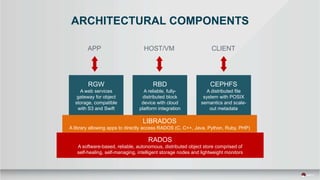
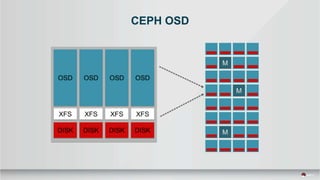
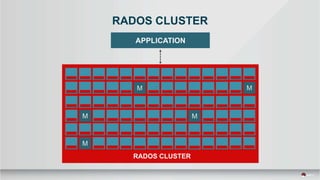
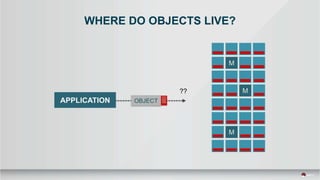
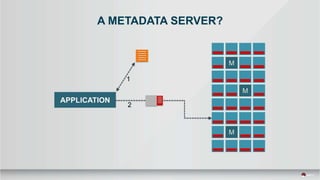
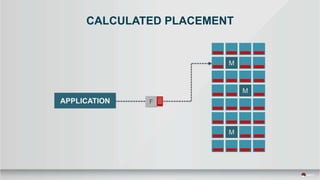
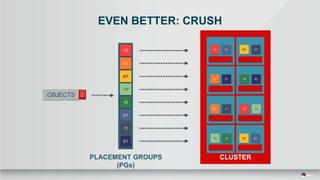
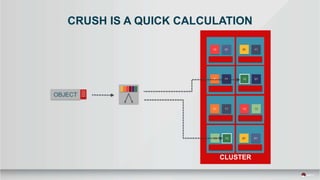
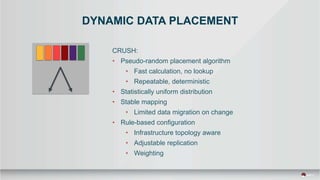
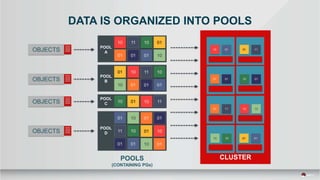
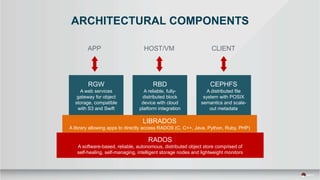
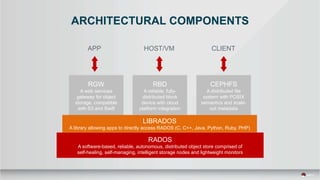
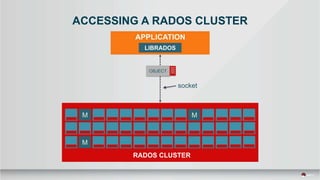
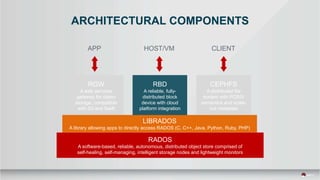
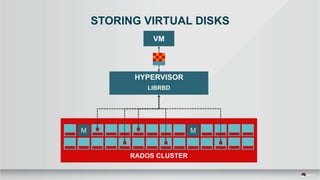
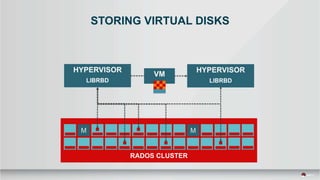
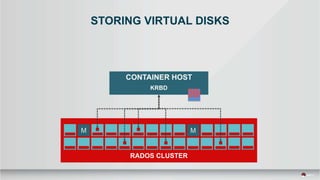
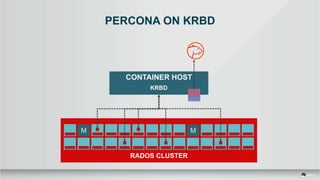
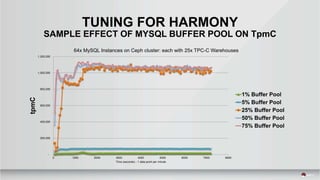
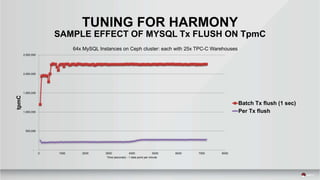
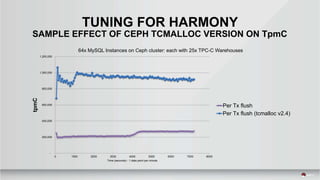
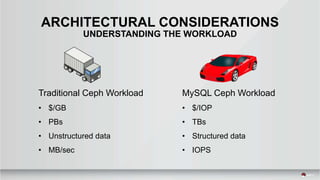
The document outlines a presentation covering MySQL on Ceph and its performance in cloud environments, highlighting advantages such as market drivers, operational efficiency, and architecture. Key components discussed include the Ceph architecture, tuning MySQL for optimal performance, and the significance of various access methods and data placement strategies. It also emphasizes the importance of hybrid cloud capabilities and high IOPS for effective database management.