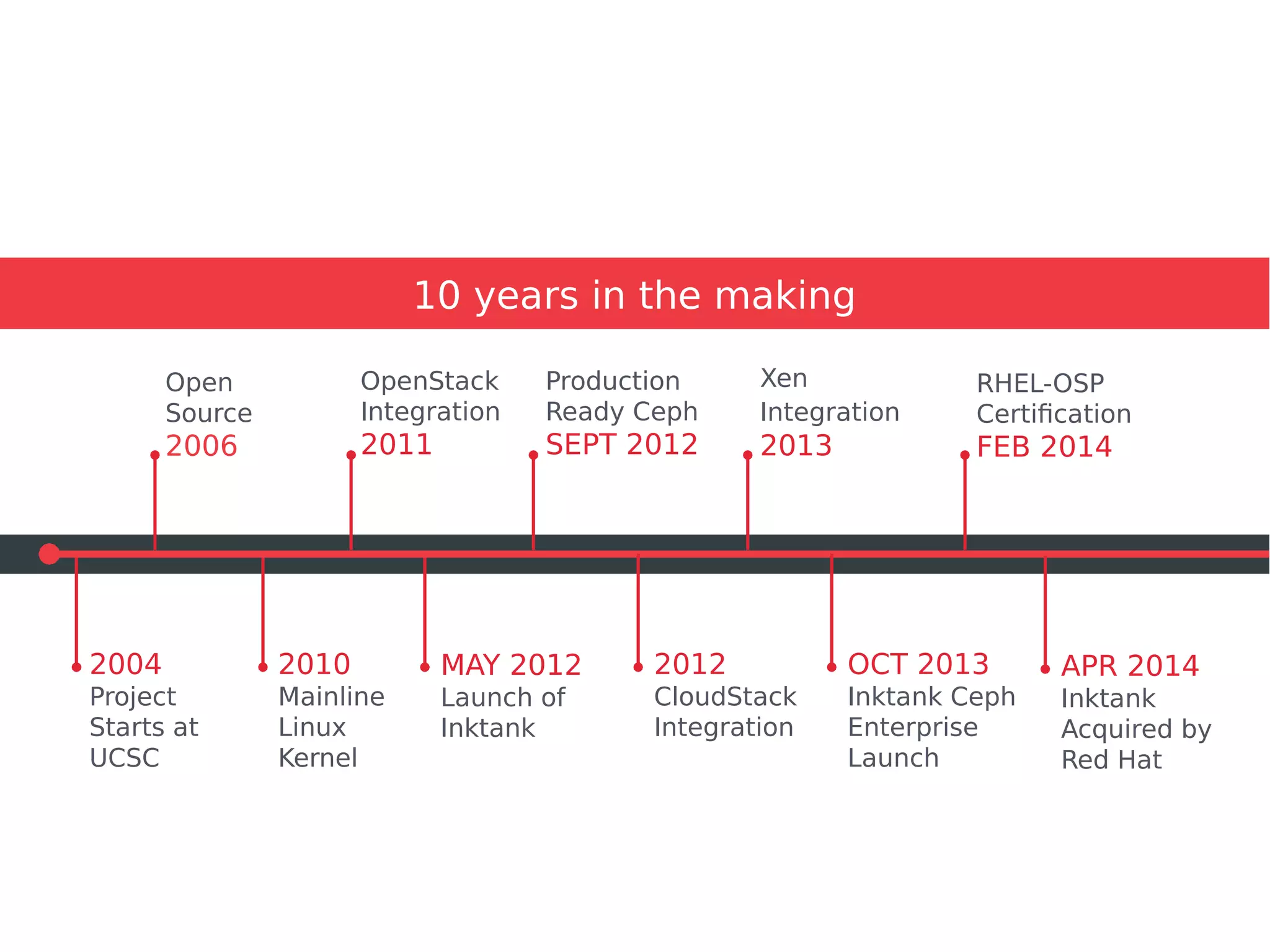
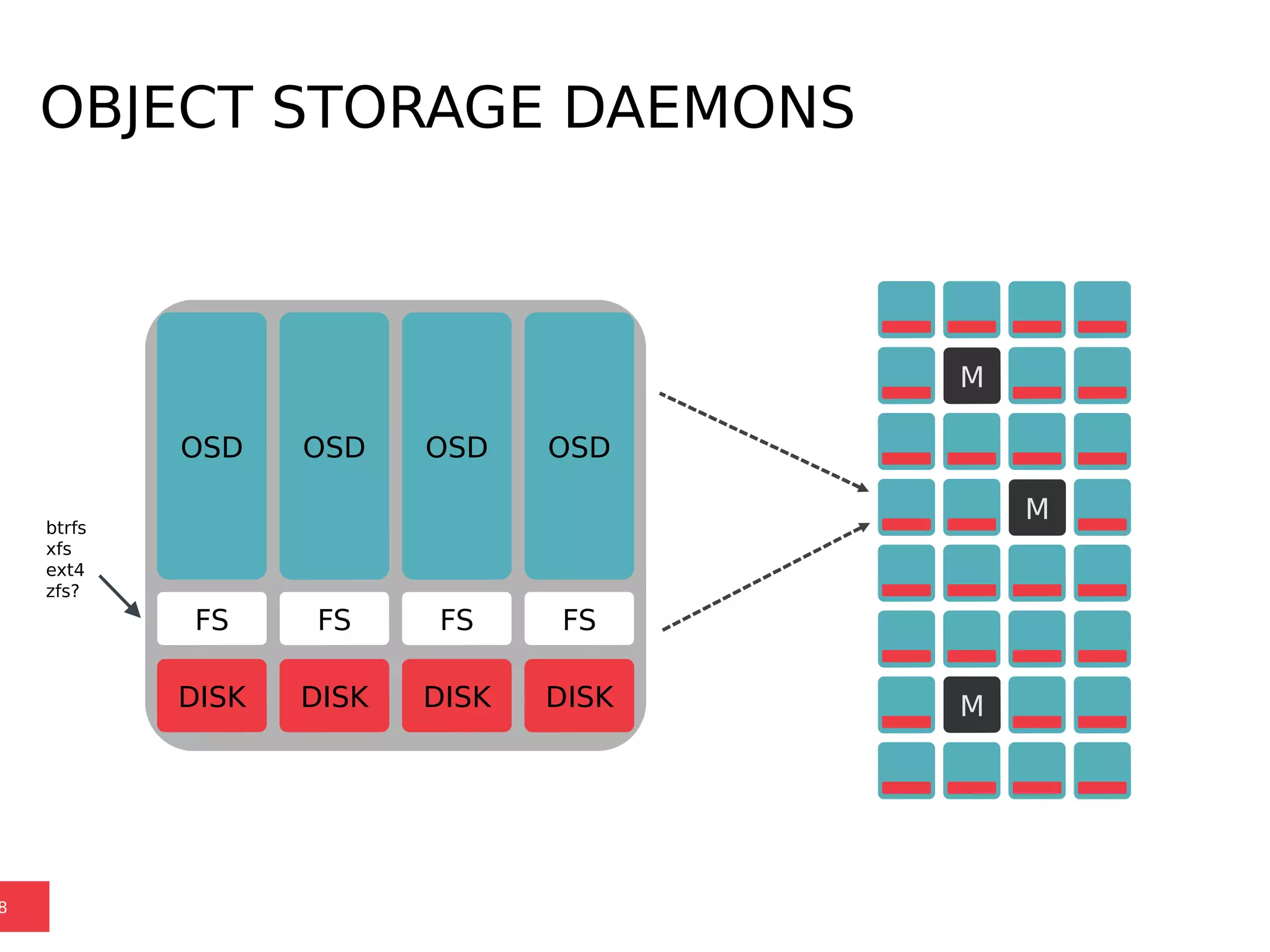
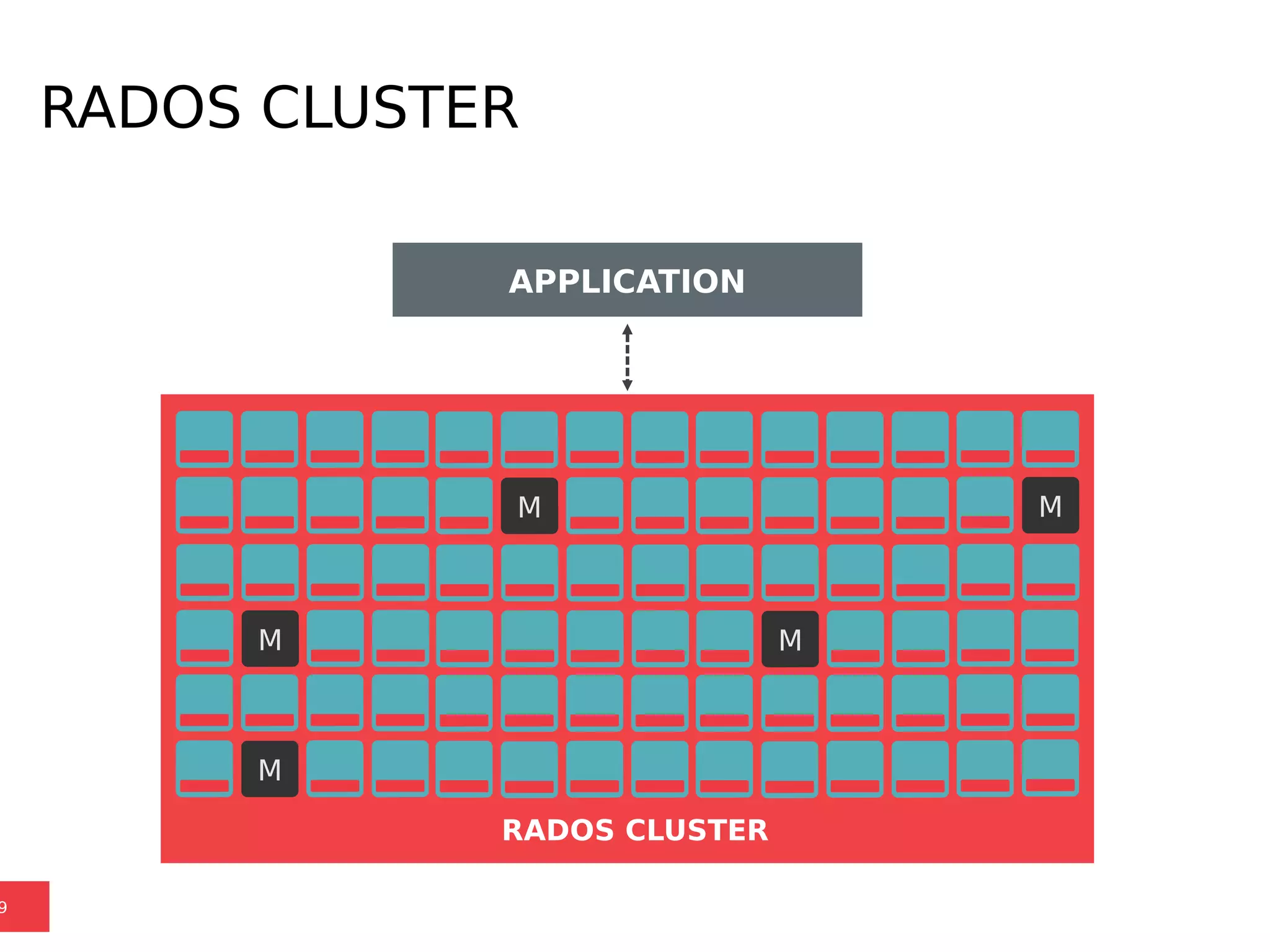
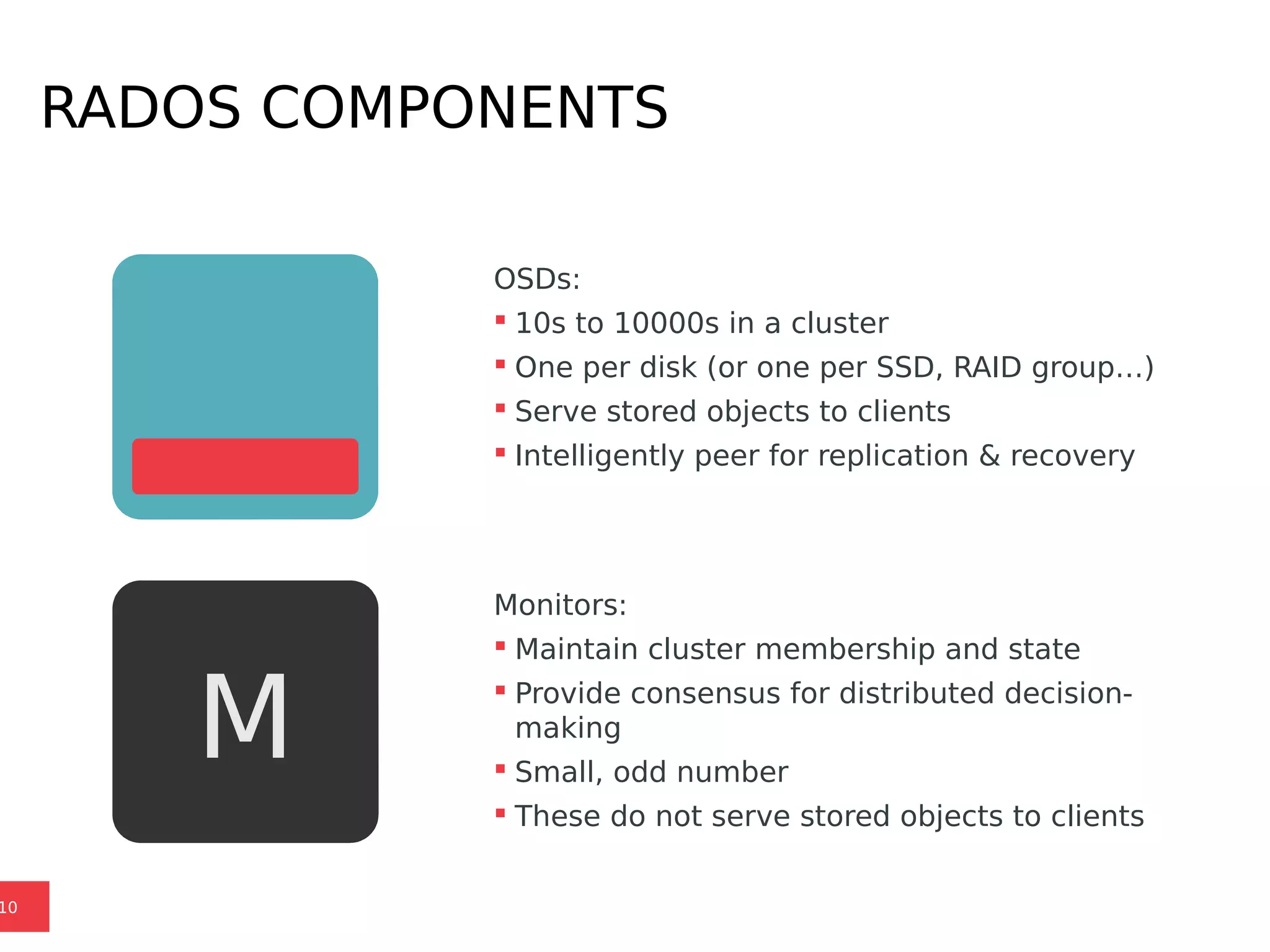
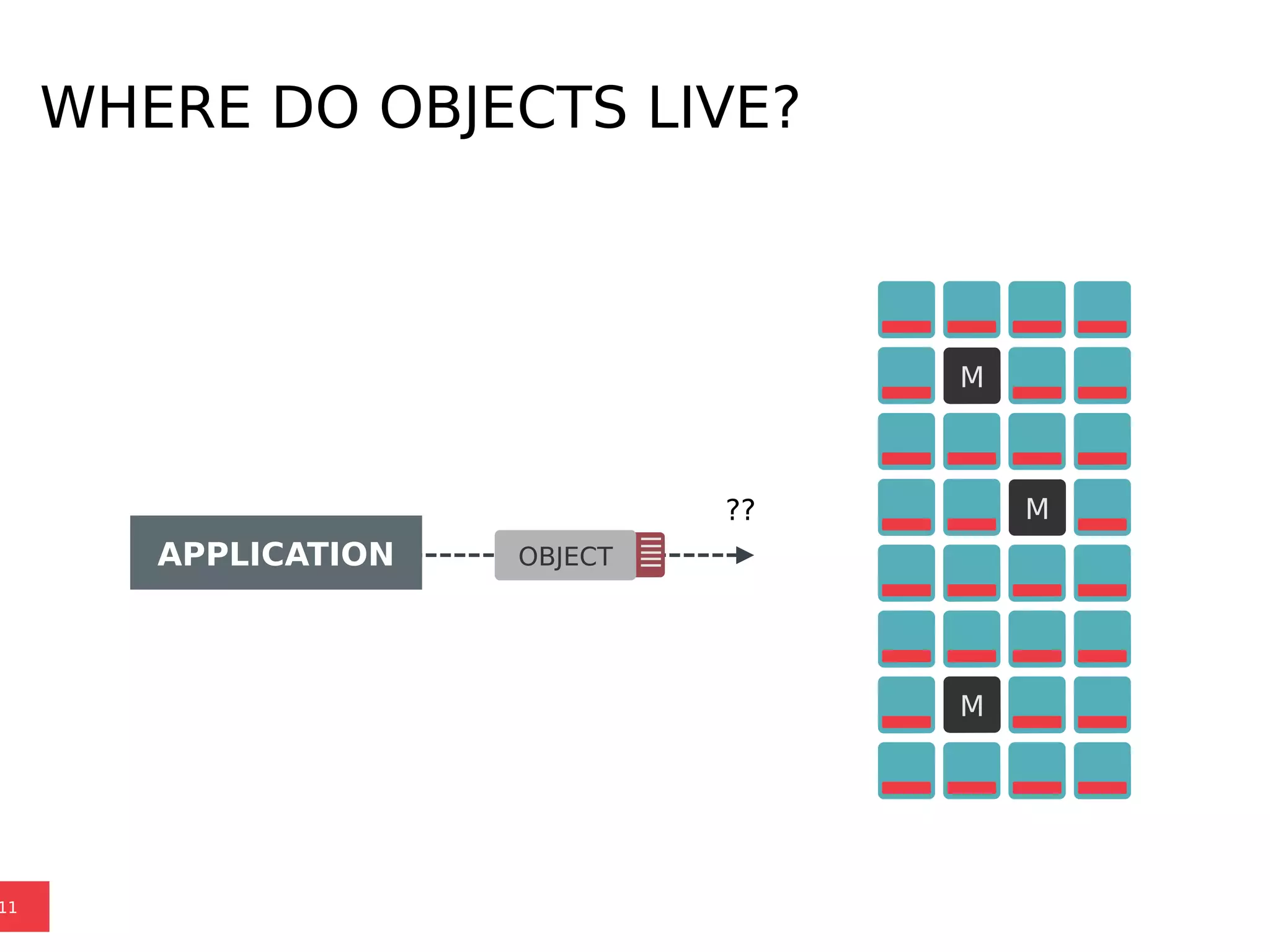
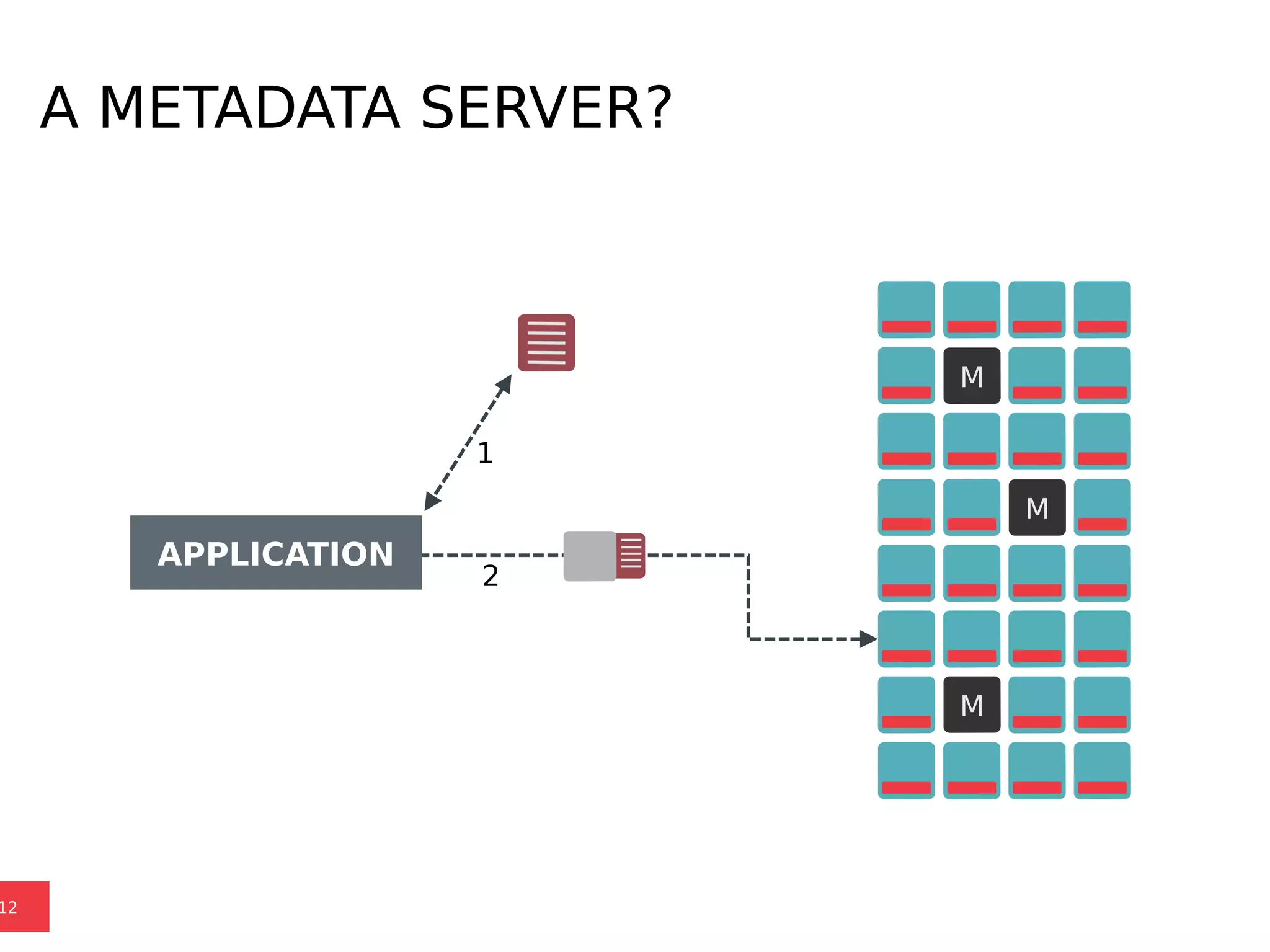
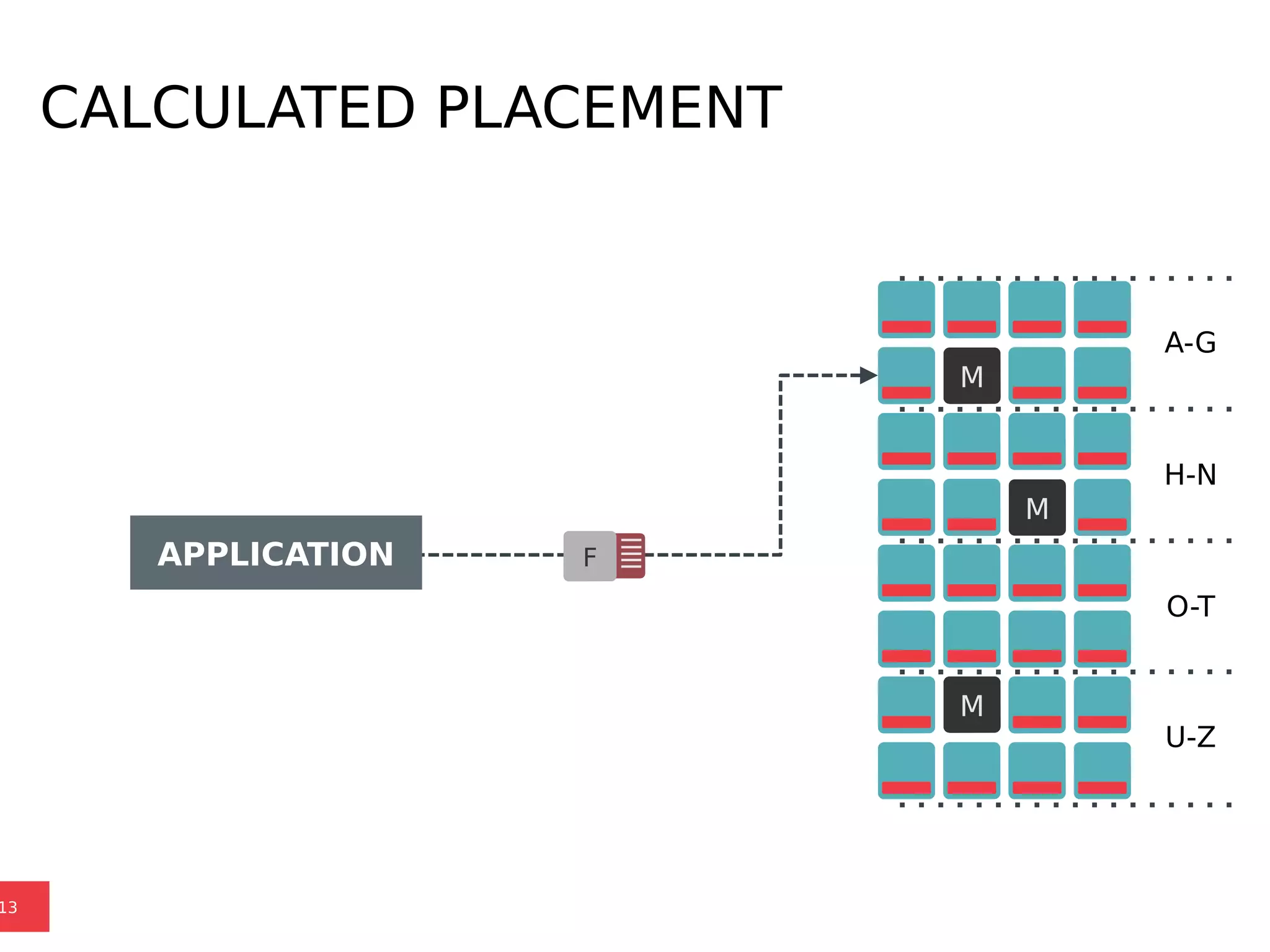
