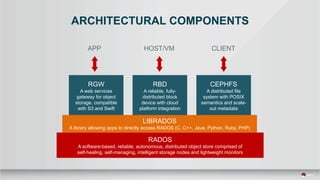
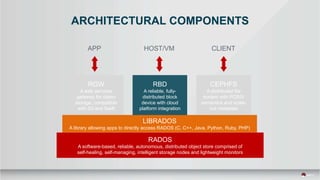
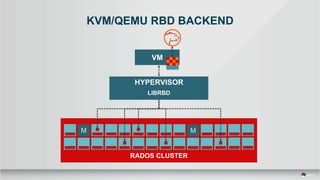
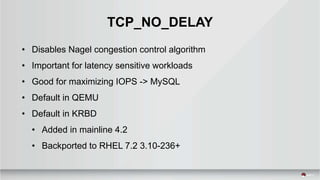
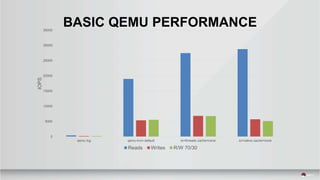
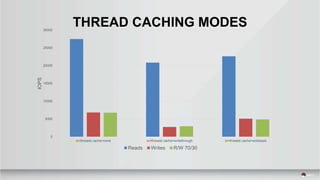
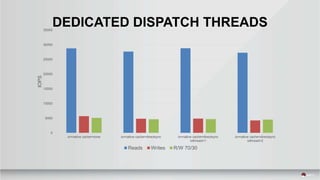
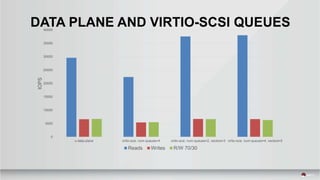
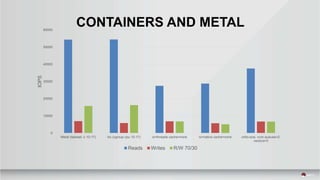
This document summarizes a presentation about tuning MySQL performance on Ceph block storage. The presentation covers Ceph architecture, tuning Ceph block devices, and tuning QEMU block virtualization. It then shows benchmarks comparing different configurations for reads, writes, and a 70/30 read/write mix using Sysbench OLTP workloads. Configurations tested include QEMU backends, caching modes, I/O threading, virtio types and queues, and containers versus metal. The goal is to understand how to optimize MySQL on Ceph block devices.