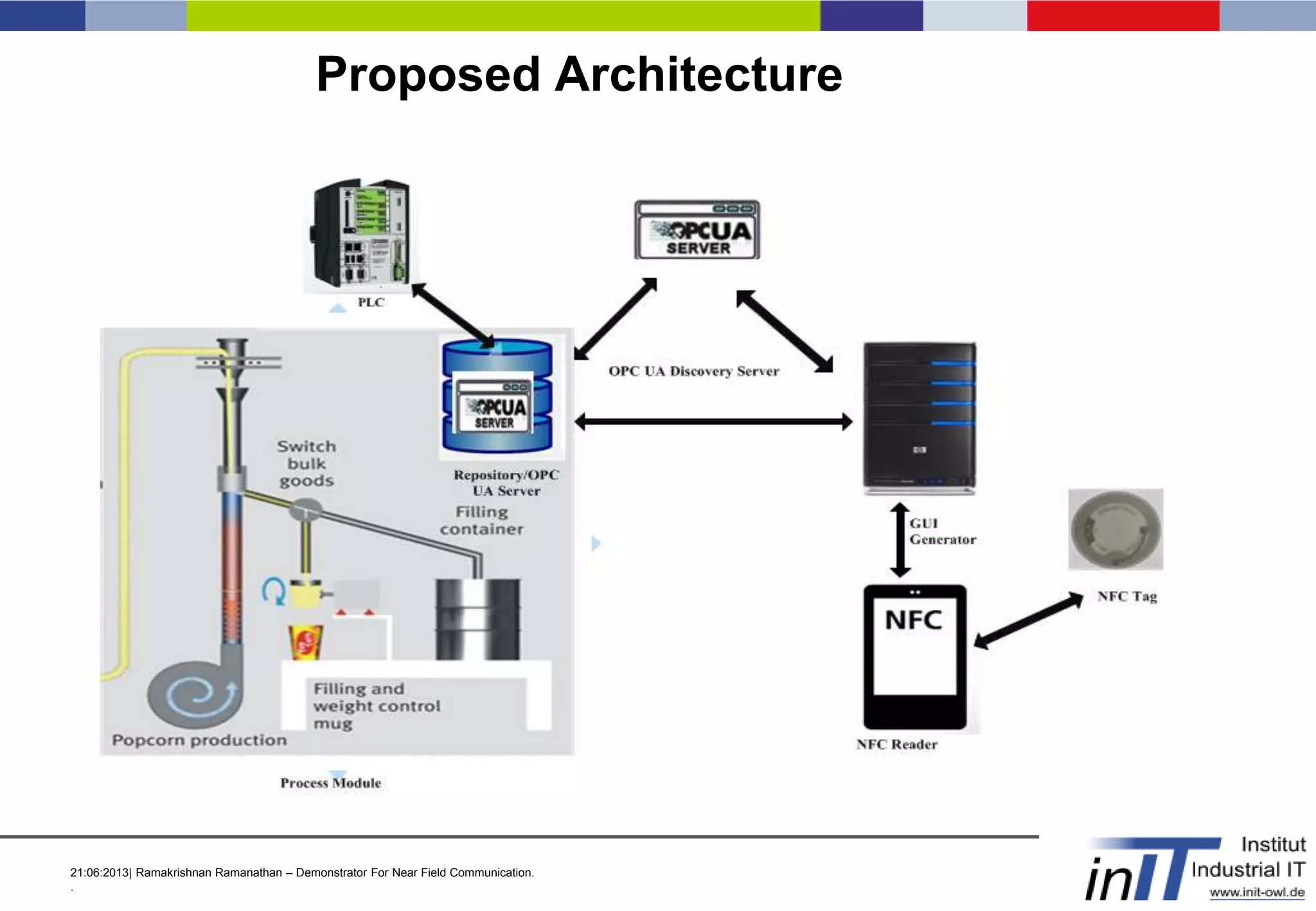
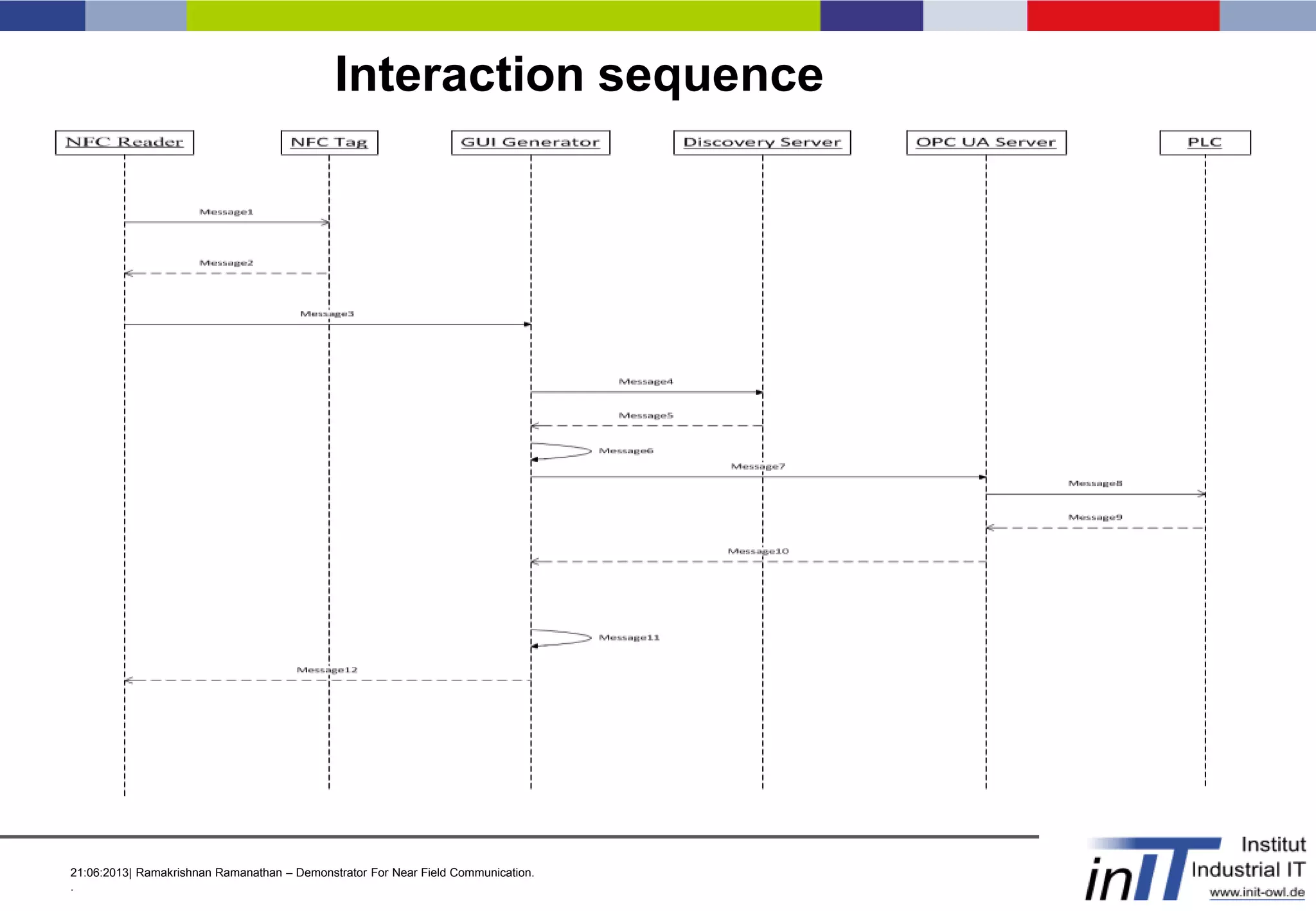
This document discusses a demonstrator for near field communication (NFC) technology in industrial automation applications. It provides an introduction to NFC including operating modes and compares it to other short-range wireless technologies. The document proposes using NFC to access real-time information from modular plant components by touching a mobile device to an NFC tag. A context-aware user interface would dynamically generate interfaces based on the component. The architecture involves NFC tags on modules communicating data via a web server to mobile devices. Future work includes implementing peer-to-peer NFC communication and context-aware interfaces in real industrial scenarios.

![21:06:2013| Ramakrishnan Ramanathan – Demonstrator For Near Field Communication.
.