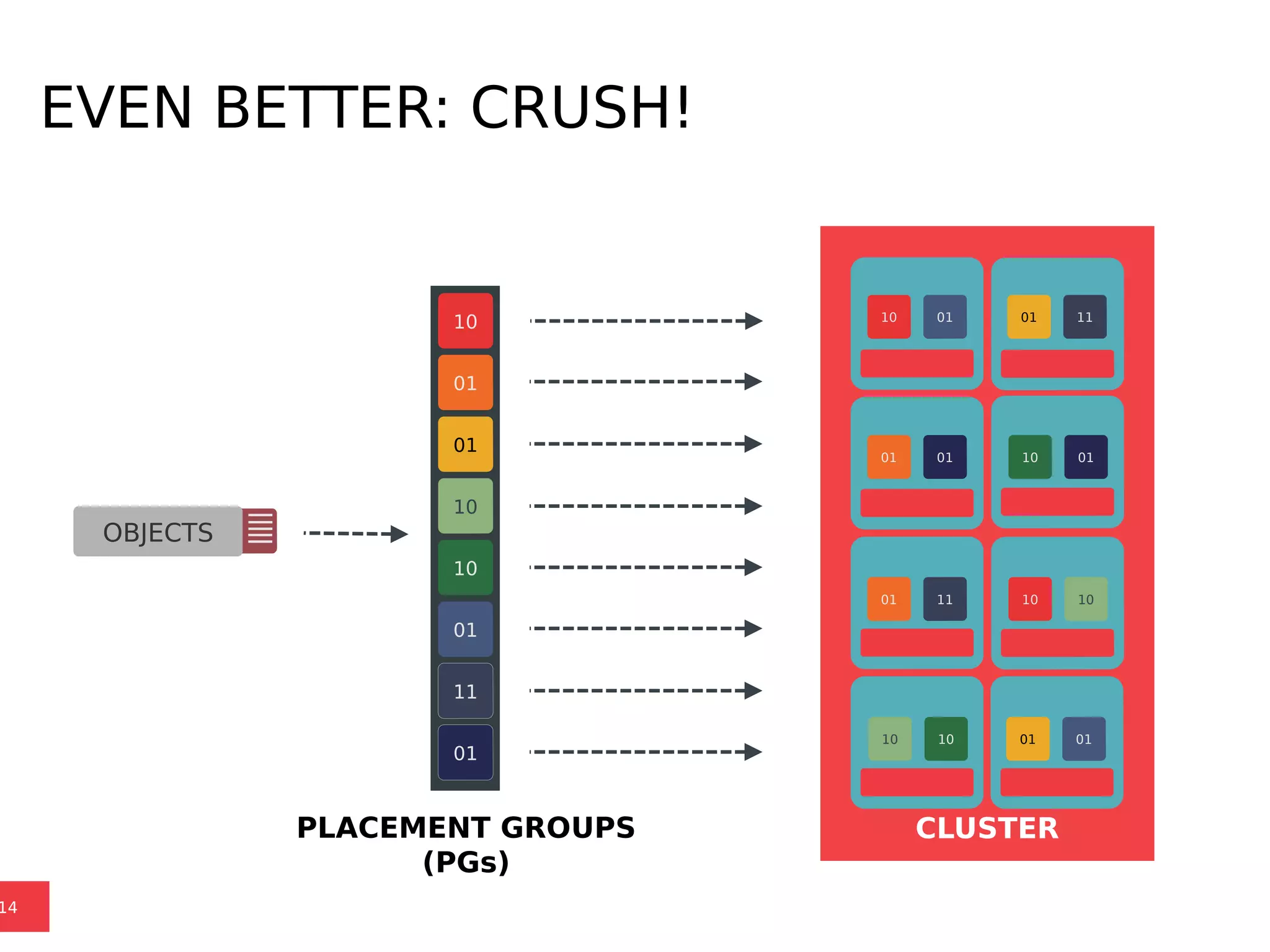
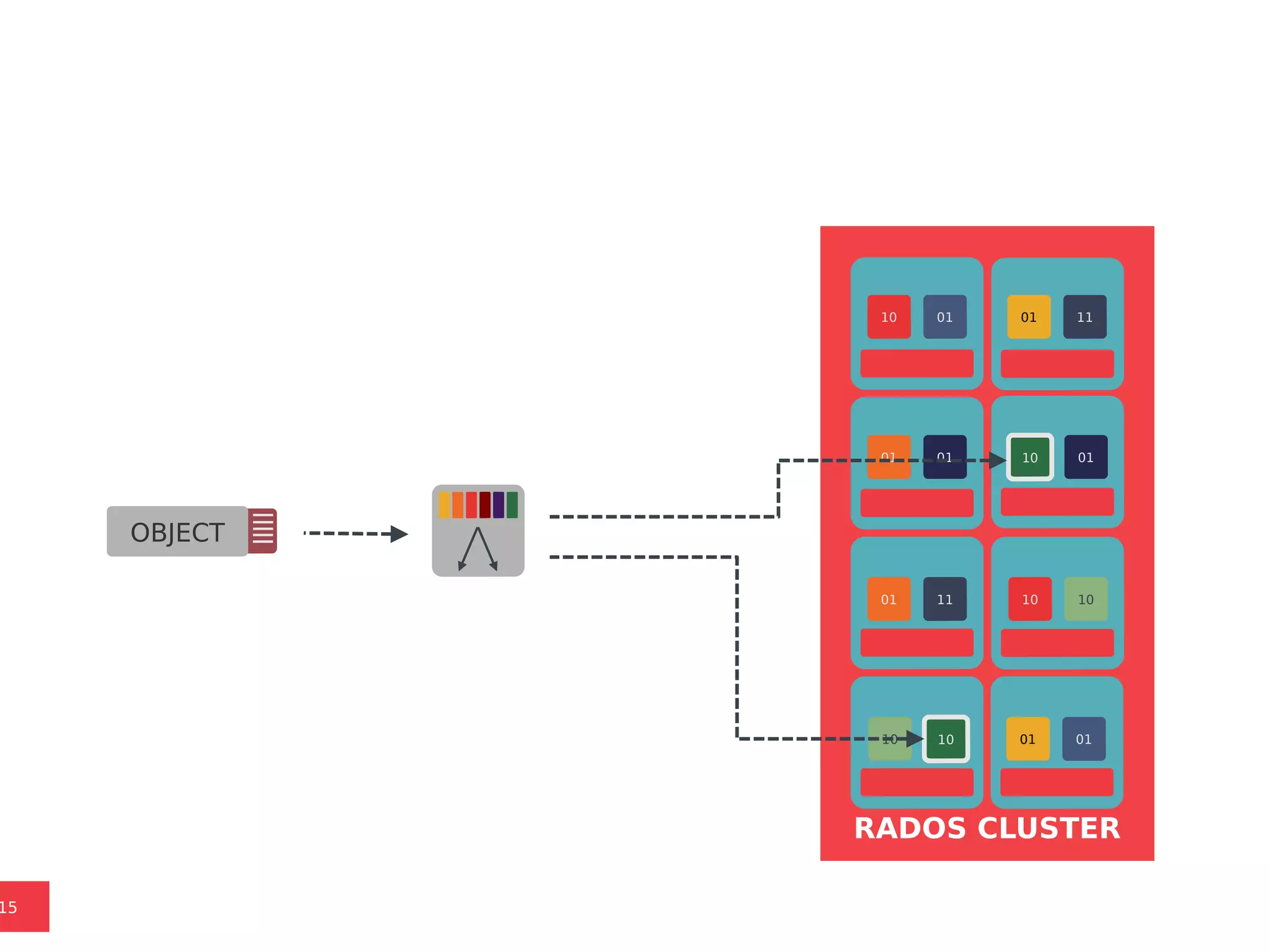
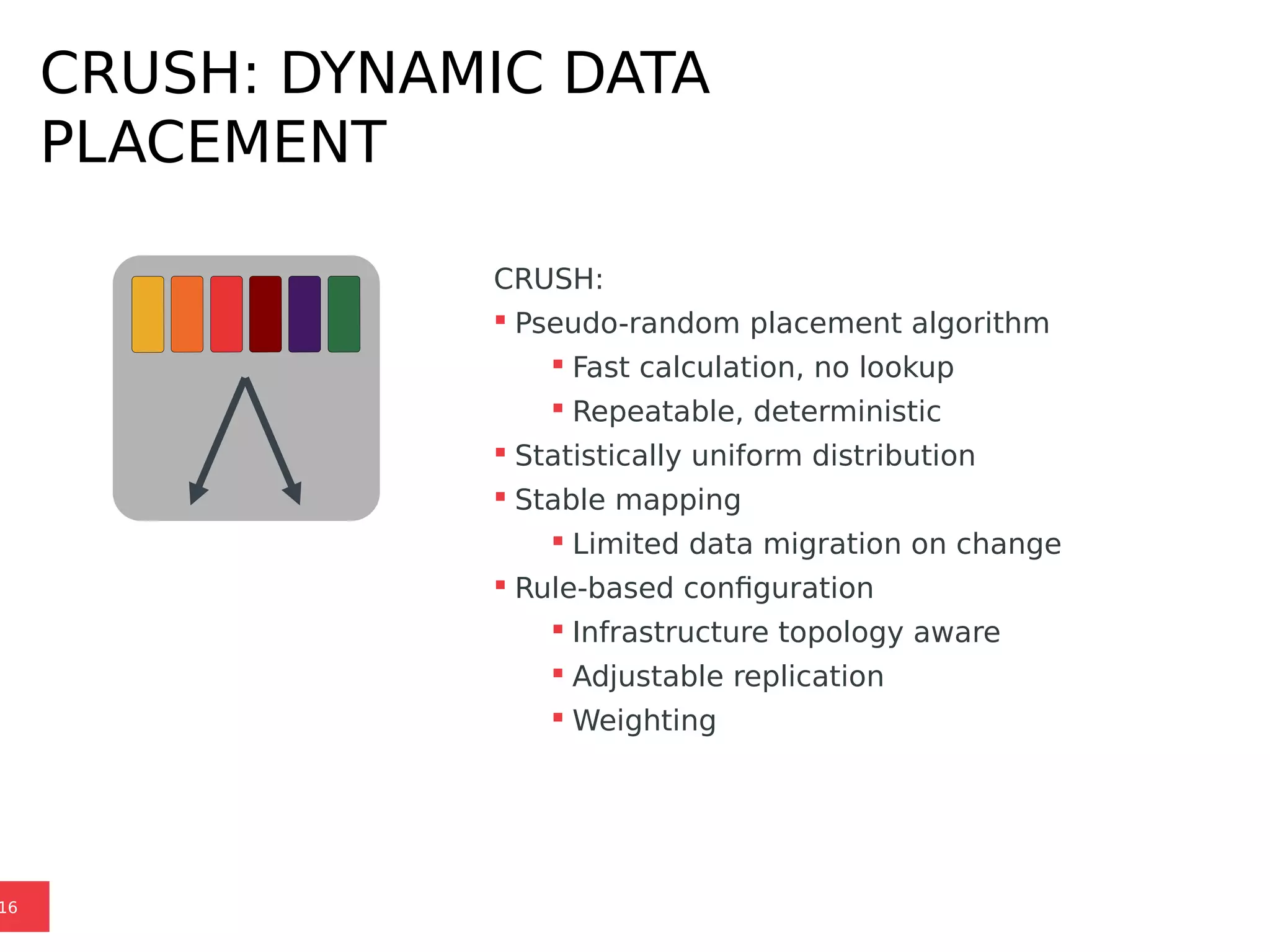
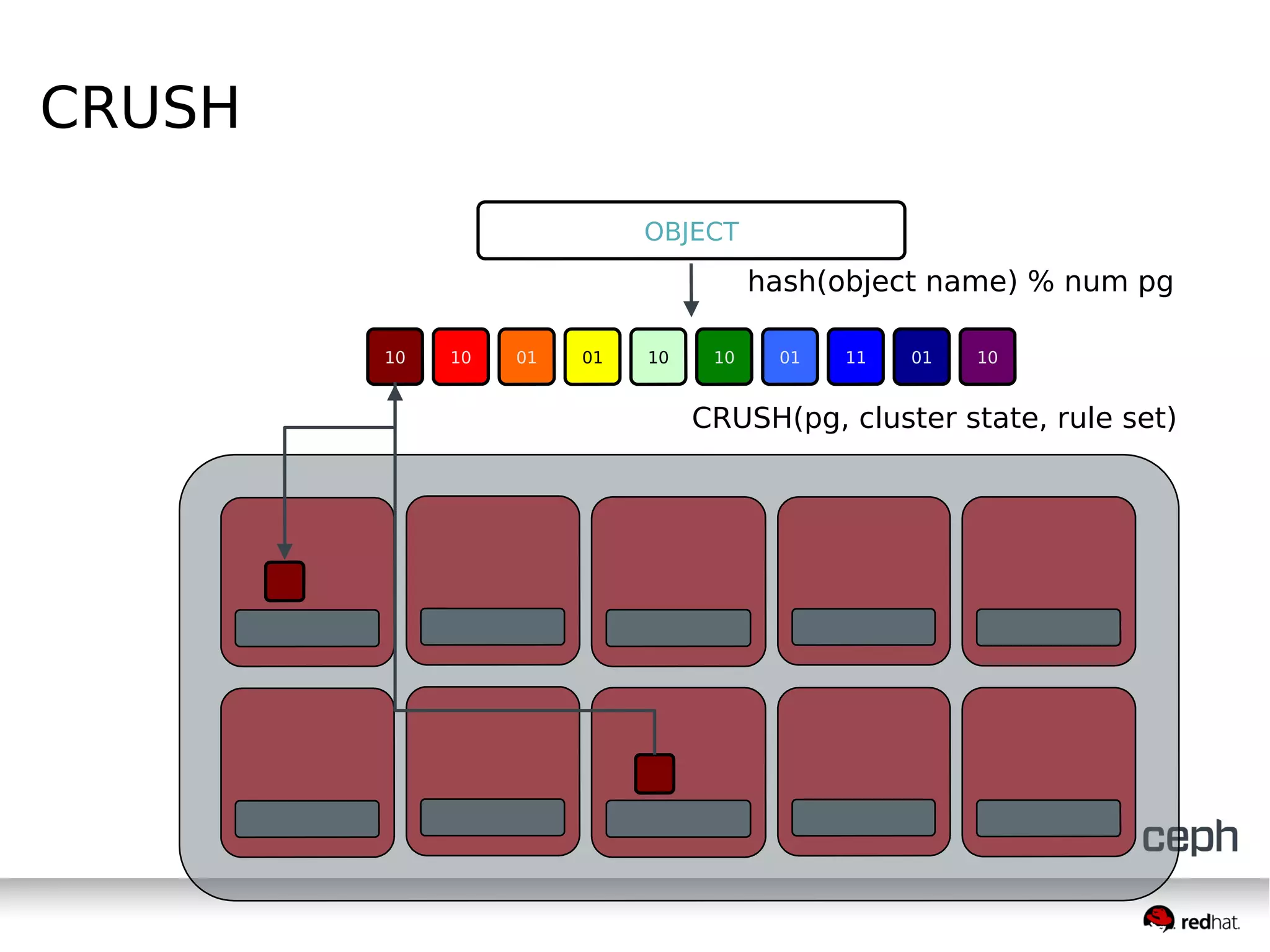
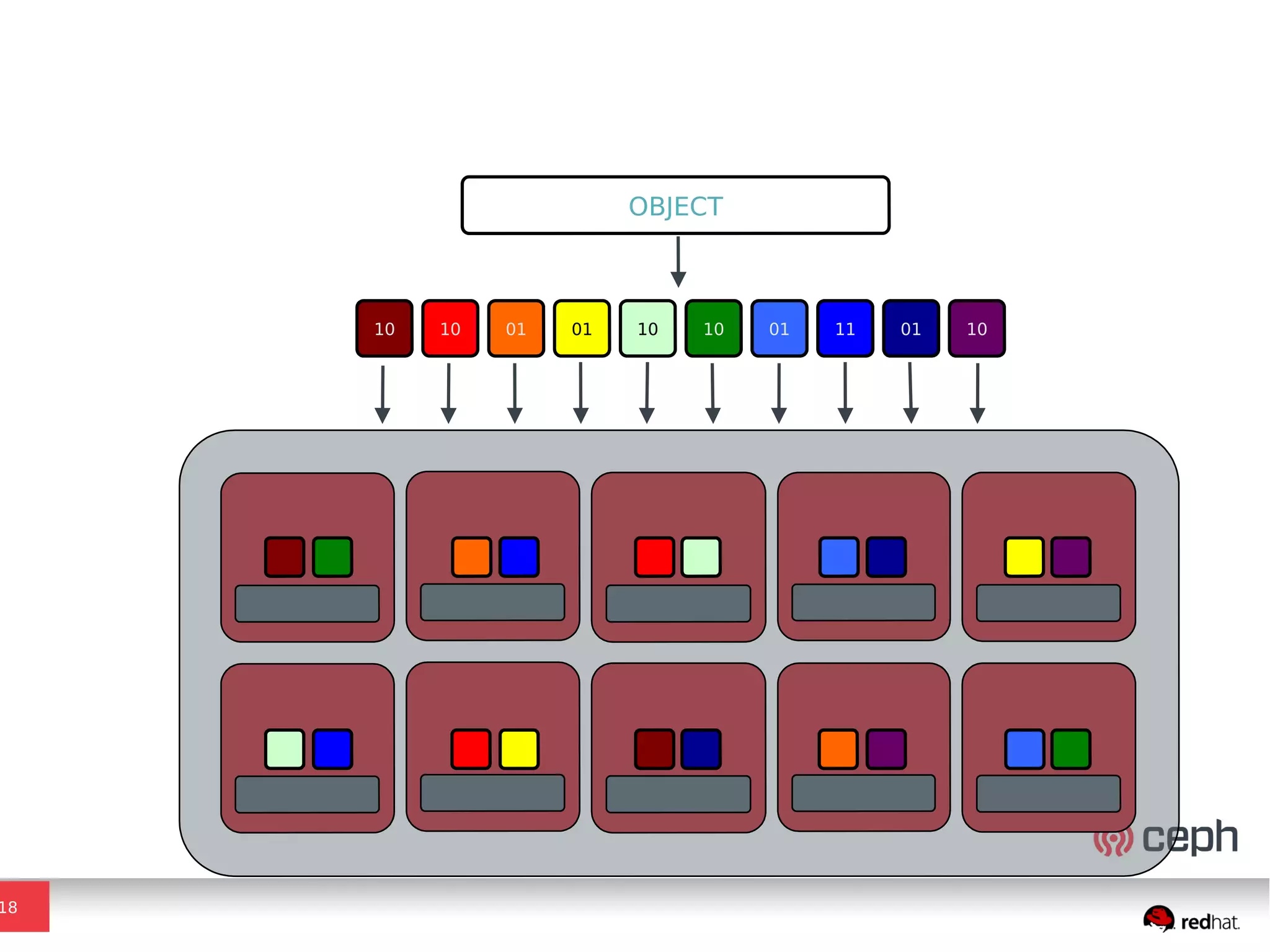
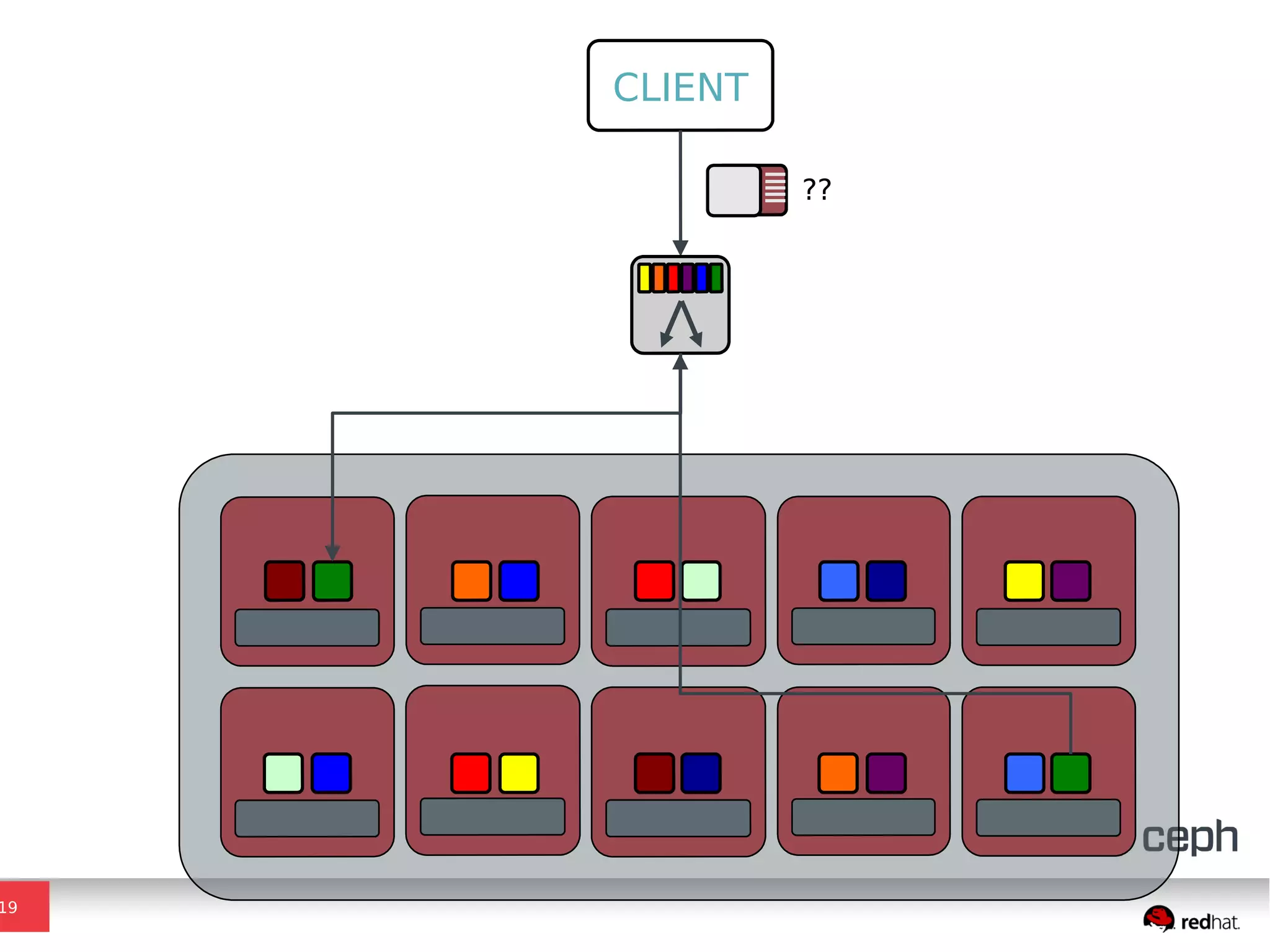
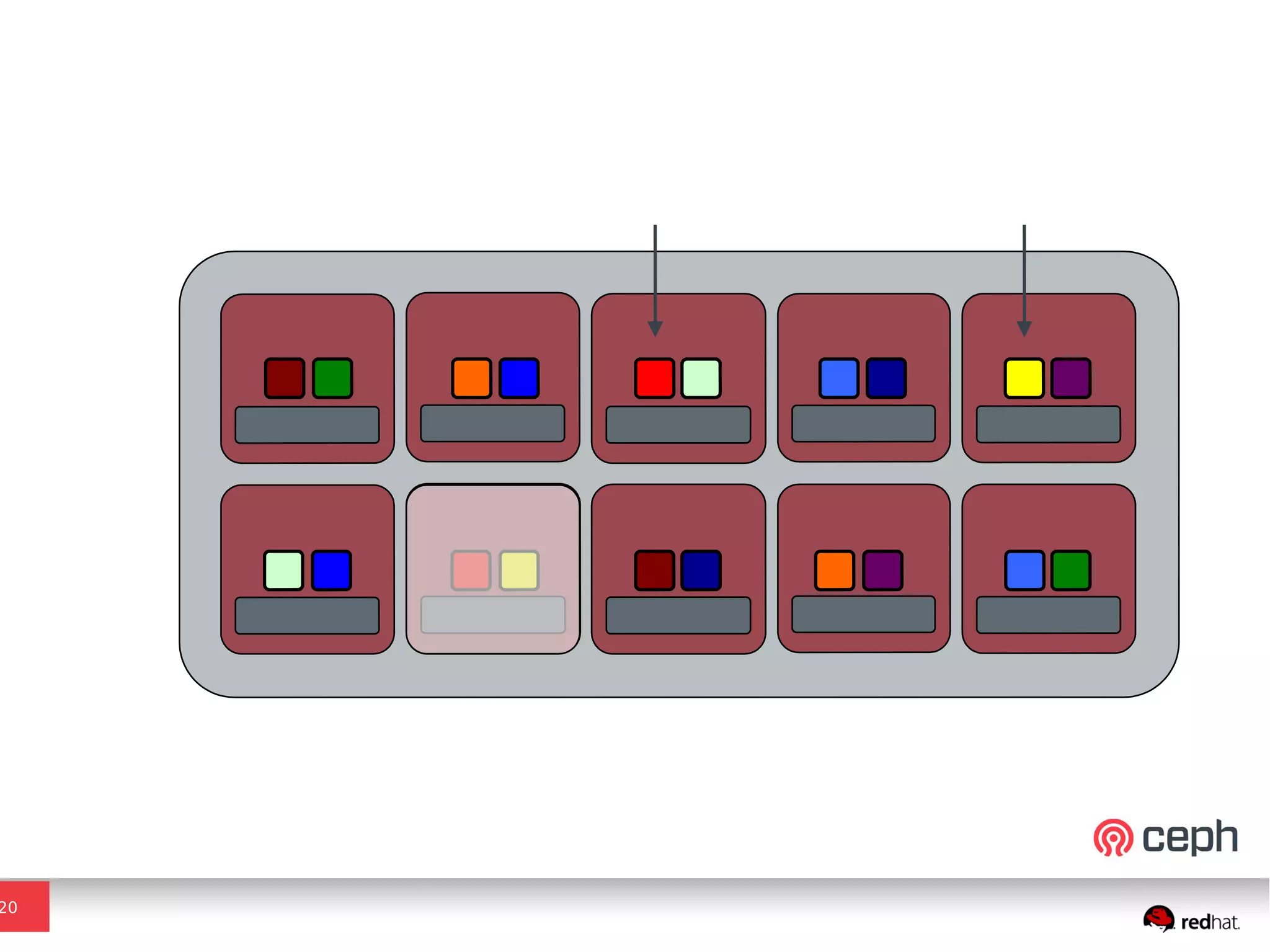
