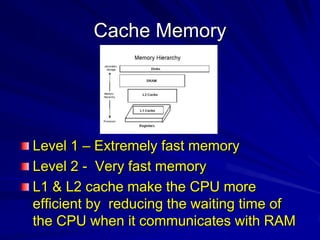
The three main internal components of a computer system unit are the central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, and memory. The CPU processes instructions and performs calculations. The motherboard houses and connects essential parts like the CPU, memory, ports, and expansion cards. Memory includes random access memory (RAM) for running programs, read-only memory (ROM) for basic settings, and cache to improve CPU efficiency. Other key internal components are the power supply, storage drives, cooling fan and heat sink, and ports for connecting peripherals. Specialized expansion cards provide network or graphics capabilities.