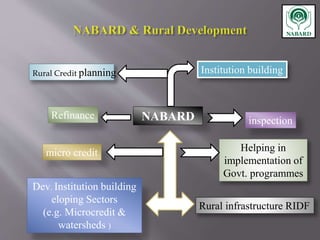
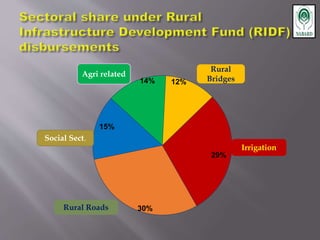
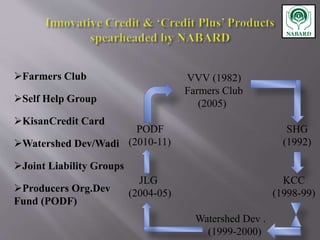
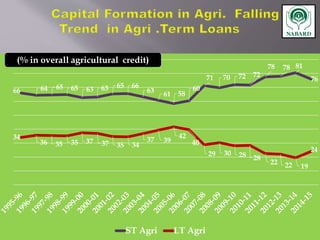
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was established in 1982 to provide credit and other services to promote rural development. It replaced previous agricultural credit institutions and aims to secure prosperity in rural areas through credit for agriculture and allied activities. NABARD serves as a refinancing body for rural lending institutions and provides direct loans. It also works to develop these institutions and coordinate rural financing through activities like rural credit planning, monitoring, and training.