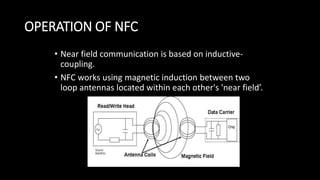
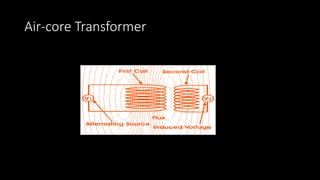
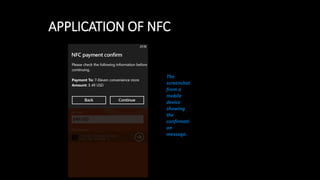
Near Field Communication (NFC) allows for contactless communication between devices over short ranges using radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and has a range of less than 10 cm. It supports both active and passive communication modes. NFC tags and readers enable two-way communication where one device acts as a reader/writer and the other as a tag. Common applications of NFC include contactless payments, data sharing, and connecting devices by simply touching them together. The technology provides a convenient way to transfer information with security and no need for manual configuration.