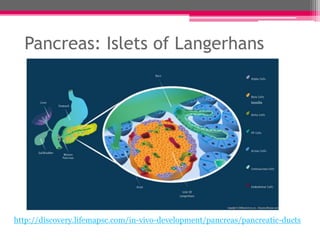
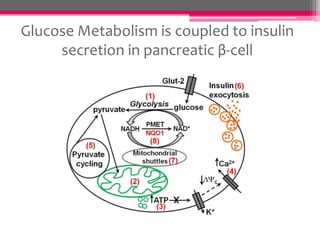
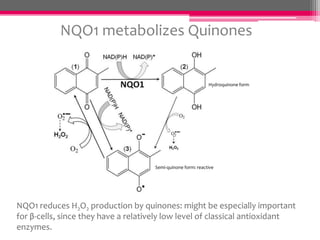
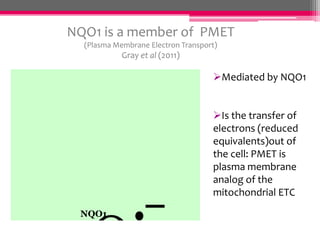
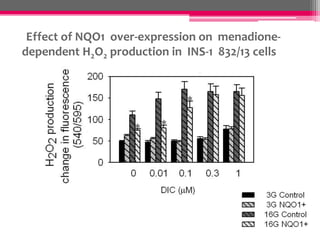
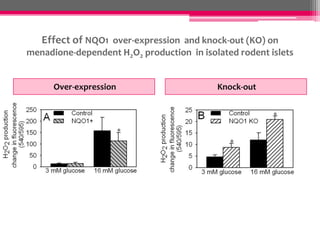
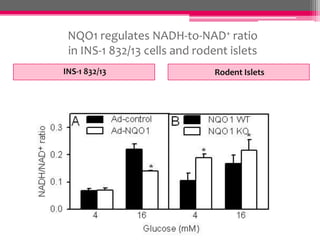
NQO1 modulates redox status and H2O2 levels in pancreatic β-cells. The study aimed to determine the role of NQO1 in β-cell health and metabolism. It was hypothesized that 1) NQO1 reduces oxidative stress in β-cells by lowering quinone-dependent H2O2 production and 2) NQO1 modulates the NAD(P)H-to-NAD(P)+ ratio in β-cells. Results showed that overexpressing NQO1 decreased menadione-dependent H2O2 production in INS-1 cells and isolated rodent islets, while NQO1 knockout increased H2O2 production. N