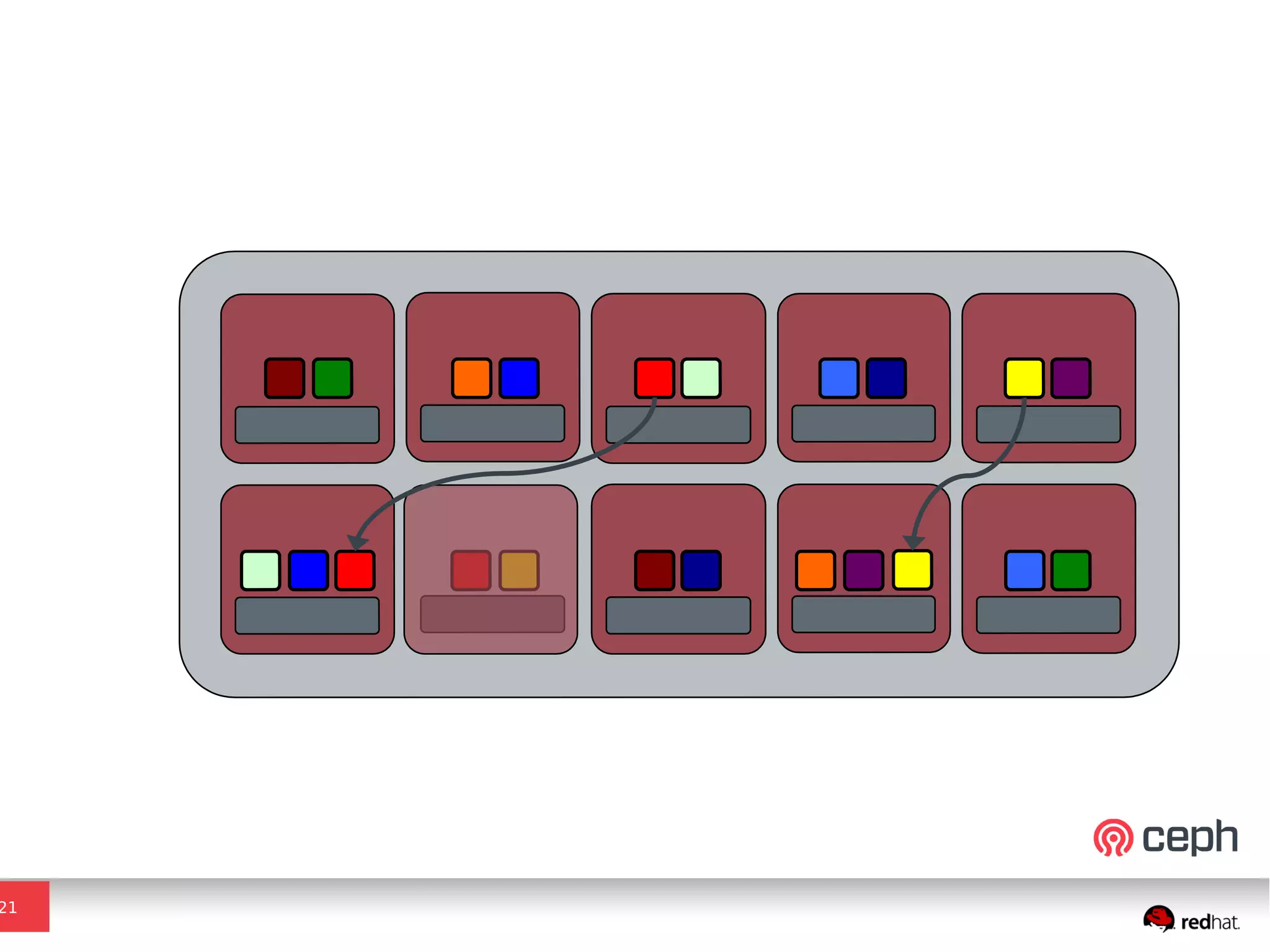
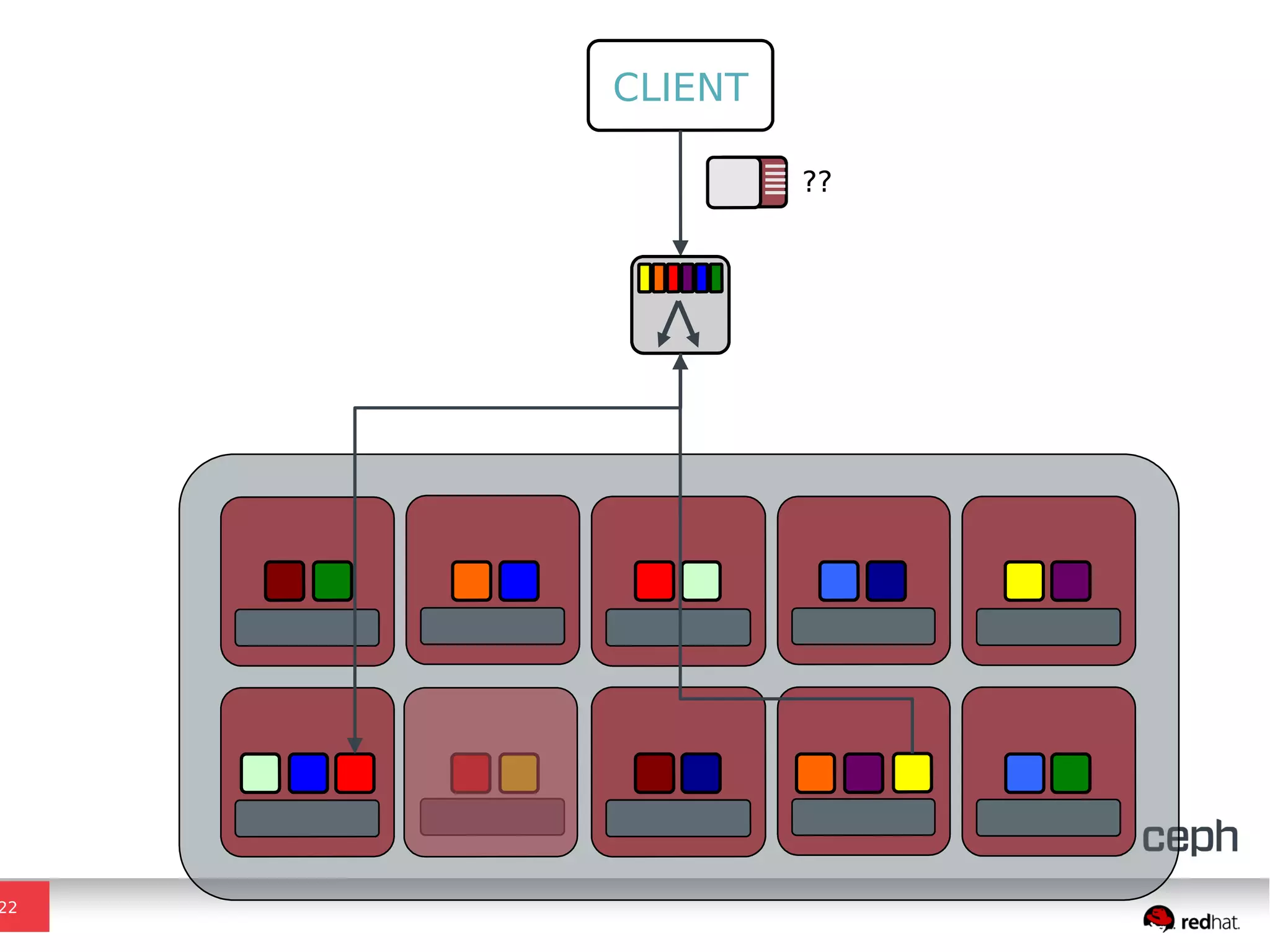
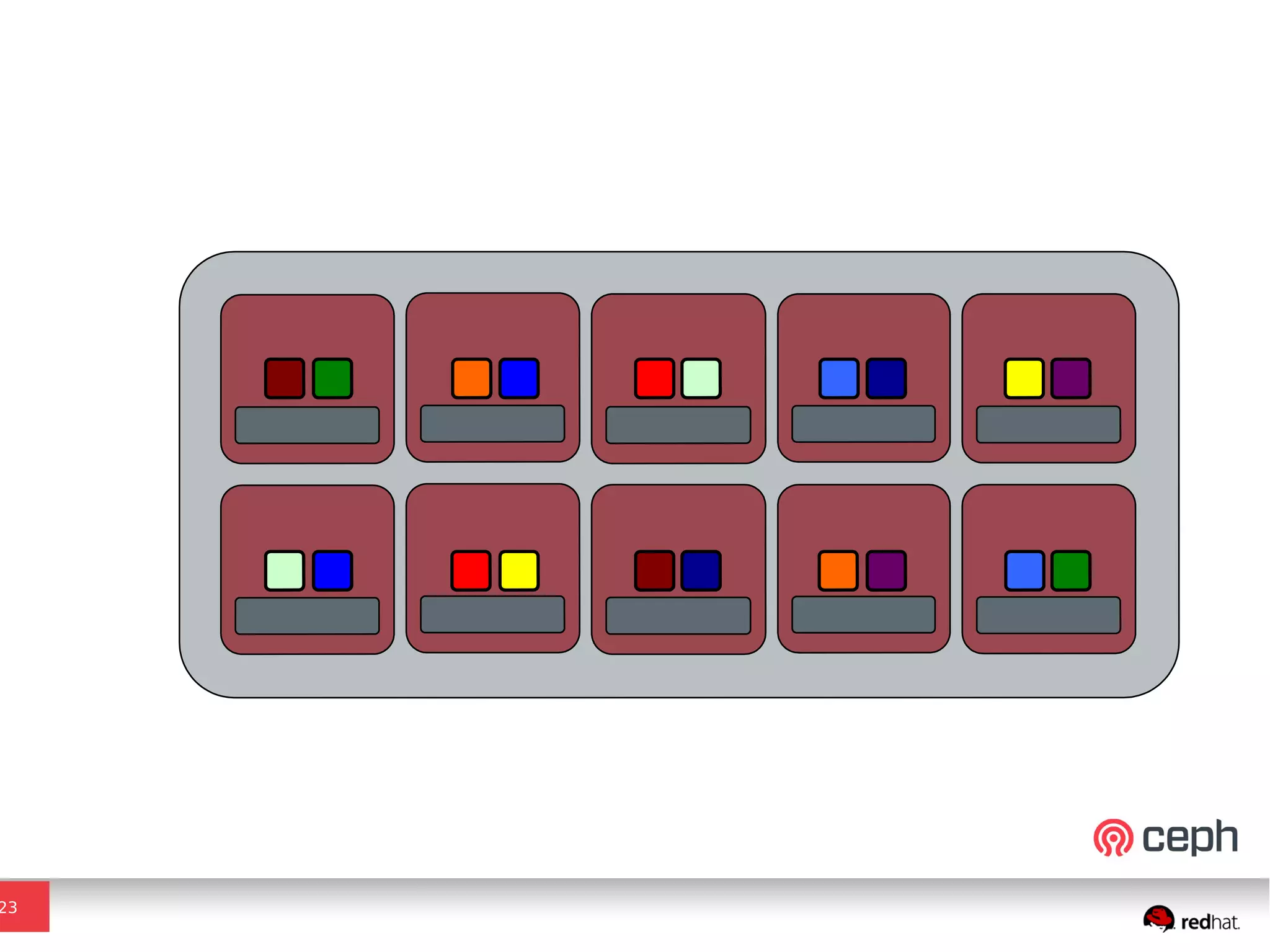
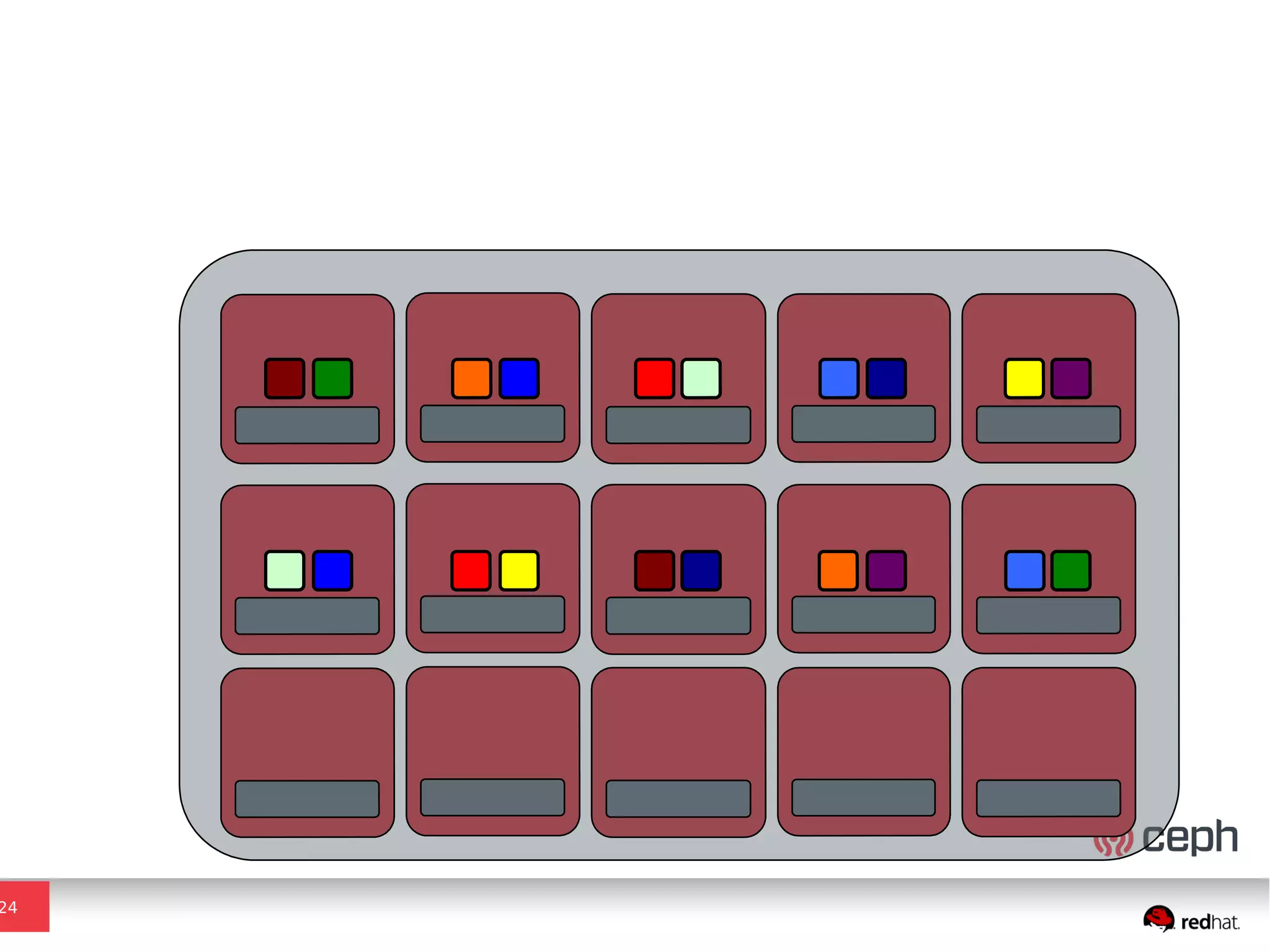
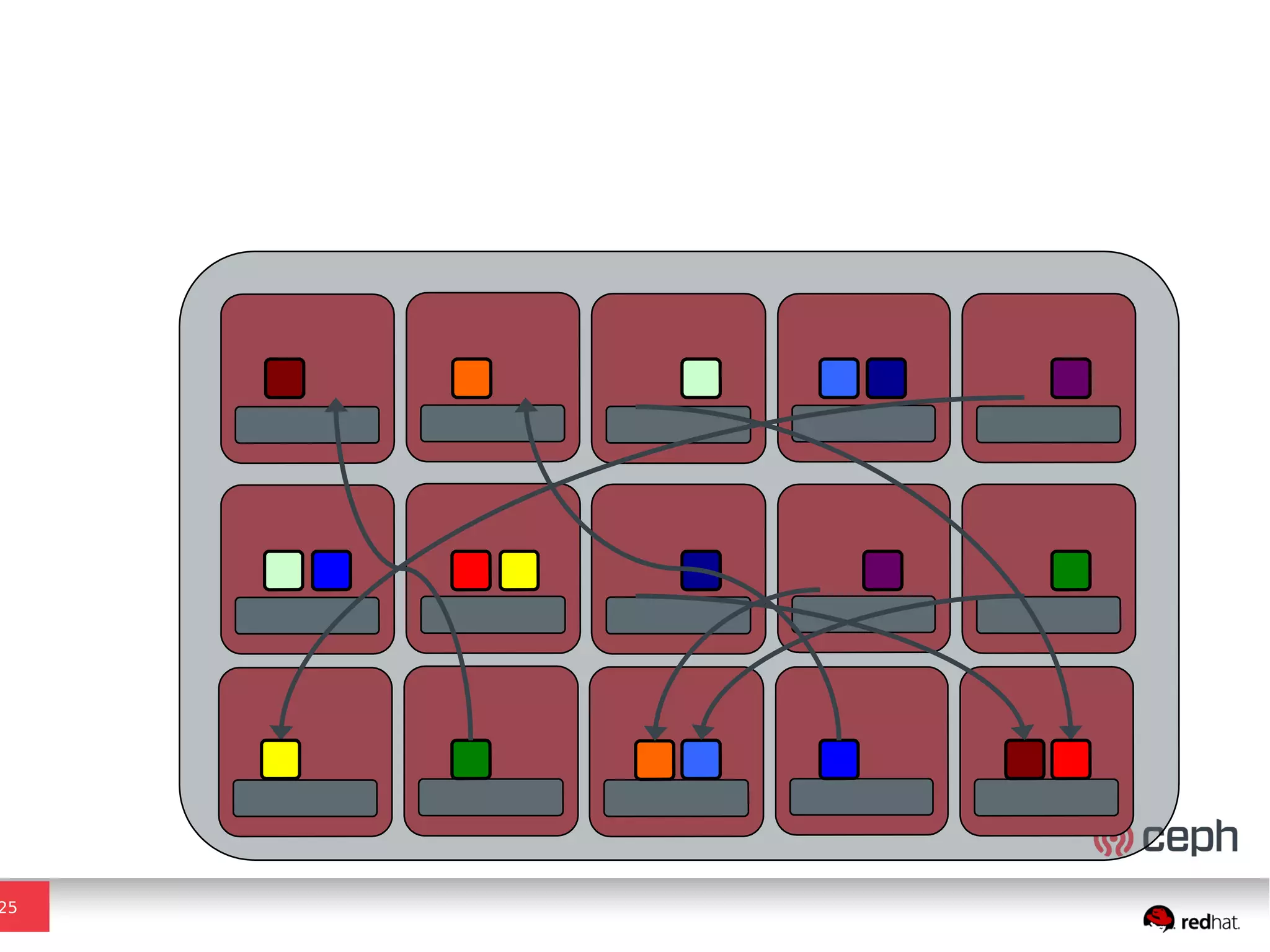
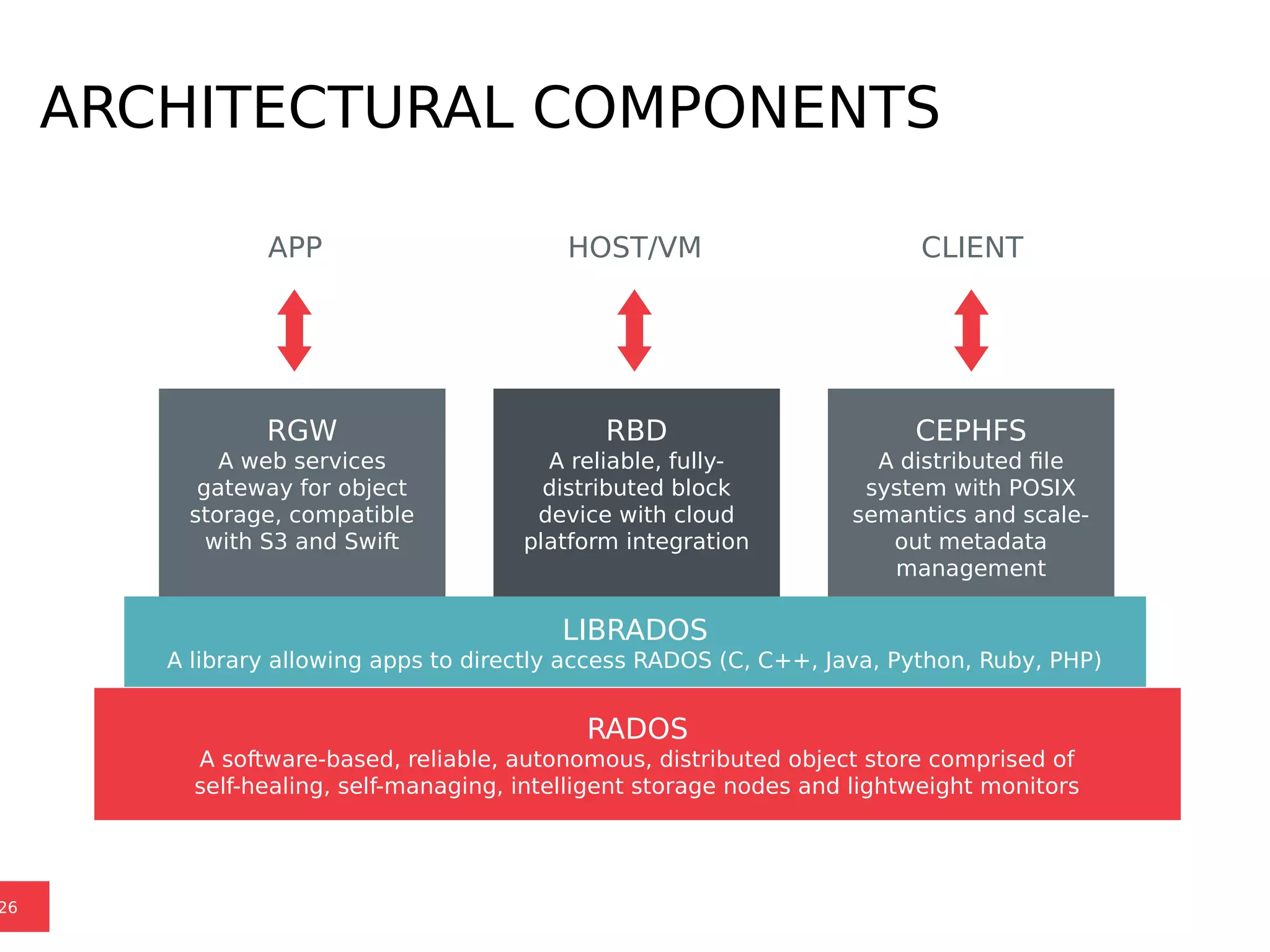
