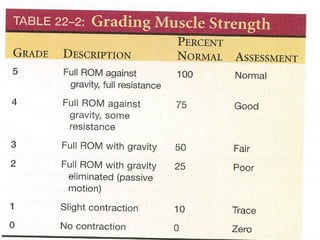
The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, muscles, joints, and cartilage that work together to allow for movement, provide support for standing, and protect internal organs. Key functions include bone marrow production and mineral storage. There are over 200 bones and joints include synovial joints that allow movement between bones covered in cartilage. Ligaments and bursae also support joints. Muscles make up 40-50% of body weight and contract to produce movement. The document provides details on assessing each body region including inspection, palpation, range of motion testing, and muscle strength testing to evaluate the musculoskeletal system.