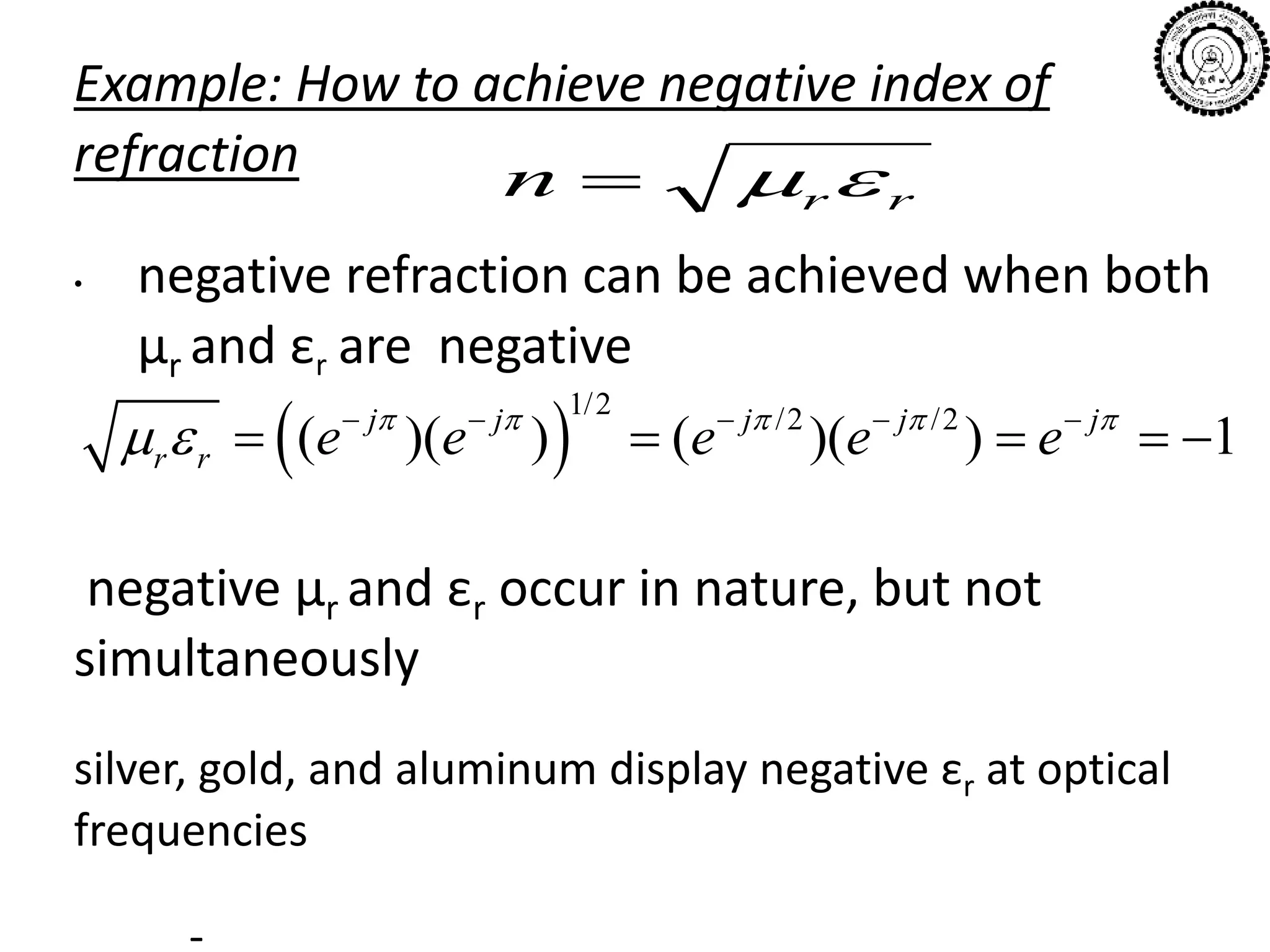
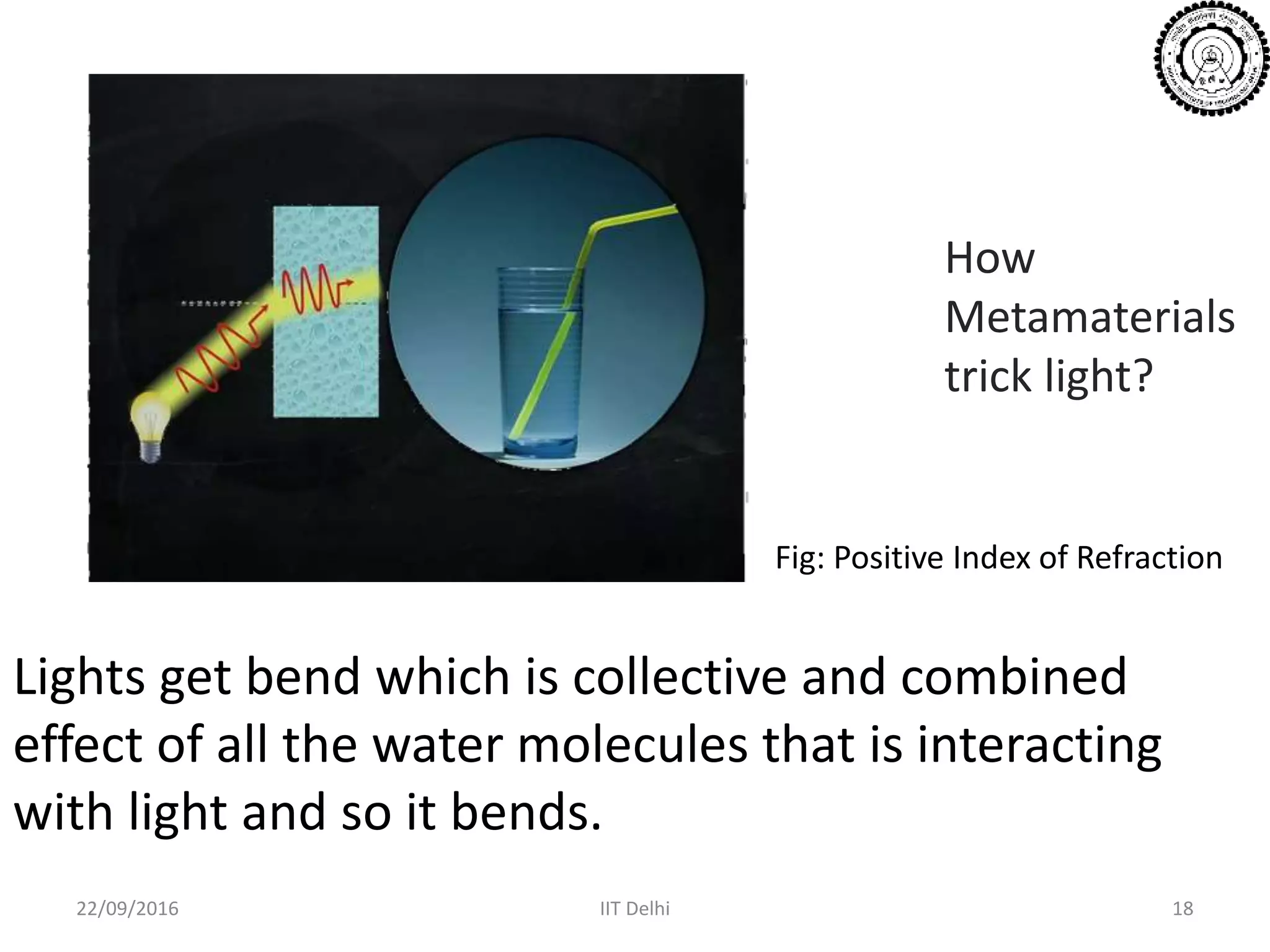
This document summarizes a seminar on nanomaterials and metamaterials presented by Deepak Raj at IIT Delhi. It discusses how the properties of nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes and quantum dots, differ from bulk materials due to increased surface area and quantum effects. It also explains how metamaterials derive their properties from their structure rather than composition, allowing properties not found in nature like negative refractive index. Potential applications of metamaterials include invisibility cloaking, improved solar cells, telecommunications, and computing.