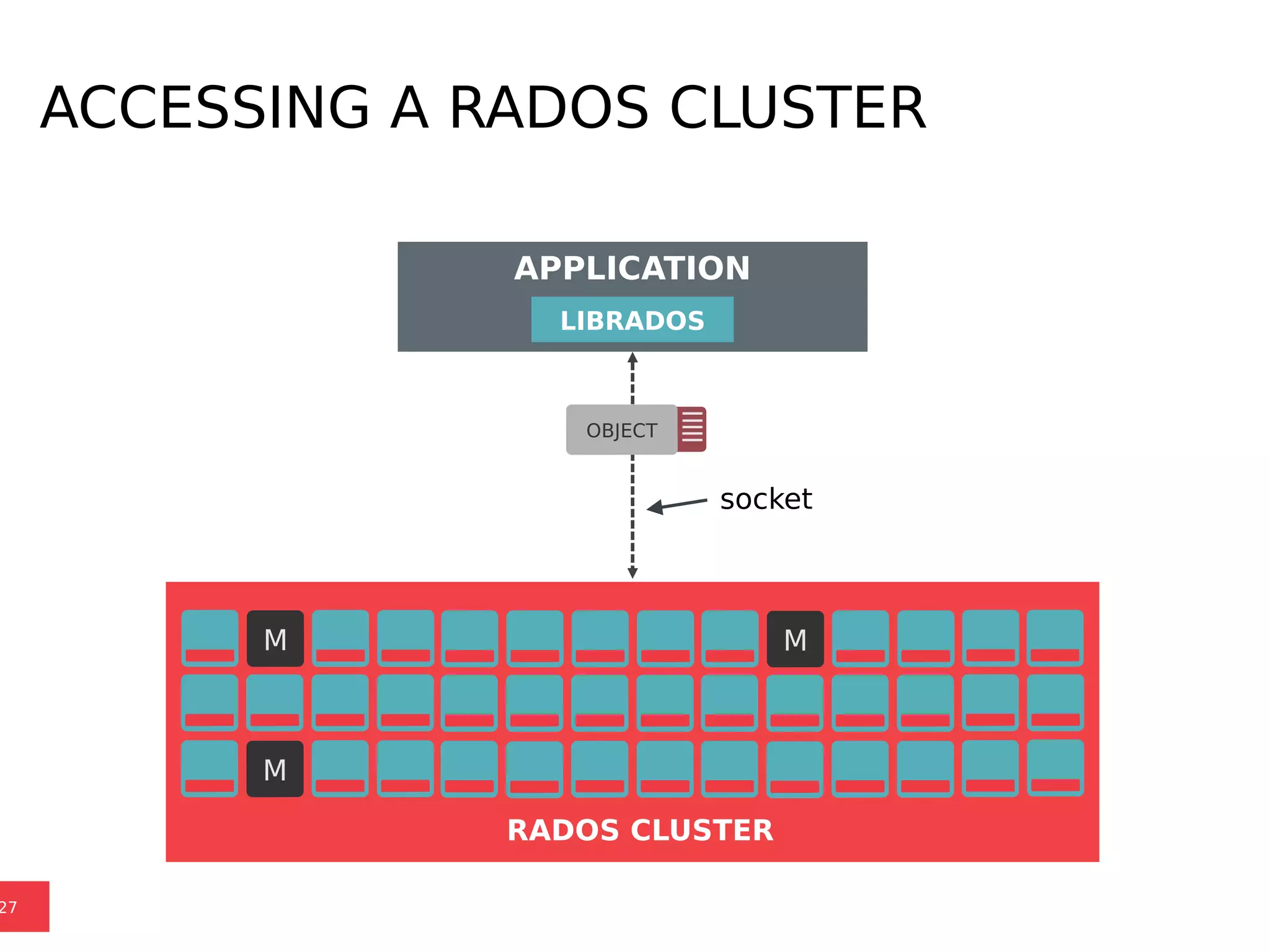
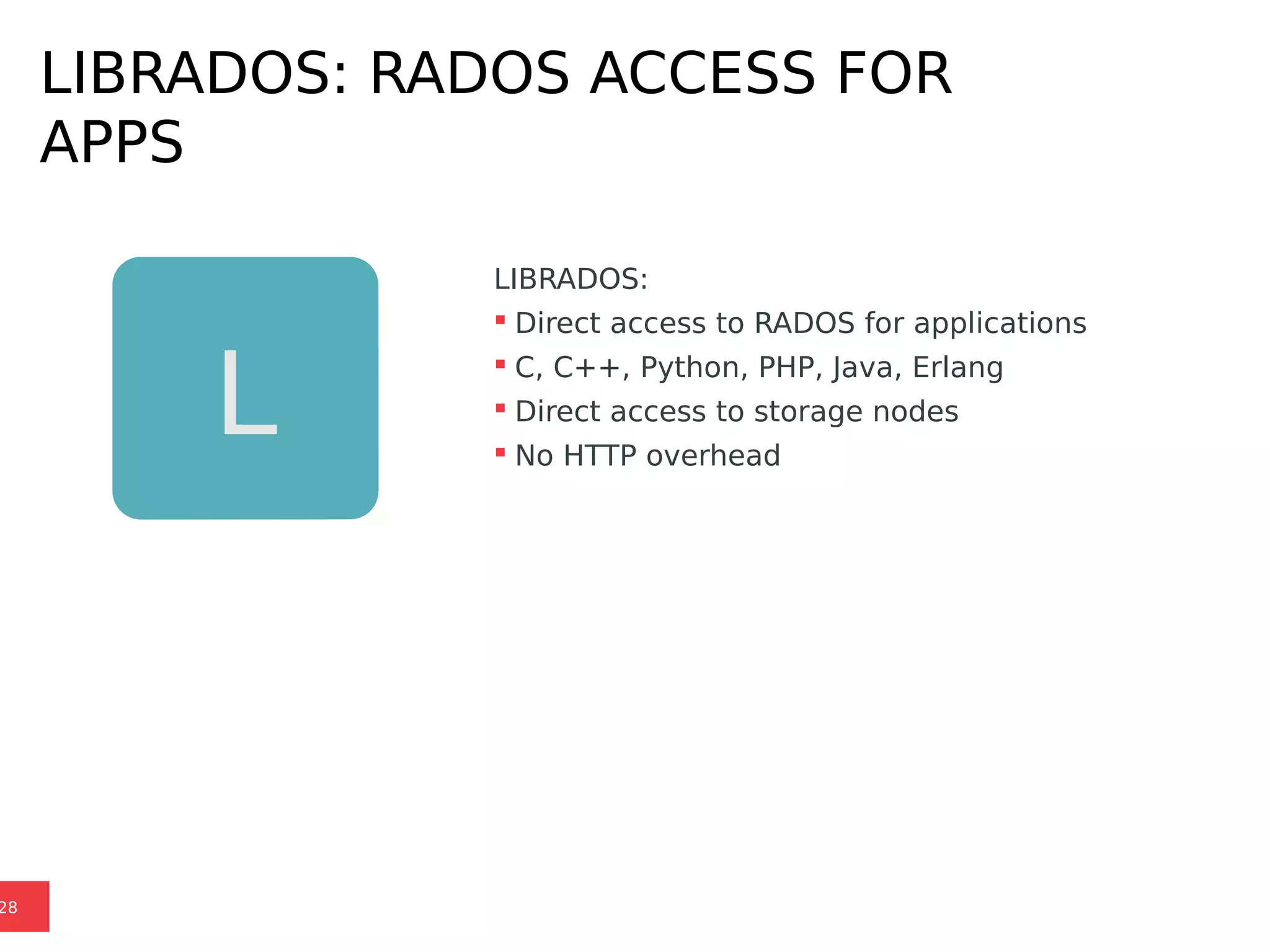
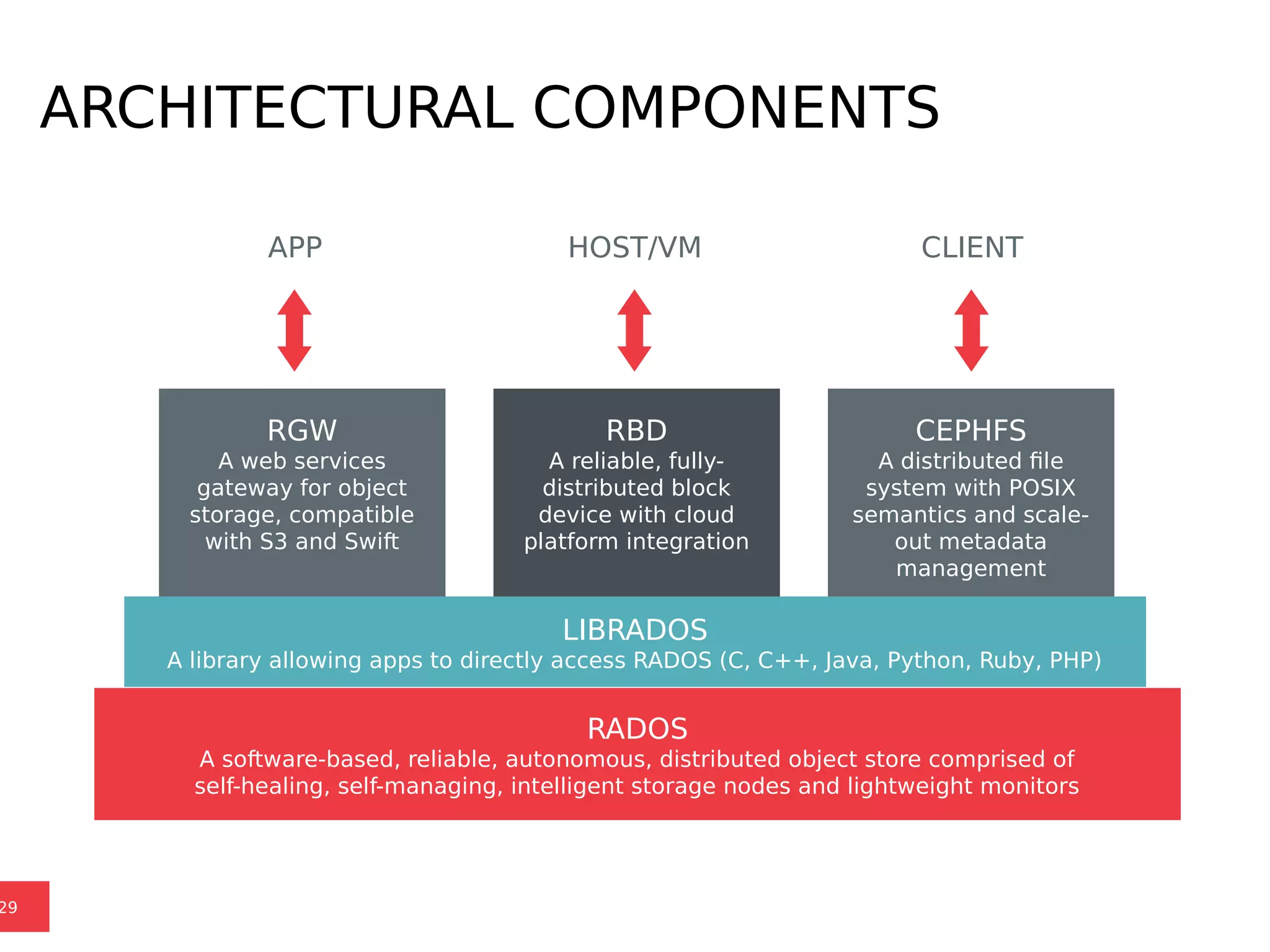
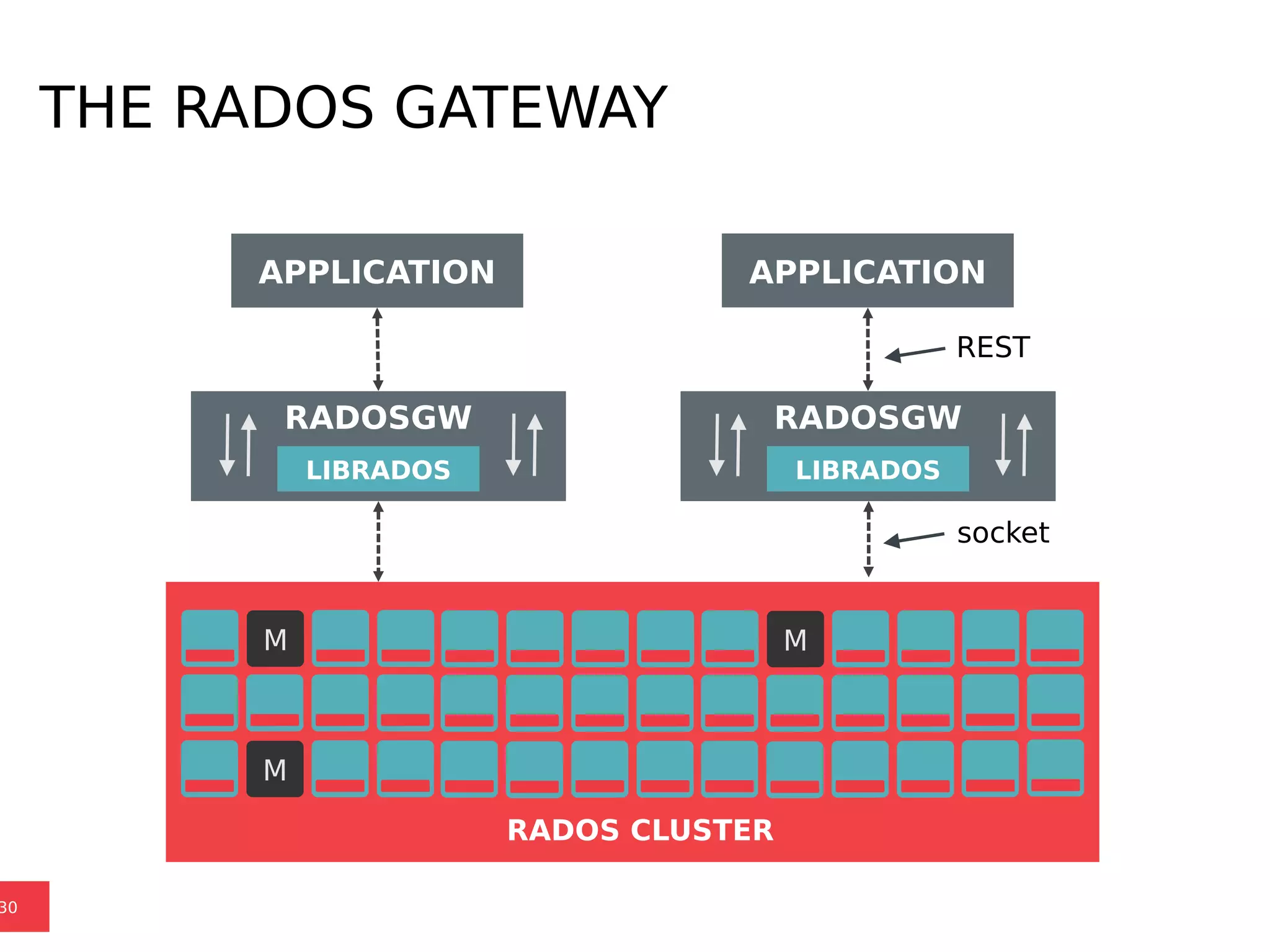
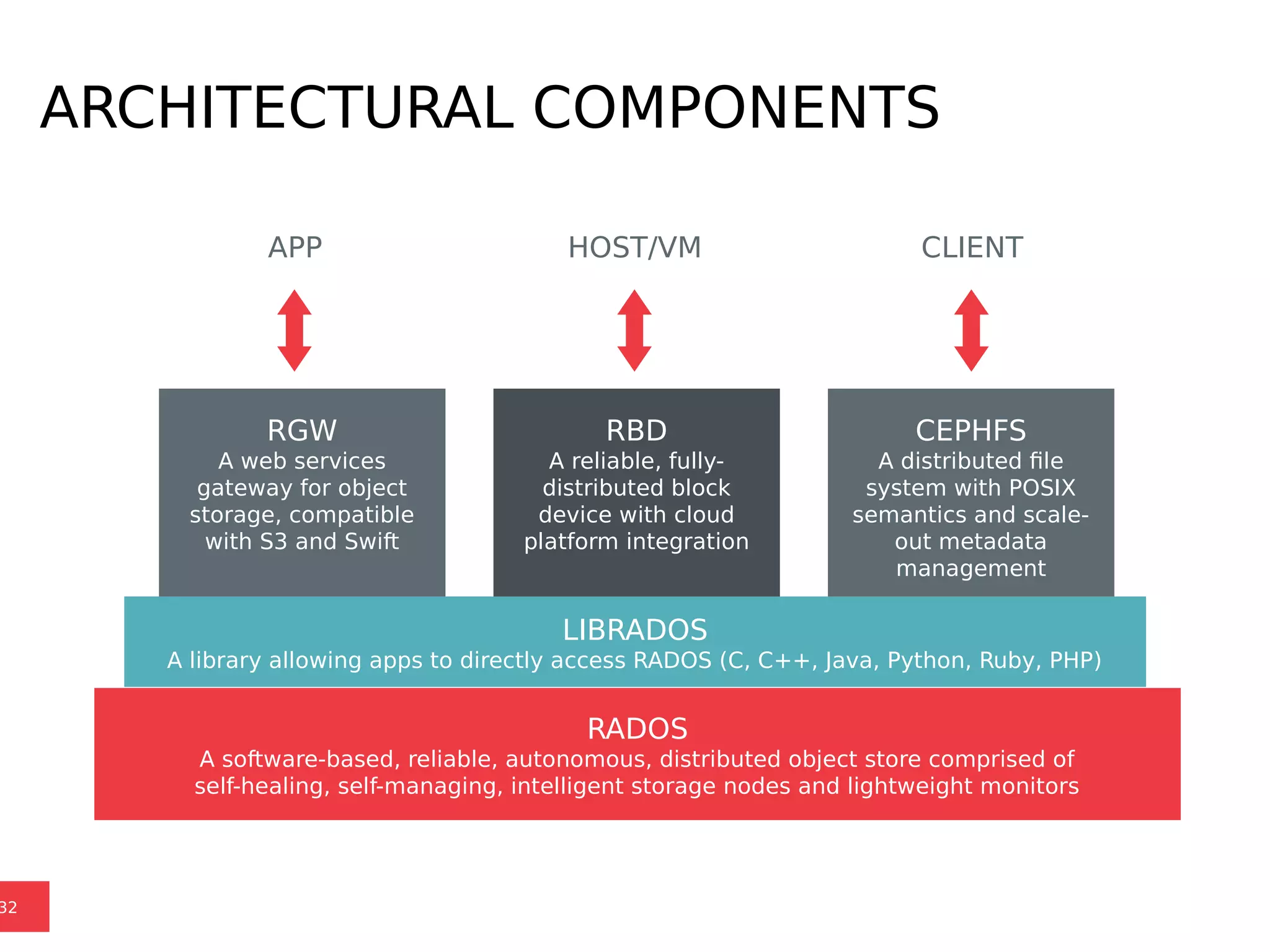
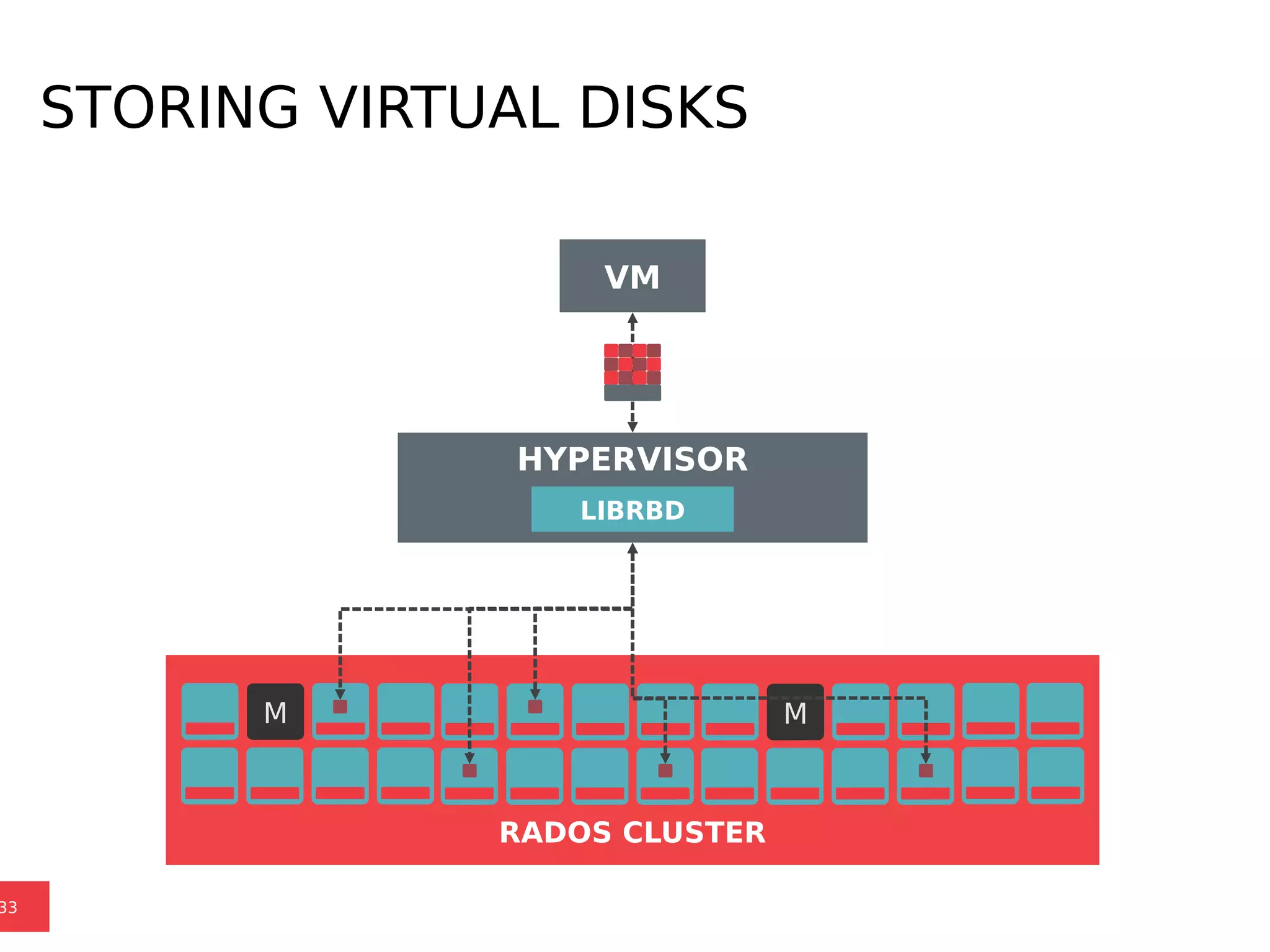
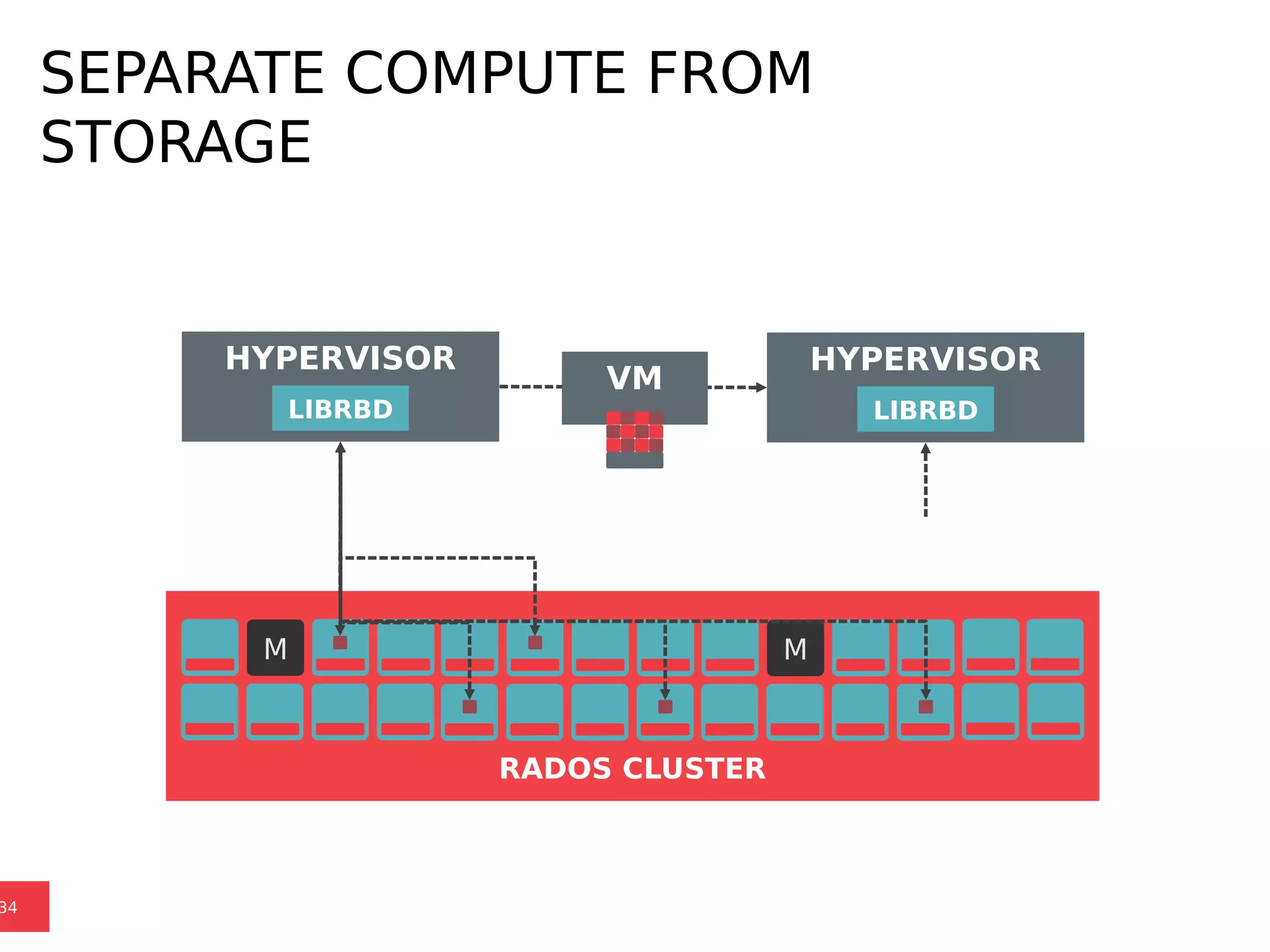
