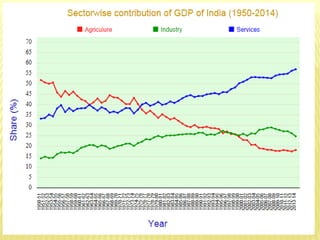
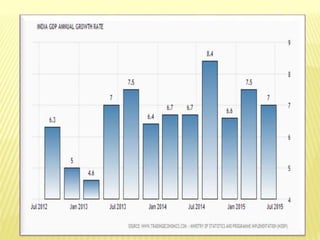
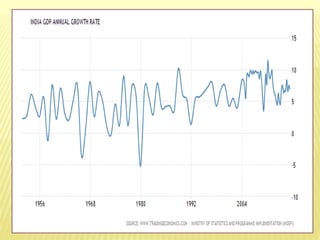
This document provides information about a seminar on National Income. It includes definitions of key concepts related to measuring national income such as Gross Domestic Product, Net Domestic Product, and Gross National Product. It discusses methods used to measure national income, including the product, income, and expenditure methods. It also outlines some of the difficulties in accurately measuring national income, such as how to account for non-market activities and government services. The document concludes by noting the importance of national income statistics for economic planning and development.