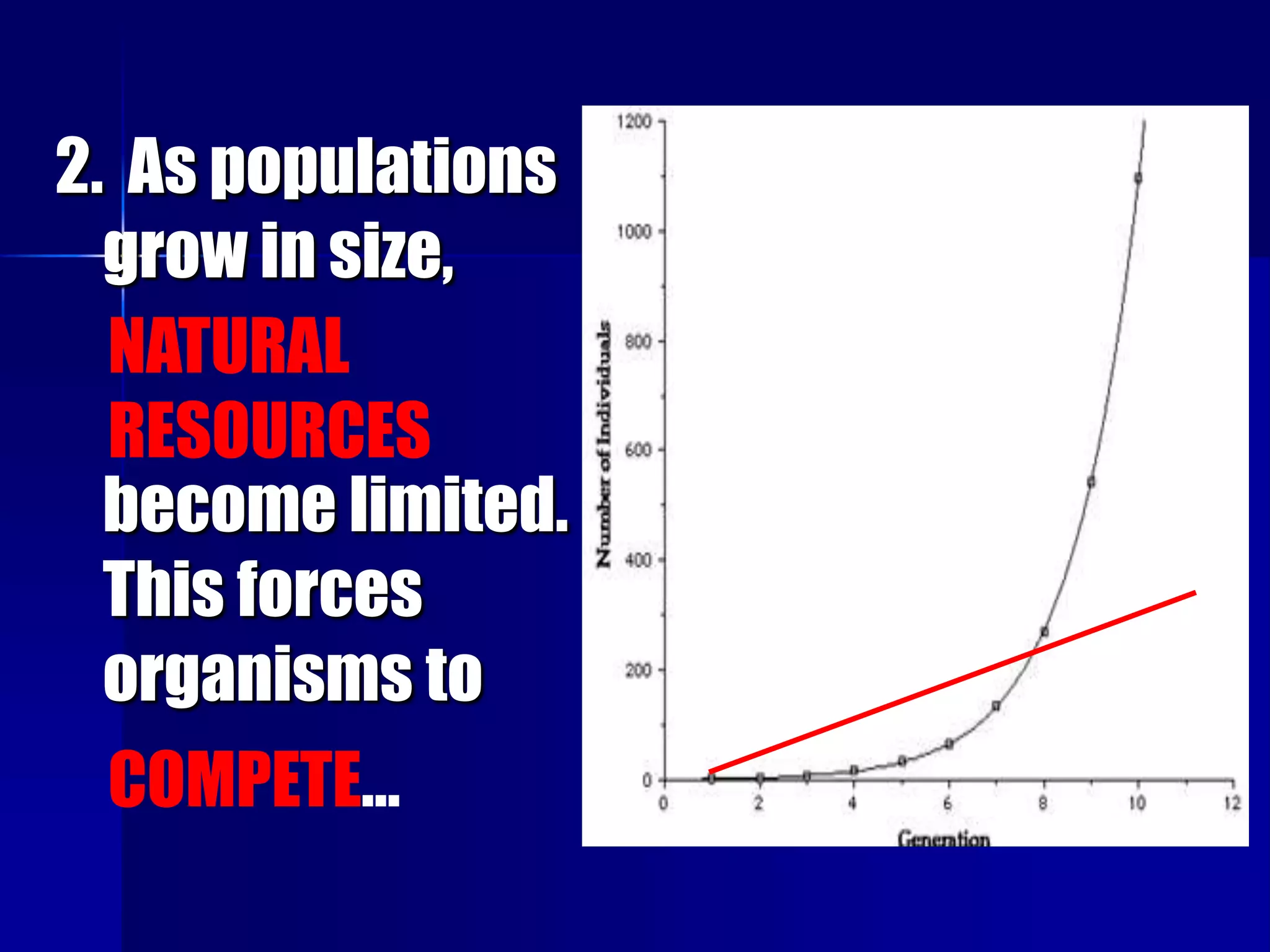
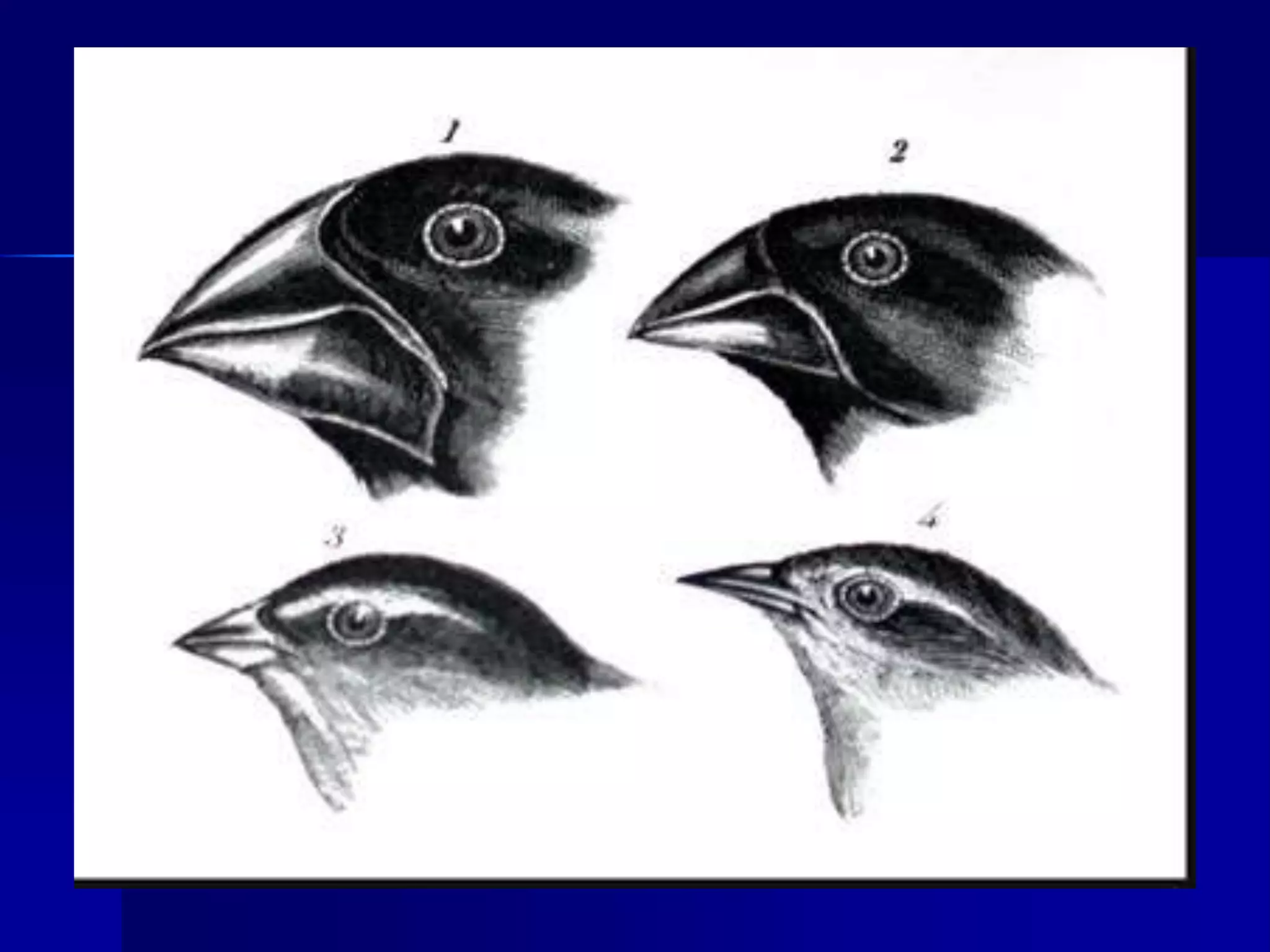
Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection provides a mechanism for evolution. [1] Organisms produce more offspring than can survive, [2] leading to competition for limited natural resources. [3] Variations between individuals provide different chances of survival, so those better adapted to the environment tend to survive and pass their traits to subsequent generations, while less fit variations die out. Over many generations, this process can result in new species developing.