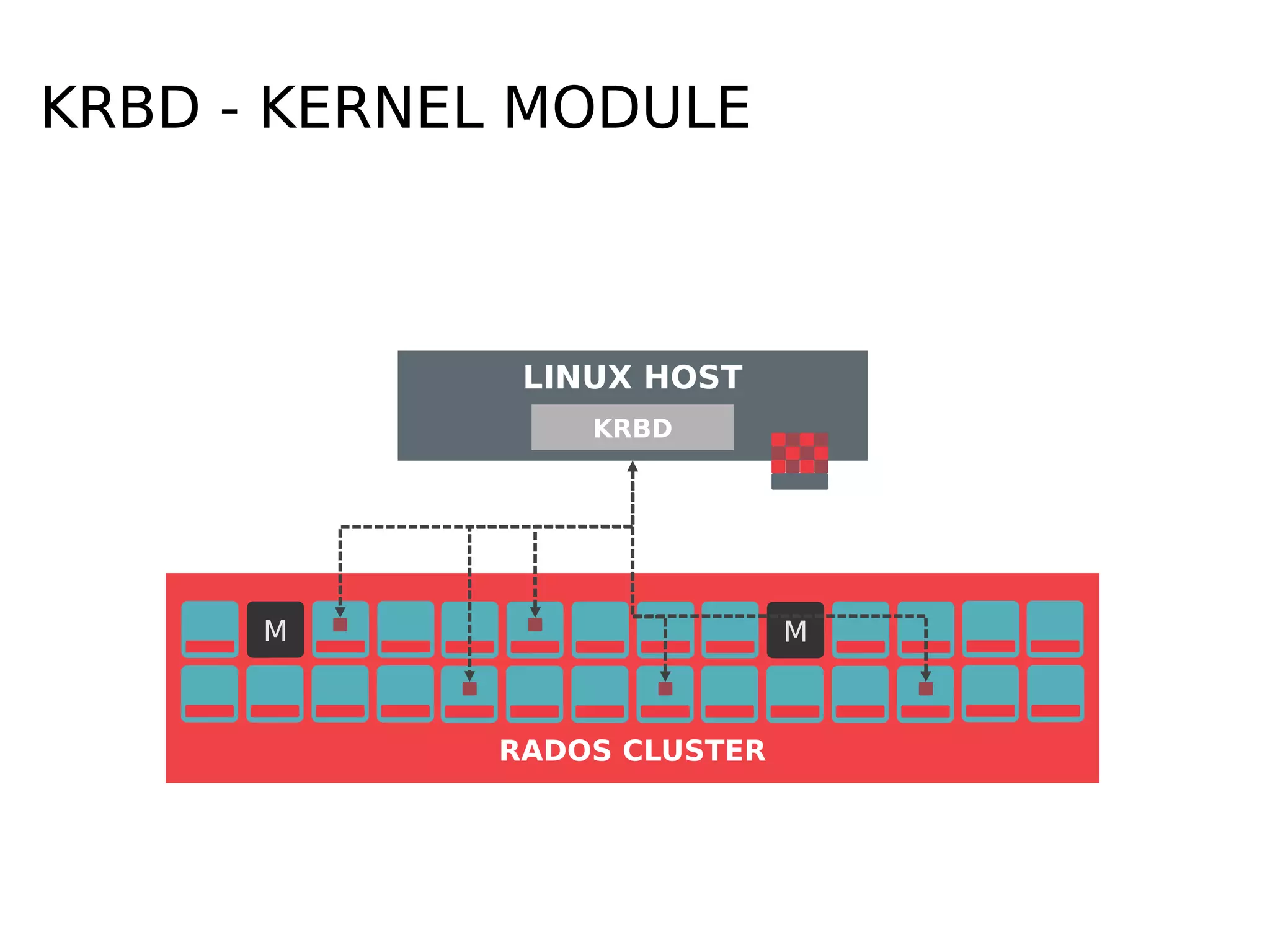
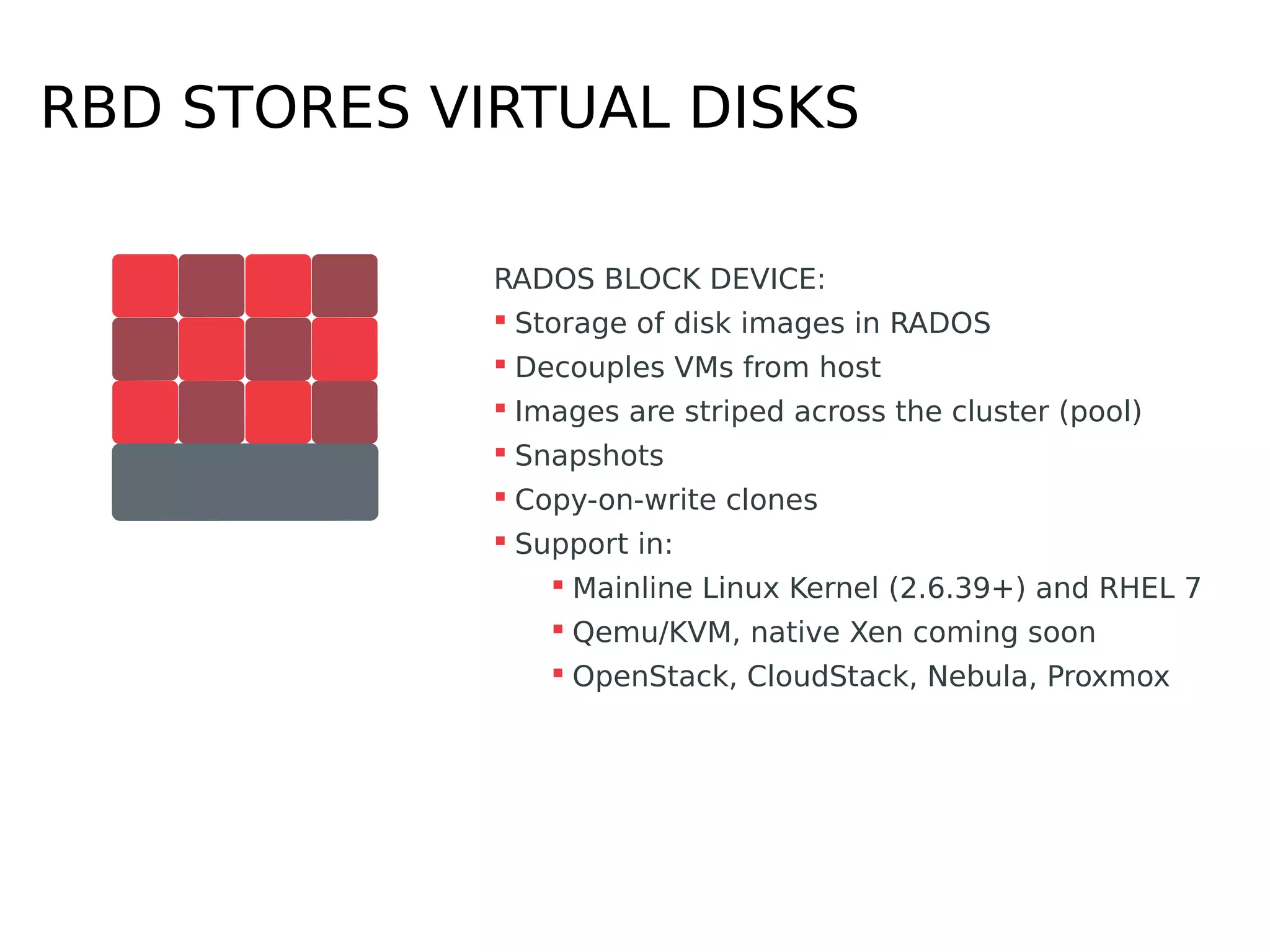
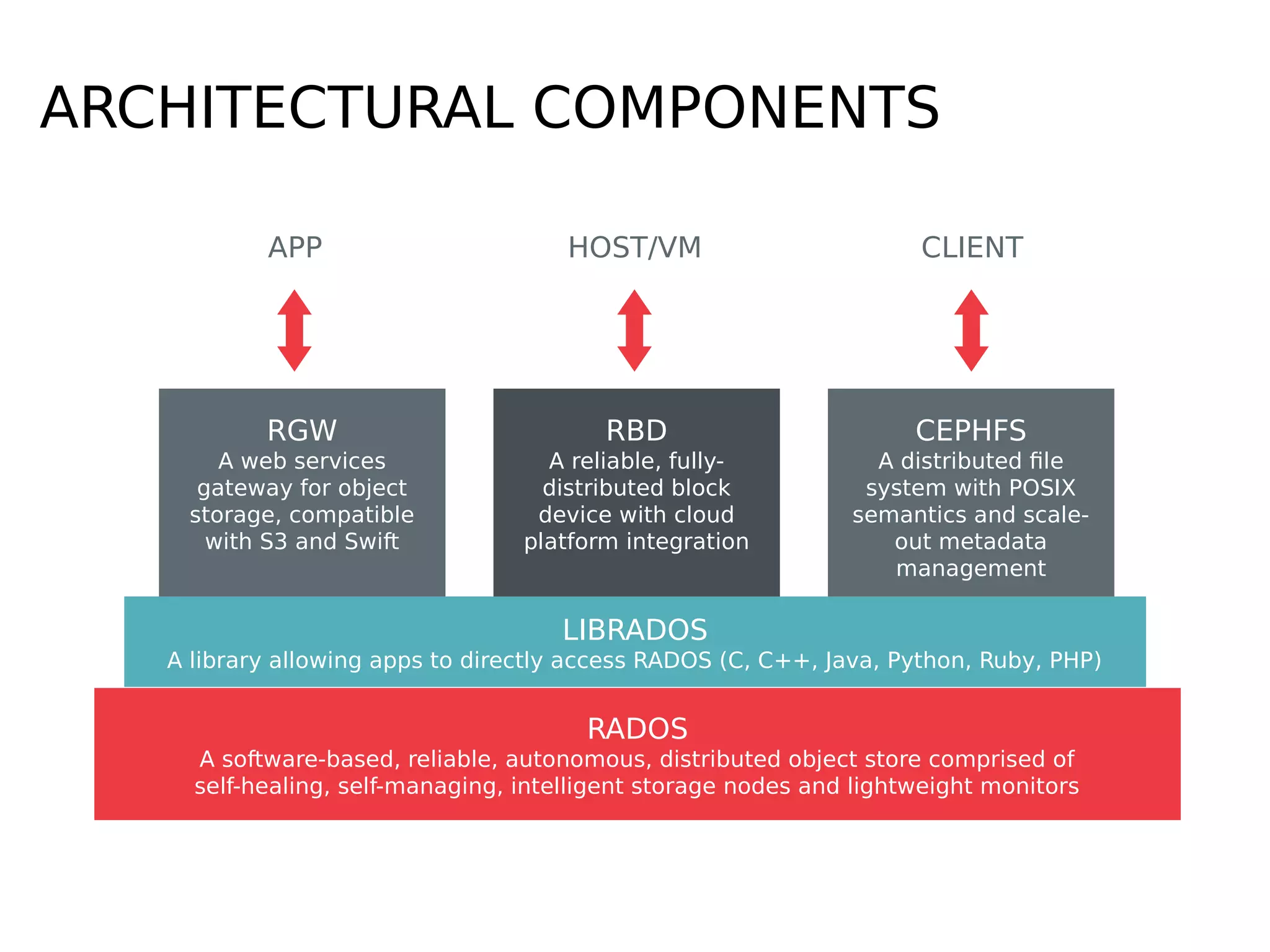
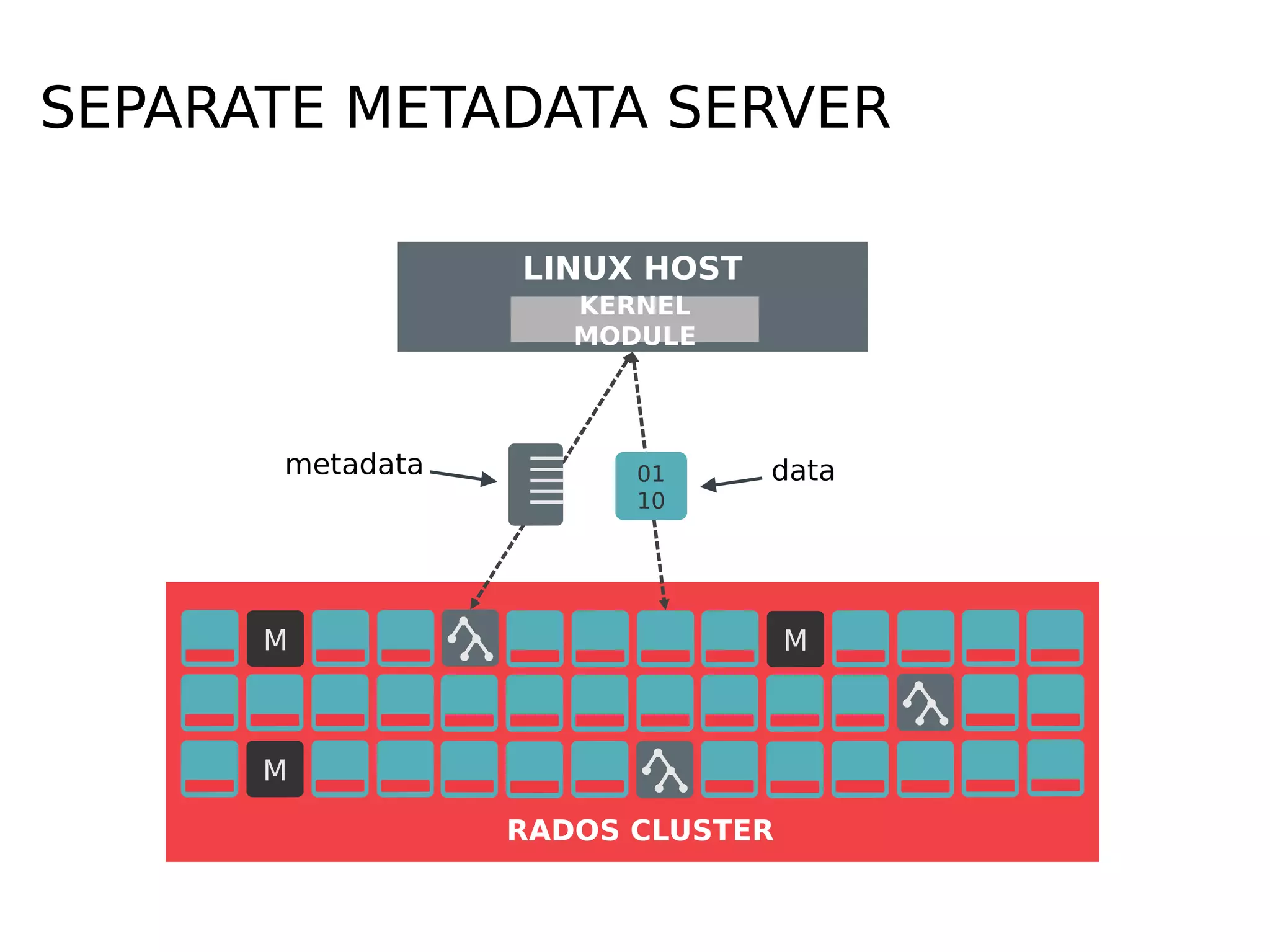
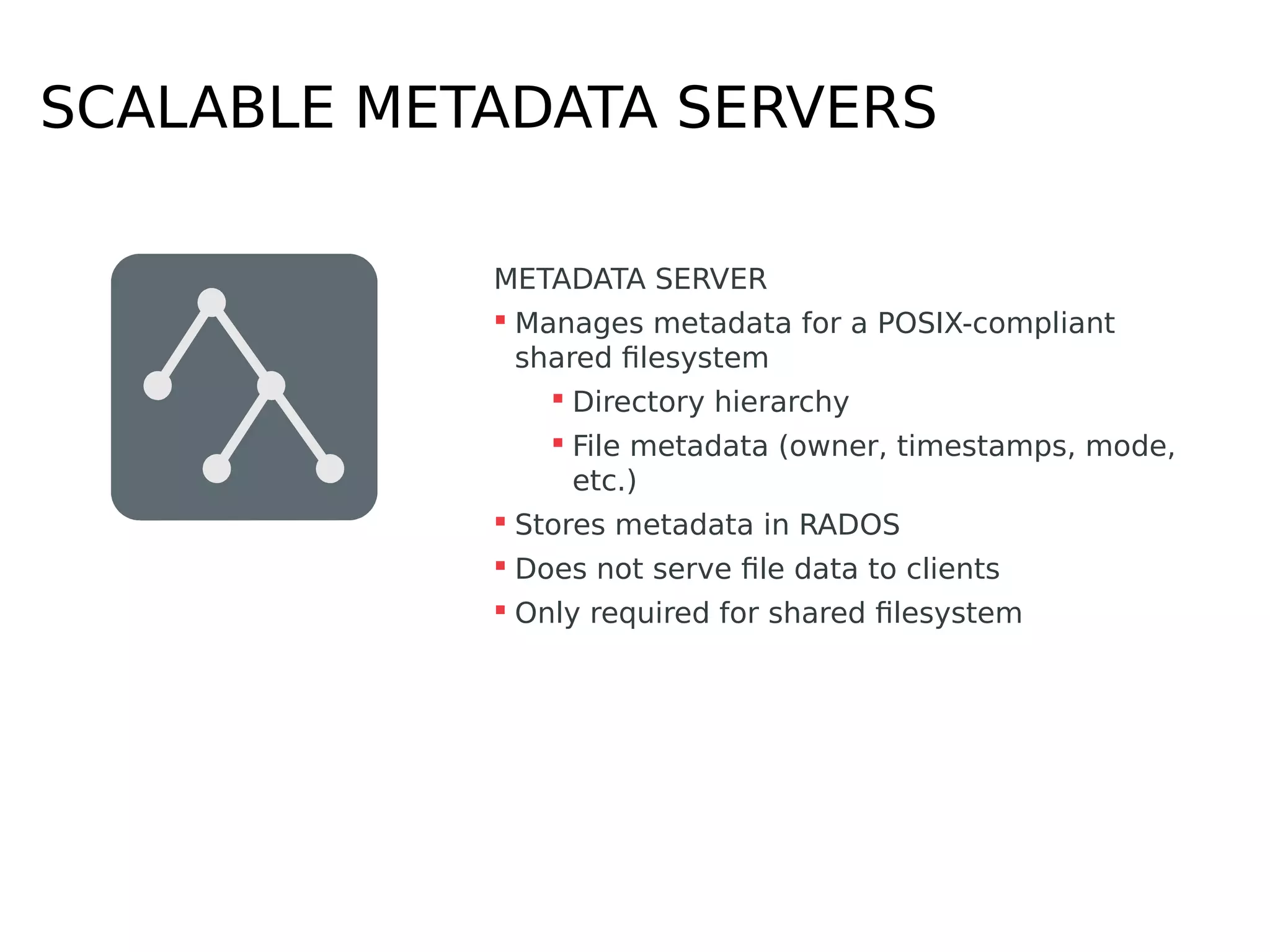
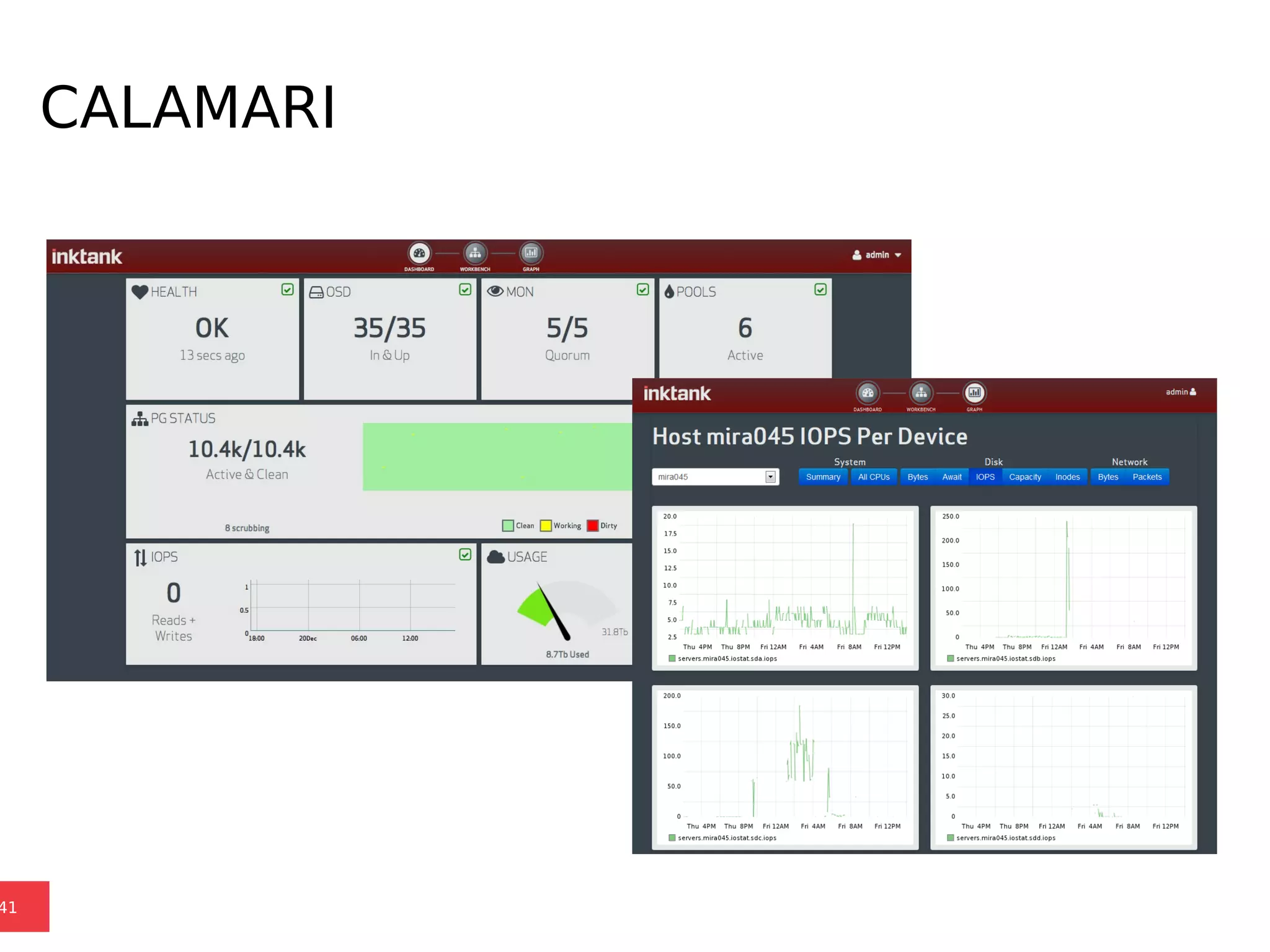
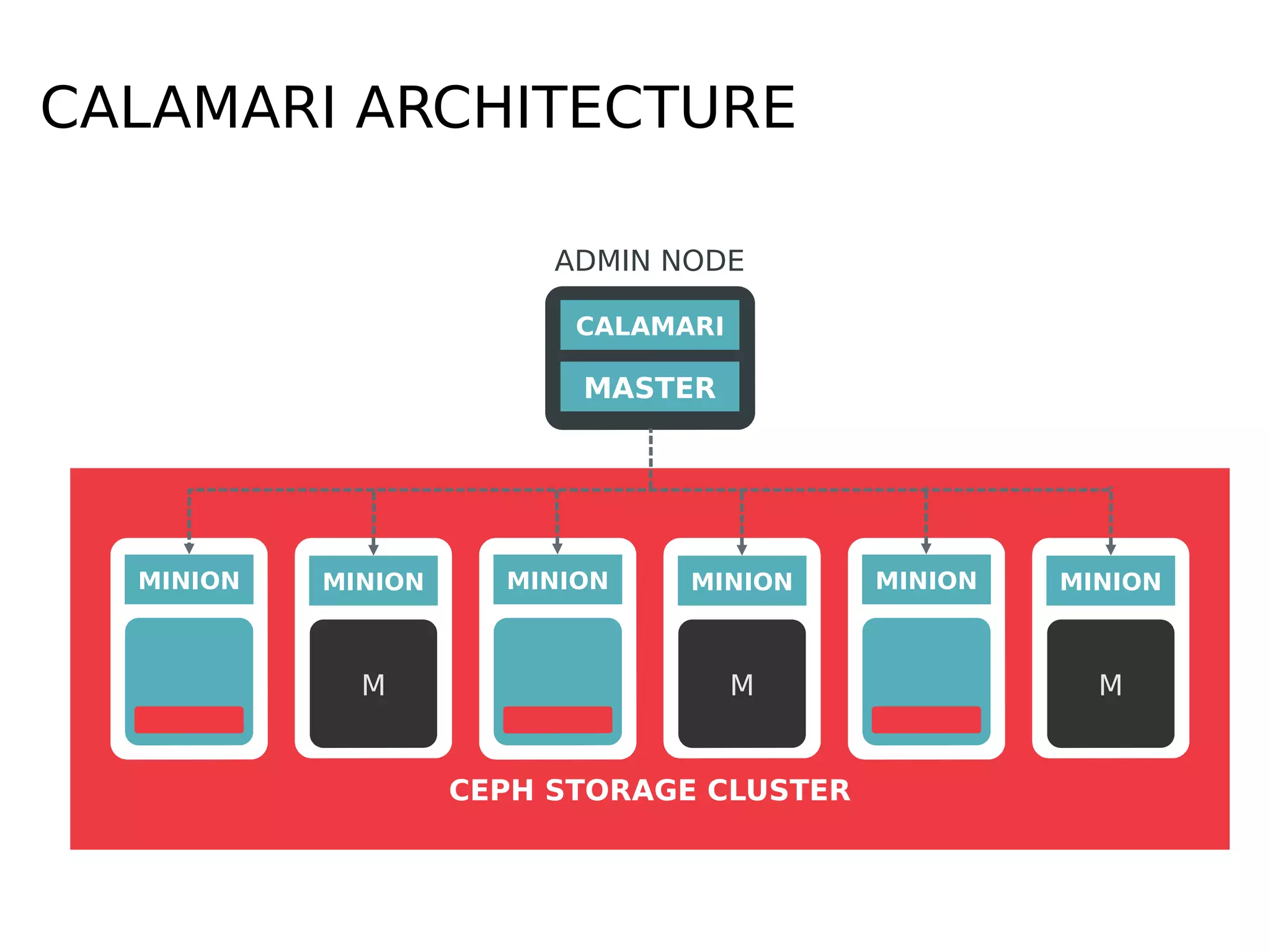
