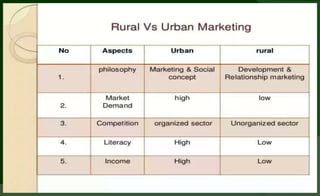
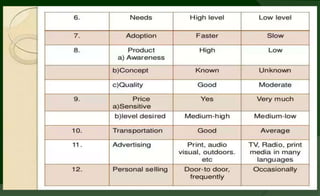
Rural marketing involves assessing, stimulating, and converting rural consumers' purchasing power into effective demand for specific products and services. It is a two-way process involving both urban to rural and rural to urban transactions.
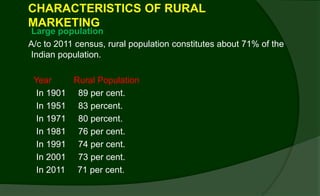
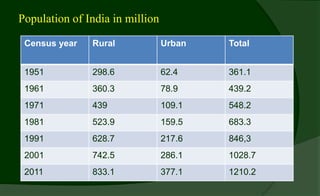
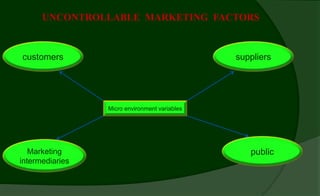
Rural markets are characterized by a large population, agriculture-based occupations, low income and literacy, traditional outlook, and inadequate infrastructure. Key factors affecting rural consumer behavior include psychological, personal, situational, economic, and socio-cultural influences.
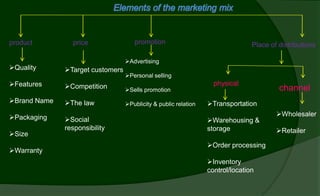
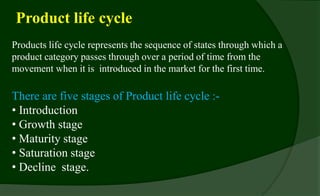
The marketing mix, or 4Ps, refers to product, price, promotion, and place strategies used by companies to market brands in rural areas. Products go through different life cycle stages from introduction to growth, maturity, saturation, and decline. Rural