The document discusses the Lead Bank Scheme in India. Some key points:
- The RBI accepted recommendations from the Nariman Committee to formulate the Lead Bank Scheme in 1969.
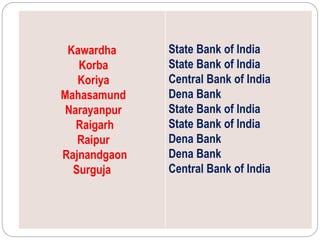
- Under this scheme, specific districts are allotted to commercial banks, with the bank having the most branches becoming the "Lead Bank" to coordinate credit efforts.
- The Lead Bank is responsible for surveying credit needs, expanding banking access, and formulating district credit plans to boost sectors like agriculture and support vulnerable groups.
- Over time the scheme has expanded nationwide and Lead Banks in Chhattisgarh are identified.