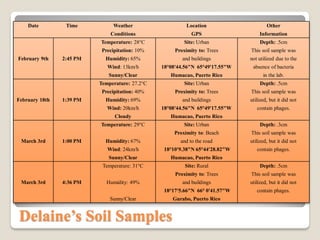
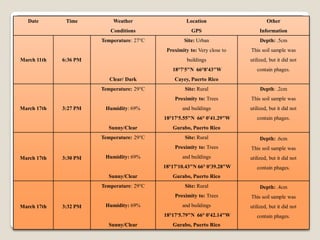
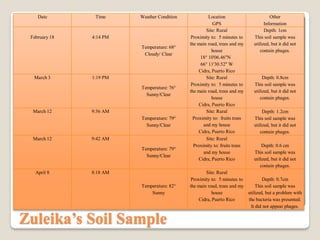
Mycobacteriophages are viruses that infect mycobacteria. The document describes experiments conducted by students to isolate and characterize mycobacteriophages from soil samples. Soil samples were collected from various locations and depths, enriched in culture, and screened for plaques indicating the presence of phages. While proper procedures were followed, none of the samples yielded phages except for one deeper sample. The experiments helped students learn aseptic technique and other lab skills, but the primary objective of isolating a phage was not achieved, possibly due to environmental or technical factors.