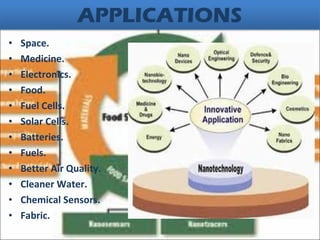
This document provides an overview of nanotechnology, its applications, opportunities, and challenges. It discusses how nanotechnology can be applied in electronics, medicine, materials, food, space, transportation, and other industries. Some key opportunities include developing new drug delivery methods, lighter stronger materials, more efficient solar cells and batteries. Challenges include safety concerns over particle inhalation, high costs, and ensuring benefits are realized. The future of nanotechnology remains uncertain but it could help solve major problems if developed responsibly with consideration for its societal impacts.