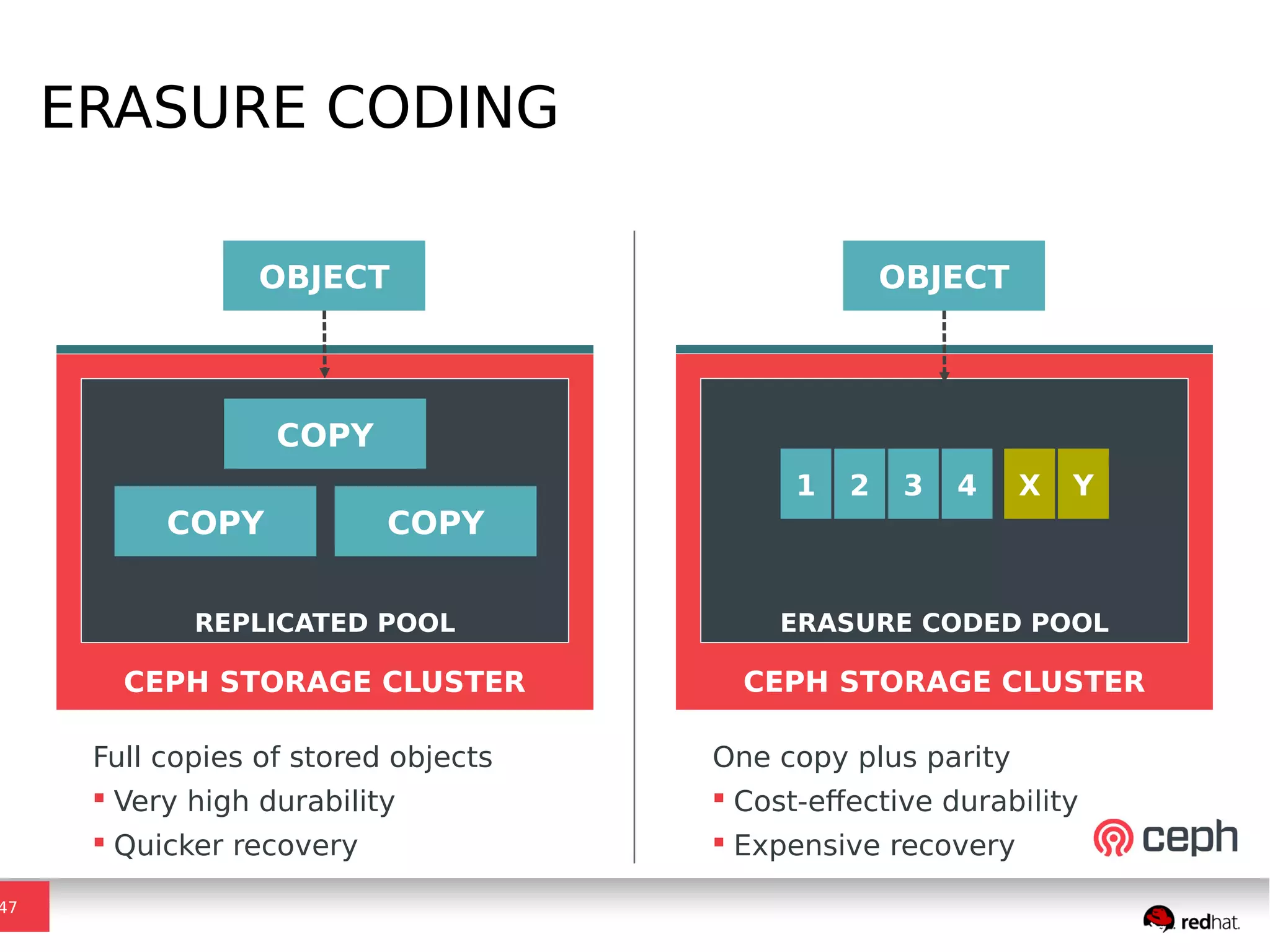
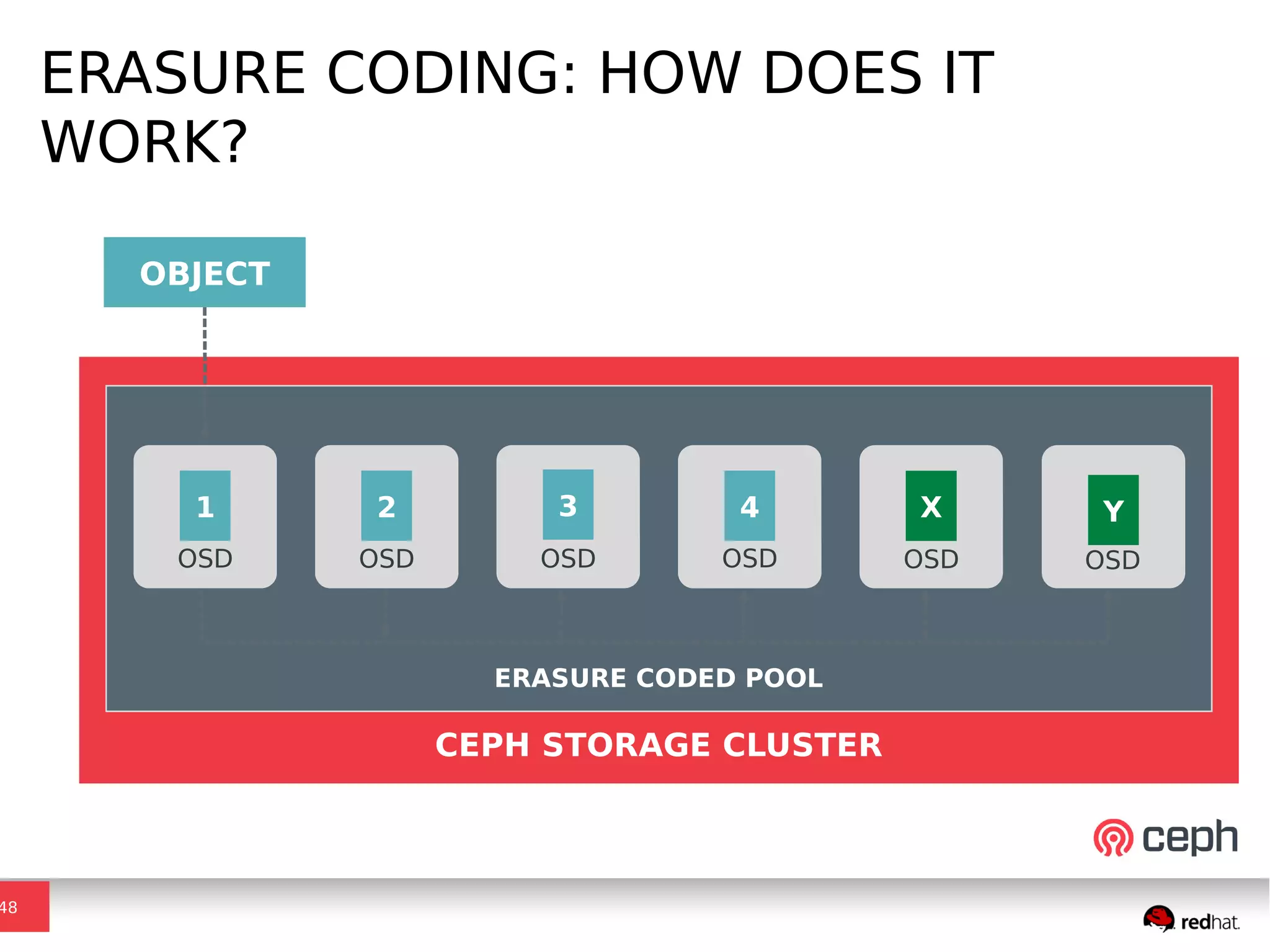
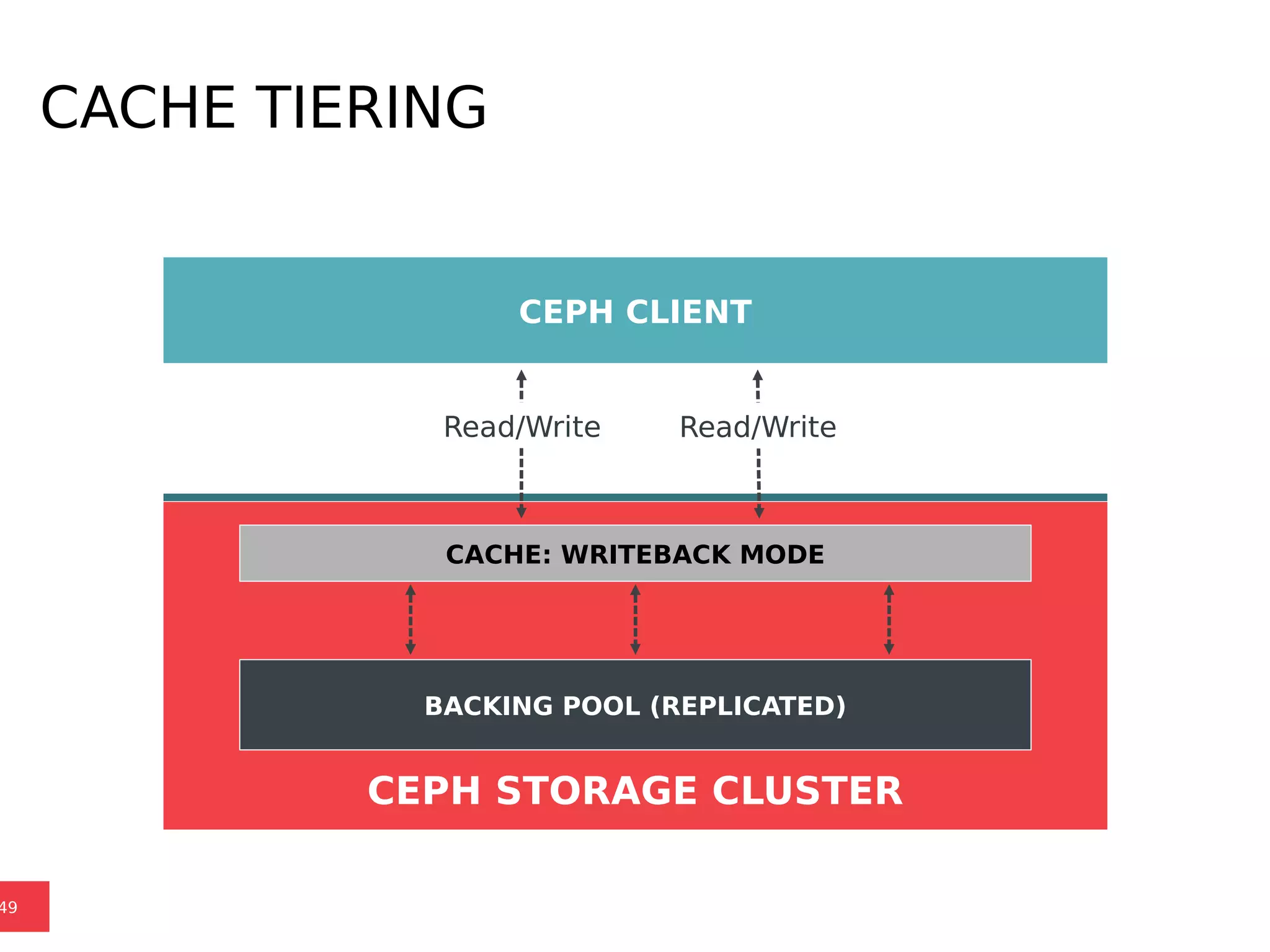
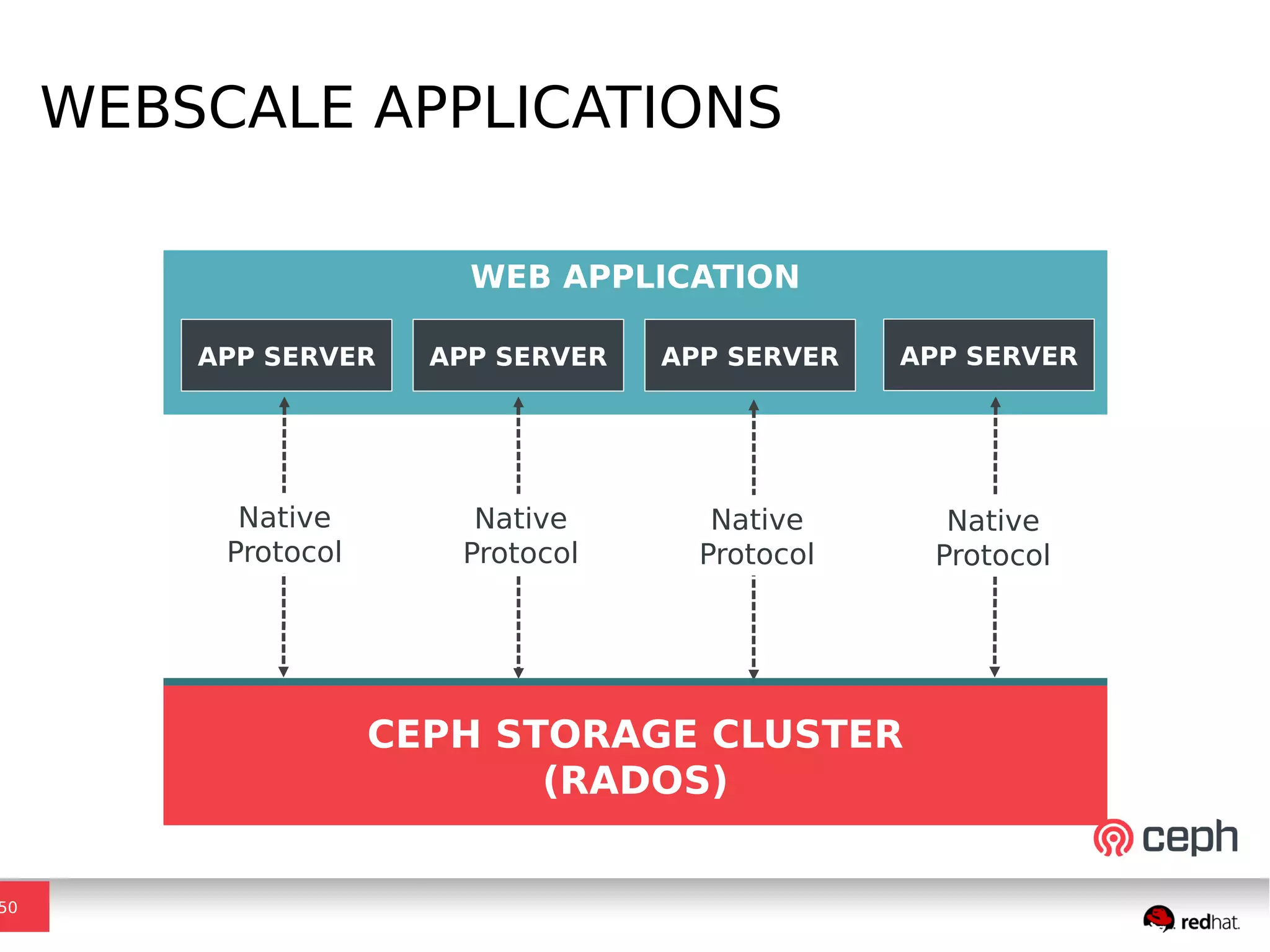
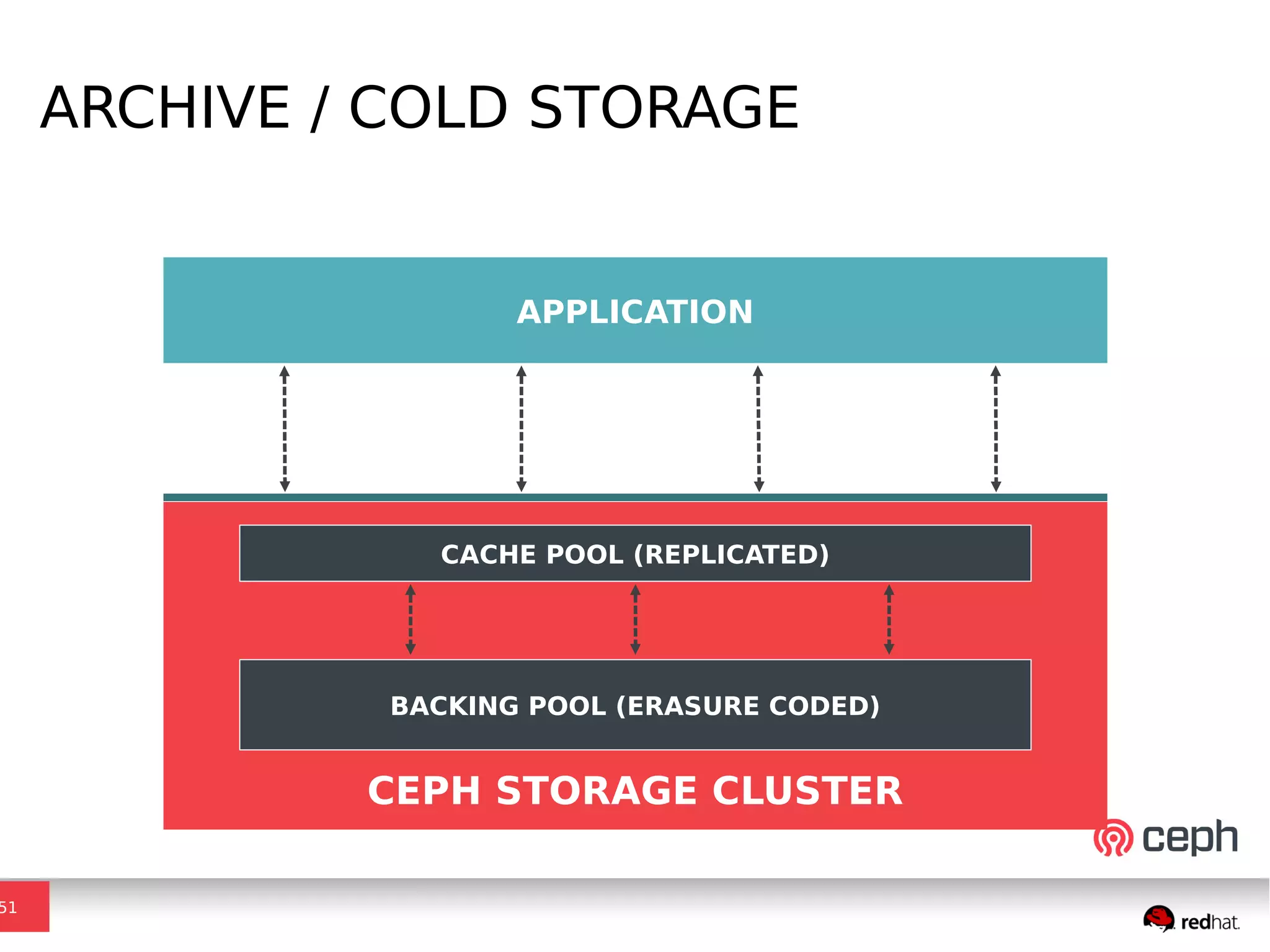
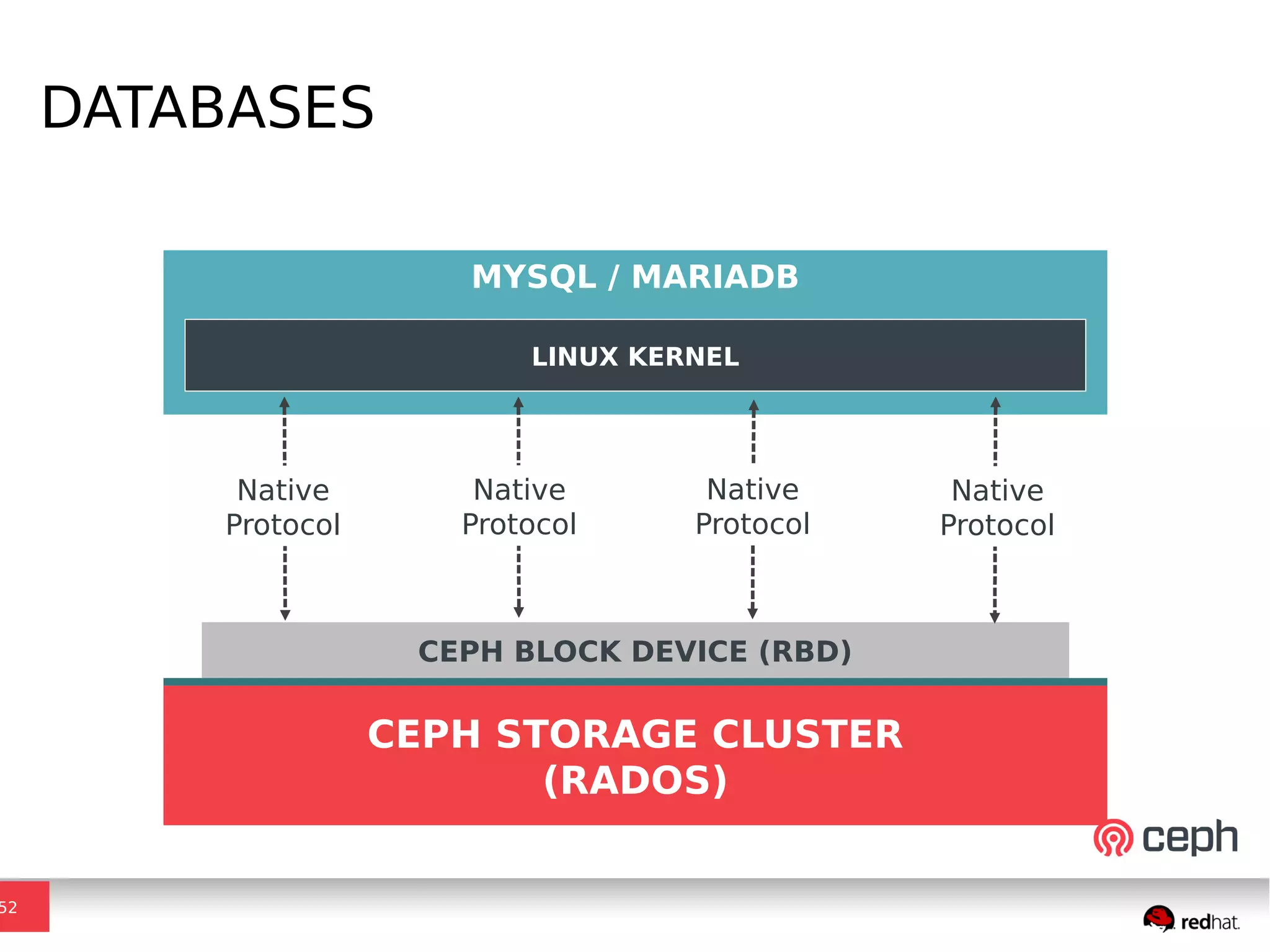
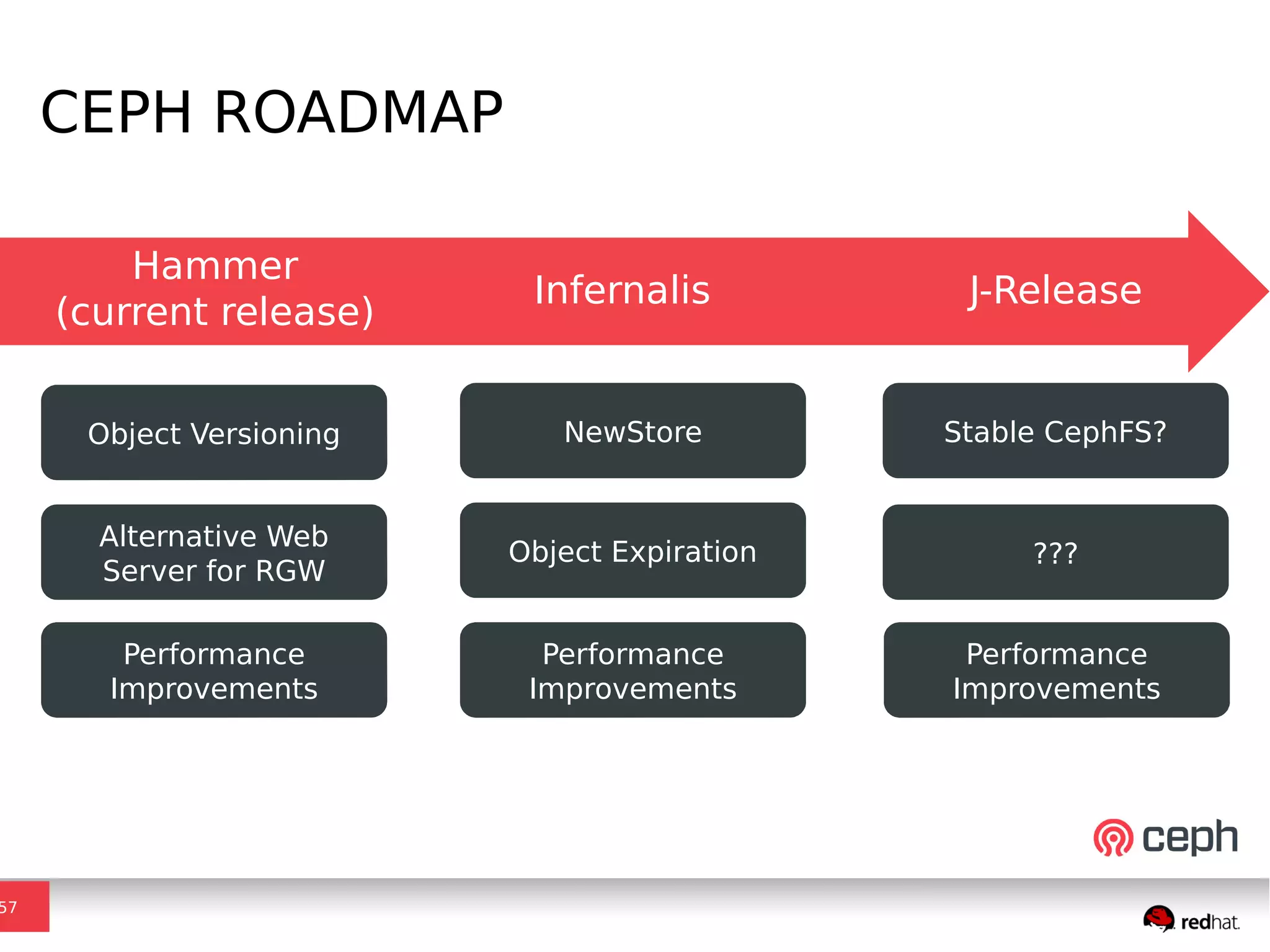
Ceph is a scalable distributed storage system that offers economic and operational benefits through a reimagined approach to storage infrastructure, suitable for various use cases, especially in cloud environments. The architecture involves components like RADOS, RBD, and CephFS, which support object, block, and file storage applications while ensuring reliability and scalability. Development milestones include its launch in 2004, RHEL-OSP certification in 2014, and continuous improvements through community engagement and contributions.