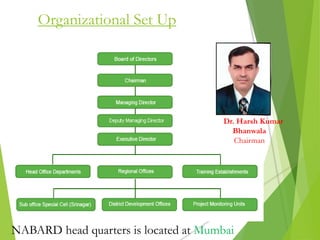
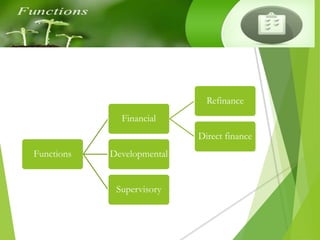
India prospers if rural areas prosper. Through its credit and development initiatives, NABARD ensures that India's food needs are met season after season and year after year by focusing on rural development. NABARD provides refinancing, direct lending, and development support to promote sustainable agriculture and rural development. It works to strengthen rural financial institutions and ensure access to credit for farmers and rural communities.