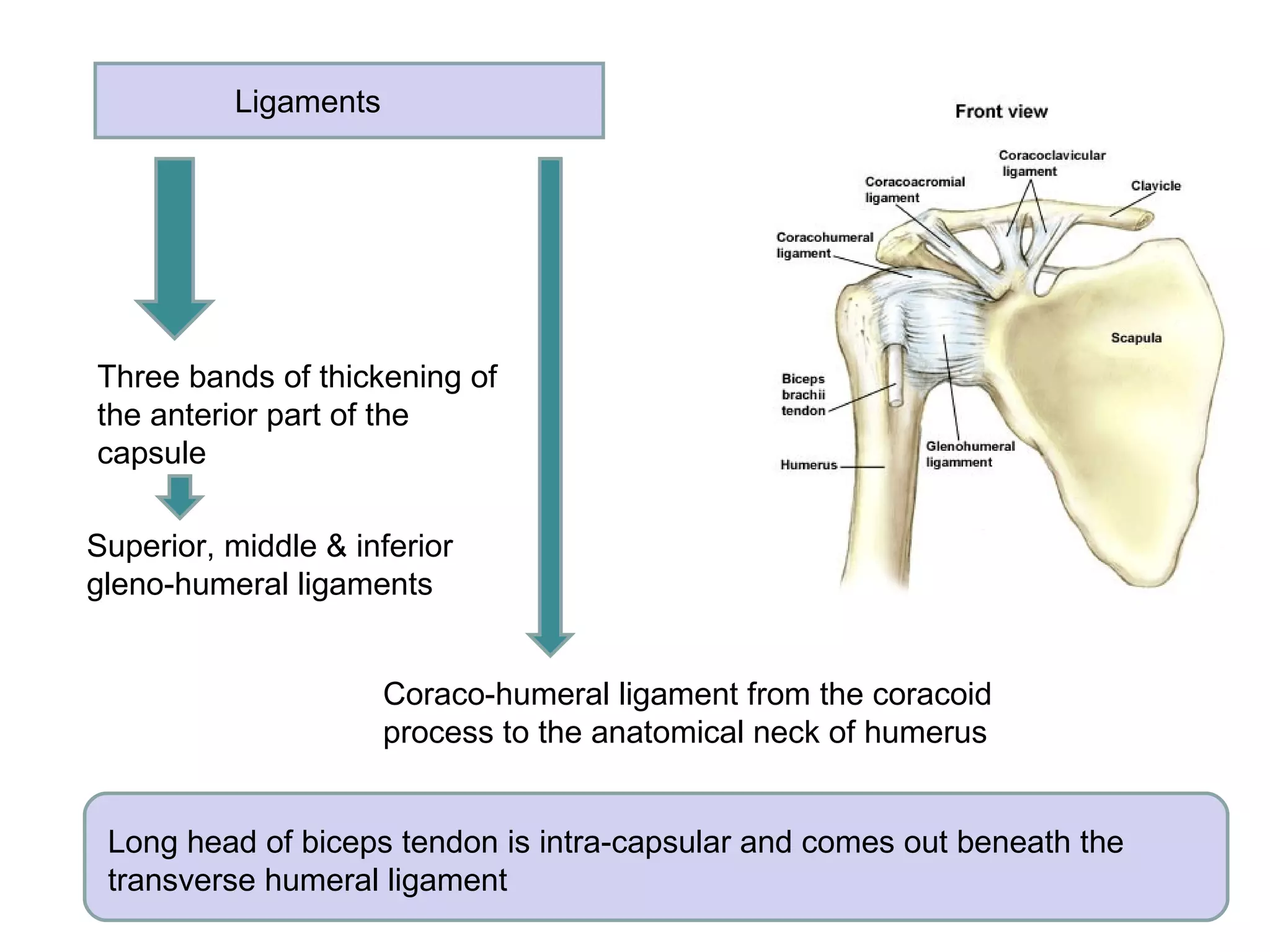
The document describes the major joints of the limbs, including their type, articular surfaces, ligaments, movements, and associated muscles. It discusses the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, ankle, and joints of the hands and feet. For each joint it outlines the key structural features, ligaments, movements produced by specific muscles, and common clinical issues.