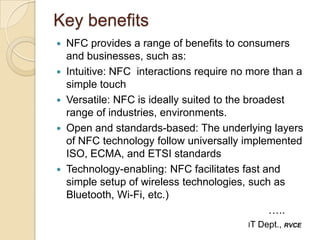
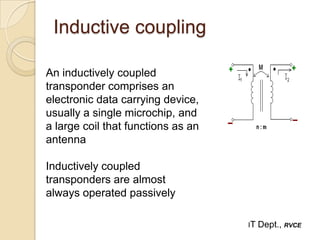
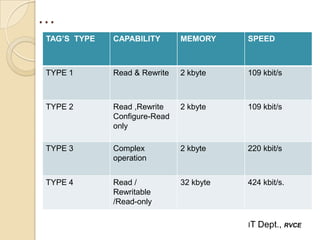
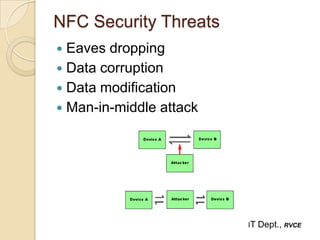
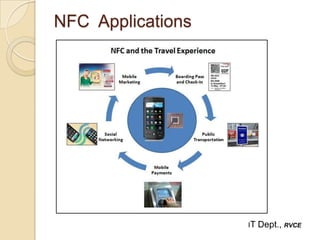
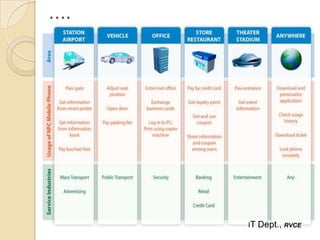
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows data transmission between devices that are 4-5 cm apart. NFC uses inductive coupling to transmit data securely at 13.56 MHz. It originated from RFID technology and was standardized by the NFC Forum in 2004. NFC provides benefits like intuitive interactions with a simple touch, versatility across many industries, and inherently secure transmissions over short ranges. Common applications of NFC include contactless payments, data sharing, and setup of wireless connections.