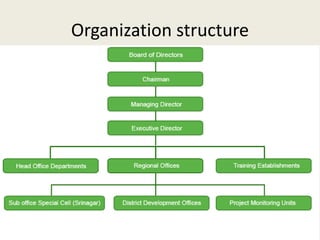
NABARD was established in 1982 to promote rural prosperity in India. It replaced existing agricultural credit and rural development institutions. NABARD operates nationwide with regional and district offices. Its mission is to support sustainable agriculture and integrated rural development through credit and other services. NABARD provides refinancing to banks and cooperatives, promotes rural policies, and works to enhance financial inclusion in rural areas through programs like Kisan Credit Cards, self-help groups, and watershed development.