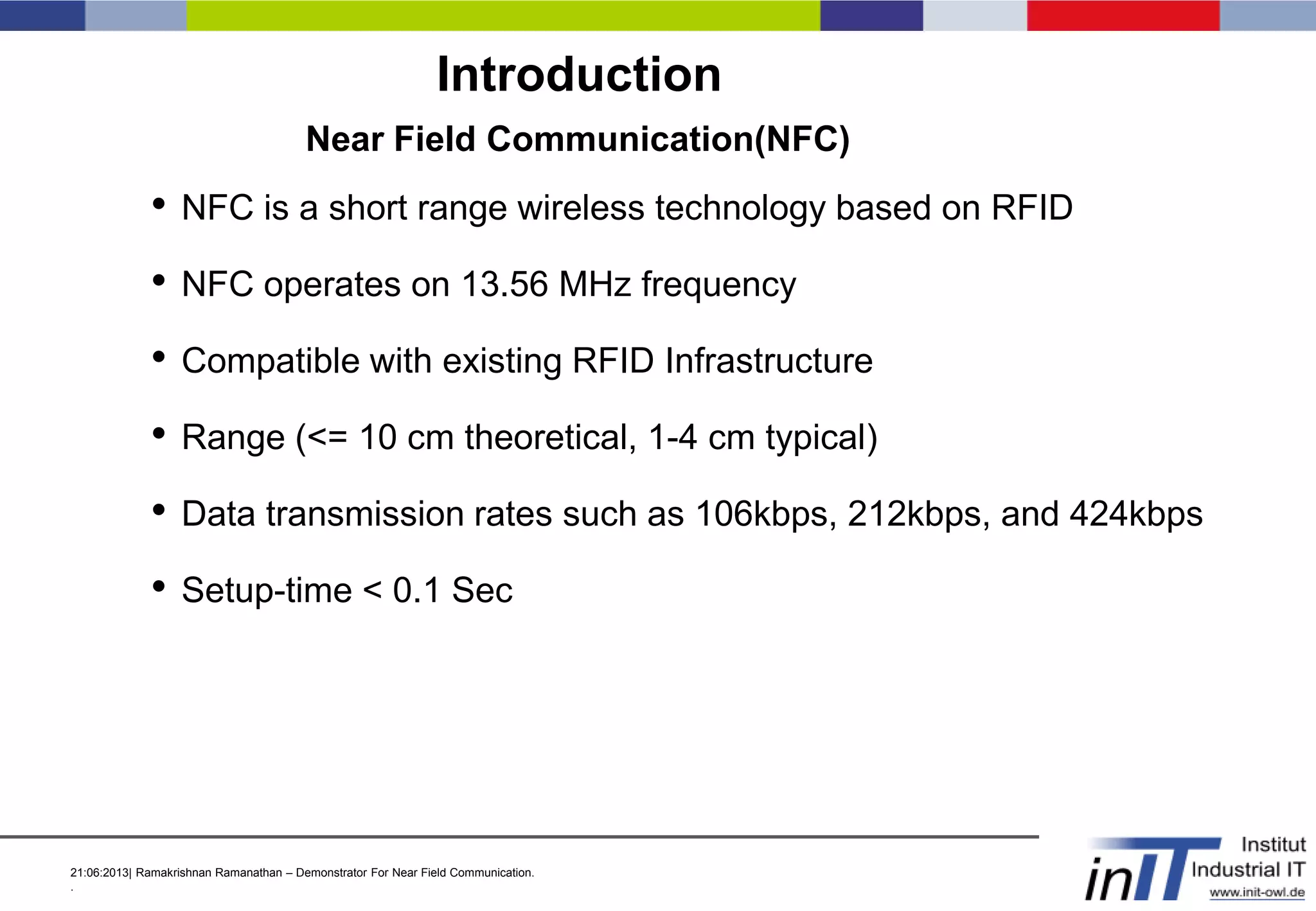
NFC Operating Modes
Reader-Writer Mode
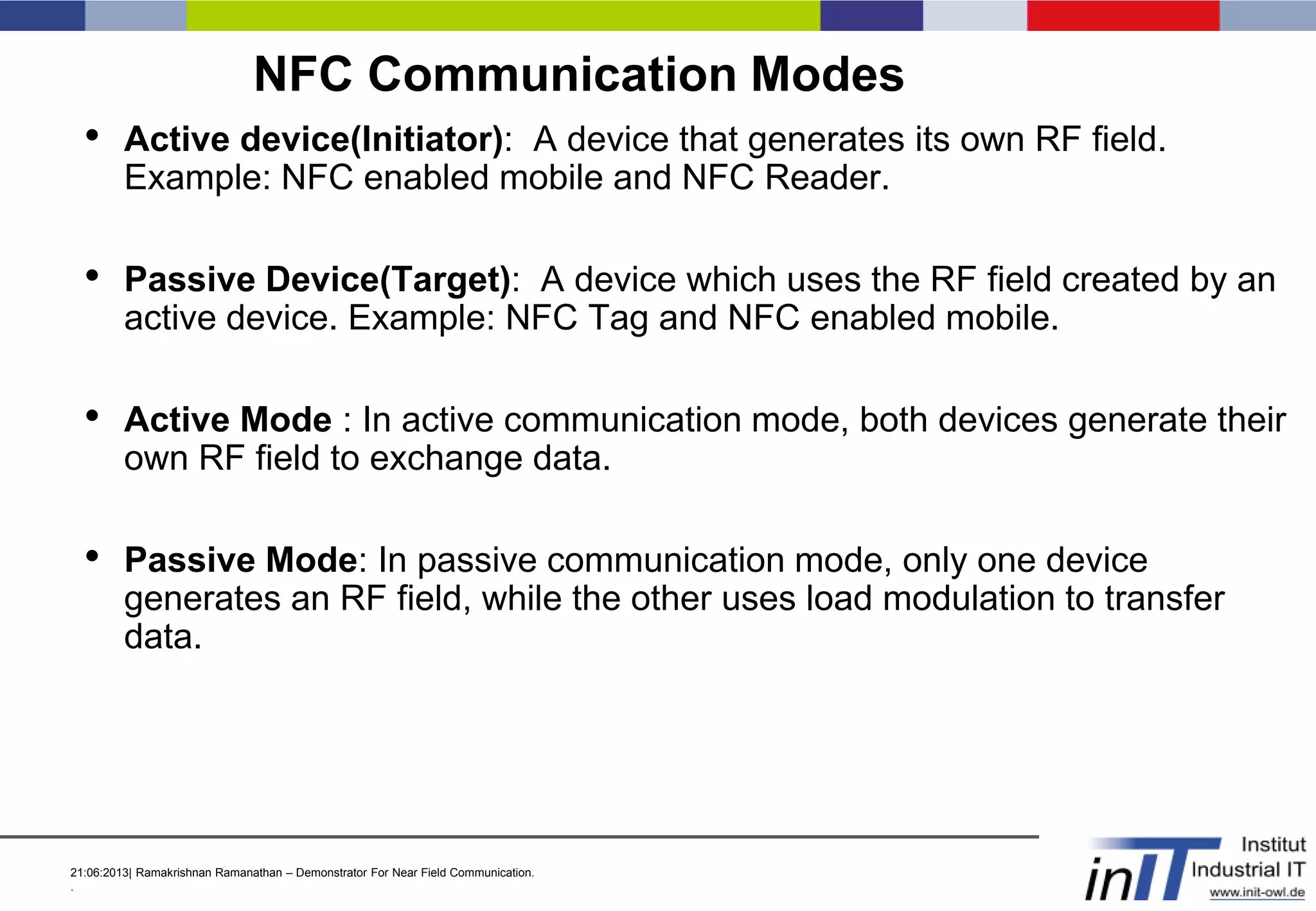
• An active NFC device reads and writes passive NFC cards/tags.
• Tag content: Text, URI (Web Link, Phone Number), Smart Poster.
• Applications:
-Mobile Coupons
-Information access
-Smart Posters
• Industrial Applications:
-Asset Management
-Maintenance systems
-Product Genealogy [2]
Figure 1. NFC Reader/Writer mode [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-130618143756-phpapp01/75/Project-5-2048.jpg)
![21:06:2013| Ramakrishnan Ramanathan – Demonstrator For Near Field Communication.
.
NFC Operating Modes
Peer-To-Peer Mode
• Peer-to-peer mode provides easy bidirectional data exchange between
two NFC Devices.
• P2P mode Provide secure exchange of private data in a few centimeters
• Applications :
- Health Monitoring [1]
- P2P Payment
- Bluetooth Pairing
• Industrial Applications :
- Industrial motor with NFC
Control [4]
- Automobiles in ignition [5]
- Controlling Sensors [6]
Figure 2. NFC peer-To-Peer mode [7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-130618143756-phpapp01/75/Project-6-2048.jpg)
![21:06:2013| Ramakrishnan Ramanathan – Demonstrator For Near Field Communication.
.
NFC Operating Modes
Card Emulation mode
• Tag emulation mode is the reverse of reader/writer mode
• In this mode the NFC enabled device acts in passive mode.
• A NFC device acts as contactless smartcard and is being recognized by
existing NFC readers
• Applications :
-Transportation ticketing (Deutsche Bahn)
-Contactless logins and
authentication on computers
-Payments (Visa pay Wave, Google Wallet)
• Industrial Applications :
- Access control to Research Labs.
Figure 3. NFC Card Emulation mode [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-130618143756-phpapp01/75/Project-7-2048.jpg)